This is an automatically translated article.
Diametil is prescribed for the adjunctive treatment of cases of type 2 diabetes, especially those who have not responded to a controlled diet and exercise regimen. During treatment with Diametil, patients need to strictly follow the instructions of the doctor in order to quickly overcome the disease effectively.
1. What is Diametil?
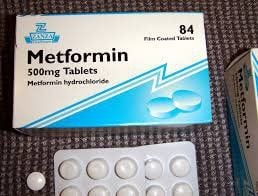
Diametil belongs to the group of hormonal drugs, used for patients with type 2 diabetes. Diametil is manufactured by Aegis., Ltd - Turkish Republic of Kibris in the form of film-coated tablets and packaged in boxes. 5 blisters x 10 tablets.
Each Diametil tablet contains the main active ingredient, Metformin, 500mg. In addition, the manufacturer also adds a number of other auxiliary excipients to increase the effectiveness of the active ingredient Metformin in the drug.
2. What are the uses of Diametil?
2.1. Effects of the active ingredient Metformin Metformin has a chemical name of 1,1-dimethylbiguanide hydrochloride, belonging to the Biguanide group. This is an oral hypoglycemic drug unlike sulfonylureas in both chemical structure and mode of action.
According to research, the active ingredient Metformin in Diametil has anti-hyperglycemic effects and has a positive effect on the composition of blood lipids in people with type 2 diabetes. Through the ability to inhibit Glucose synthesis. In the liver and reduce glucose absorption in the intestine, Metformin helps to increase the use of glucose in the cells, while significantly improving the binding of insulin to other receptors and promoting the anaerobic digestion of glucose. . In addition, the active ingredient Metformin also helps reduce total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and blood triglycerides. After treatment with Metformin, patients with type 2 diabetes also reported increased fibrinolysis and decreased platelet aggregation.
In general, Metformin only lowers high blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, but has no effect on people with normal health. According to experts, the mode of action of Metformin includes:
Inhibiting the absorption of glucose in the intestine. Promotes glucose utilization in cells. Prevents gluconeogenesis in the liver. 2.2. Indications and contraindications to the use of Diametil Currently, the drug Diametil is prescribed by doctors for the following cases:
Treatment of type 2 diabetes, especially in people who are overweight and have a diet. Drinking or exercising alone is not effective in controlling blood sugar levels. Diametil as monotherapy or in combination with other oral antidiabetic agents or insulin. Diametil alone or in combination with insulin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in children over 10 years of age and adolescents. However, it is necessary to avoid arbitrarily using Diametil for the following patients without a doctor's prescription:
People with a history of hypersensitivity or allergic reaction to the active ingredient Metformin or any excipients with in drug formulations. Diametil is contraindicated in patients with diabetic pre-coma, ketoacidosis, severe infection, shock or dehydration. Do not use Diametil for people with dehydration, kidney failure, X-ray test results show the use of iodine-containing contrast. Diametil is contraindicated in patients with conditions that cause tissue hypoxia, such as myocardial infarction, cardiogenic shock, respiratory failure and heart failure. Diametil is contraindicated for people suffering from alcoholism, acute alcohol intoxication and undergoing major surgery. Relative contraindications Diametil for pregnant women or nursing mothers.
3. How should Diametil be taken?
Diametil is made in the form of tablets for oral use. The patient should swallow the tablet whole, avoiding chewing or crushing it. The most suitable time to take Diametil is during or at the end of a meal.
Before using Diametil, patients should carefully read the instructions for use written on the package or follow the specific instructions of the doctor. Avoid self-medicating or adjusting the dose without approval. The following is the dose of Diametil according to the general recommendations of the doctor:
Initial dose: Treatment of non-insulin dependent diabetes with an initial dose of 1 tablet x 2 times / day and a maximum of 4 tablets / day. Maintenance dose: Oral dose of Metformin 500mg or 850mg x 2-3 times/day.
4. Side effects of the drug Diametil
During the treatment of type 2 diabetes with Diametil, patients may inadvertently experience some of the following side effects:
Metal taste in the mouth. Nausea or vomiting. Increased lactic acid leads to acidosis. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea or diarrhea (occurring in about 10-15% of patients). This side effect should subside as you take Diametil after a meal and gradually increase the dose. Vitamin B12 deficiency when taking Diametil for a long time because Metformin affects the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine. Anorexia, weight loss and bitter mouth with prolonged use of Diametil. Some symptoms may go away on their own without treatment, but some rare reactions have the potential to get worse if management is delayed. Ideally, when any adverse side effect occurs while taking Diametil, the patient needs to stop the treatment and promptly notify the doctor so that there can be an early remedy.
5. Things to note when using Diametil 500
In order to ensure the full effect of Diametil, and at the same time prevent the risk of experiencing adverse reactions, you should note a few things as follows:
When using Metformin, it is necessary to periodically monitor the tests. clinical laboratory tests, including blood glucose measurements, to determine the minimum effective dose of the drug. In addition, patients should also be vigilant about the risk of lactic acidosis and other situations that predispose to this phenomenon. Treatment of type 2 diabetes with Diametil is only a support measure and is not a substitute for a reasonable daily diet. Therefore, patients need to regulate their eating and always control the portions recommended by the doctor to manage diabetes well. Before performing an iodinated contrast X-ray, you need to stop using Diametil 2-3 days before and for 2 days after the scan. Diametil should be reintroduced only after a reassessment of renal function has been performed and a normal result has been obtained. The distribution of the active substance Metformin will be affected if the patient is co-administered with drugs that affect renal function. Before carrying out major surgery, patients need to stop treatment with Diametil. Pregnant women or nursing mothers should consult a doctor before deciding to use. Diametil should only be used when absolutely necessary and the required benefits outweigh the risks. Metformin overdose can lead to lactic acidosis. At that time, the patient needs to stop treatment and go to the doctor immediately to have the acidosis corrected through intravenous injection of 7.5% sodium bicarbonate solution. If the patient has severe acidosis, the doctor may order hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. In case you miss a dose of Diametil, you need to take it as soon as possible, but avoid taking it too close to the next dose or taking a double dose at the same time. Check the quality and expiry date of Diametil before use. If the medicine is past its expiration date and shows signs of mold, color change, or watery tablets, you need to dispose of the medicine according to the instructions. Avoid taking Diametil at the same time with iodine-containing contrast agents, alcohol preparations, beer, wine, Beta 2 blockers, diuretics, Glucocorticoids and ACEIs. Ideally, patients should inform their doctor about the list of medications they are taking to prevent potential interactions with Diametil. Above is all information about Diametil, patients need to carefully read the instructions for use, consult a doctor / pharmacist before using. Note, Diametil is a prescription drug, patients need to use the drug as prescribed by the doctor, absolutely do not self-treat at home.