This is an automatically translated article.
Clamogentin drug is prepared in the form of a powder for injection, with the main ingredients being Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid. The drug is used in the treatment of a number of different bacterial infections.
1. What does Clamogentin do?
Clamogentin medicine has the ingredients: Amoxicillin (as Amoxicillin sodium) combined with Clavulanic Acid (as potassium clavunat). Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid is a bactericidal combination that does not change the mechanism of Amoxicillin (inhibiting bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis) but also has a synergistic bactericidal effect. Specifically, the two drugs in combination have extended the spectrum of action of Amoxicillin to combat many beta-lactamase-producing bacteria previously resistant to Amoxicillin when used alone (due to Clavulanic Acid's high affinity for binding to beta-lactamases). of bacteria and inhibiting bacteria). The bactericidal spectrum of these two components is quite wide, including both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Because the drug has a risk of causing cholestatic jaundice, it should not be used for more than 14 days. Before starting treatment with Clamogentin , the causative organism should be identified and an antibiogram should be made . Pending the results, the patient should be treated with a combination drug if beta-lactamase-producing bacteria are suspected. If the test results show resistance, the drug should be stopped immediately.
Indications for use of Clamogentin:
Short-term treatment (less than 14 days) of infections caused by beta-lactamase-producing strains that do not respond to treatment with aminopenicillin alone:
Infections Severe upper respiratory tract infections: otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis treated with common antibiotics but did not improve; Lower respiratory tract infections by beta-lactamase-producing strains of H.influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis: Acute and chronic bronchitis, pneumonia - bronchiolitis; Severe infections of the urinary tract - genitourinary by bacteria Klebsiella, E.coli and Enterobacter producing sensitive beta-lactamase: urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis; Skin and soft tissue infections: Abscesses, boils, insect bites, cellulitis, wound infections; Dental infections: Alveolar abscess; Bone and joint infections: Osteomyelitis ; Other Infections: Maternal infections, infections due to miscarriage, intra-abdominal infections or prophylaxis of surgical infections. Contraindications to the use of Clamogentin:
People with a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylaxis) to any other beta-lactam antibiotics such as monobactam, cephalosporin, carbapenem; Patients with a history of jaundice or liver failure due to the use of Amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid; People with hypersensitivity to the ingredients and excipients of the drug.
2. How to take Clamogentin
Some notes to remember when taking Clamogentin include:
Do not use the drug for more than 14 days without checking and reviewing the treatment; Clamogentin is only for injection or intravenous infusion, not intramuscular. Direct intravenous injection very slowly (for 3 minutes), intravenous infusion about 30 minutes; Mix the drug solution only before injection. When reconstituted, the drug solution may be temporarily pinkish in color, then turn pale yellow or slightly milky. The drug should be mixed with distilled water for injection or 0.9% sodium chloride solution for injection. For infusion, sodium lactate solution (M/6), Hartmann's solution or Ringer's solution can be used. The drug should not be mixed with solutions containing sodium bicarbonate, glucose or dextran. Do not mix the same syringe or infusion bottle with another drug, especially a corticosteroid or an aminoglycoside. This drug is incompatible with amino acid solution, hydrocortisone succinate, lipid emulsion, proteolytic fluid, mannitol solution, neosynephrine hydrochloride; The stability of the drug preparation solution depends on the concentration. After reconstitution, the drug should be used immediately. It is necessary to adhere to the correct volume of phase, method of preparation and duration of drug administration.
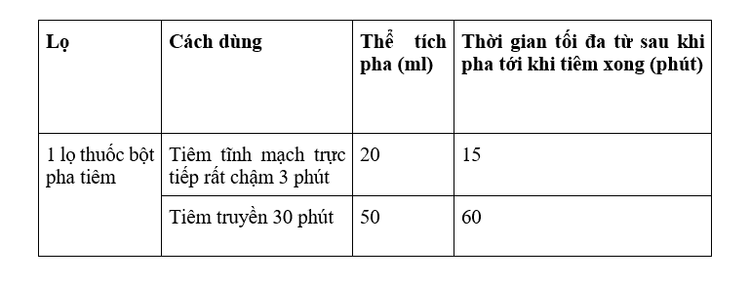
*Note: Each bottle of Clamogentin 1.2g powder for injection is mixed with 20ml of solvent for injection, the final volume is 20.9ml. When reconstituted into a solution for injection, the drug can only be used within the maximum period from the time it is prepared to the time of injection as specified in the table above.
3. Dosage of Clamogentin
Clamogentin dosage is expressed as Amoxicillin in the compound. Specific dosage is as follows:
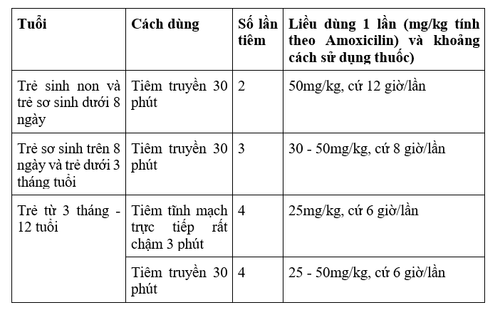
Adults and children over 12 years old: Very slow direct intravenous injection or rapid infusion 1g/time, 8 hours/time. In more severe infections, the dose may be increased by injection every 6 hours or up to 6g/day. Note, not to exceed 200mg of Clavulanic Acid per injection, not more than 1200mg of Clavulanic Acid in 24 hours; Prophylaxis of infection during surgery: Intravenous injection 1 dose of 2g/200mg (or 1g/200mg + 1g Amoxicillin) at pre-anesthesia. If surgery lasts more than 4 hours, 1 dose of 1g/200mg is given. In gastrointestinal surgery, the duration of antibiotic prophylaxis should not exceed the duration of the intervention. In percutaneous endoscopic gastric surgery, the intervention time does not exceed 2 hours, so it is not necessary to inject a dose of 1g/200mg; Children, nursing children, infants: Use 500mg injection vial, do not exceed 5mg/kg body weight for Clavulanic Acid in each injection; Children from 3 months to 12 years old: Use a dose of 100mg/kg/day, divided into 4 times, should be administered intravenously very slowly or by infusion. For severe infections, up to 200mg/kg/day can be used, divided into 4 infusions. The maximum dose of Clavulanic Acid is 20mg/day; Infants over 8 days old and children under 3 months old: Use dose from 100 - 150mg/kg/day, divided into 3 infusions. The maximum dose of Clavulanic Acid is 15mg/kg/day; Premature babies and infants under 8 days old: Use a dose of 100mg/kg/day, divided into 2 infusions. The maximum dose of Clavulanic Acid is 10mg/kg/day. Dosage in Renal Impairment: Dosage or frequency of administration may need to be adjusted in response to renal impairment.
Dosage in adults with renal failure, calculated according to Amoxicillin content is:
Creatinine clearance over 30ml/min: No dose adjustment is required; Creatinine clearance 10 - 30ml/min: Initial dose 1g, then 500mg every 12 hours; Creatinine clearance less than 10ml/min: Initial dose 1g, then 500mg/day injection; Hemodialysis: Initial dose of 1g, then injection of 500mg/day, an additional dose of 500mg immediately after hemodialysis. Dosage in children with renal failure, calculated according to Amoxicillin content is:
Creatinine clearance over 30ml/min: No dose adjustment is required; Creatinine clearance 10 - 30ml/min: Dose 25mg/kg/time x 2 times/day; Creatinine clearance less than 10ml/min: Use dose 25mg/kg/day; Hemodialysis: Administer 25mg/kg/24 hours, then add an additional dose of 12.5mg/kg immediately after dialysis, followed by 25mg/kg/day. Overdose: When Clamogentin is used in an overdose, a few patients have a rash, drowsiness or increased agitation. The treatment should be stopped immediately, supportive treatment and symptomatic treatment if necessary. Some patients with Amoxicillin overdose have interstitial nephritis leading to renal failure oliguria, crystal urine,... Need to provide enough water and electrolytes for the body to maintain the ability to urinate, reduce the risk of urination. crystals. Convulsions may also occur in patients with renal failure or in patients receiving high doses of the drug. At that time, the patient needs to stop taking the drug and treat the accompanying symptoms. Kidney damage is usually reversible once the medication is stopped.
Hypertension may occur in people with compromised renal function due to decreased excretion of Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid. Hemodialysis can be used to remove these two drugs from the circulation. In addition, patients who overdose on drugs may have digestive disorders, water and electrolyte disorders, need to be treated symptomatically and replenish water - electrolytes.
4. Clamogentin side effects
When using Clamogentin, patients may experience some side effects such as:
Bacterial and parasitic infections: Candida infection, overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms; Hematologic and leukemic system disorders: Thrombocytopenia, reversible granulocytopenia, reversible leukopenia (including neutrophils), hemolytic anemia, prolongation of prothrombin time and bleeding time blood; Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, angioedema, serum sickness-like syndrome, hypersensitivity vasculitis; Nervous system disorders: Headache, dizziness, convulsions, aseptic meningitis; Vascular disorders: Thrombophlebitis; Digestive system disorders: Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, dyspepsia, antibiotic-associated colitis; Hepatobiliary system disorders: Increased ALT or AST, hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice; Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Pruritus, rash, urticaria, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, bullous - exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome,...; Urinary system disorders: Interstitial nephritis, crystalluria. If an allergic reaction occurs when taking Clamogentin such as anaphylaxis, erythema, Quincke's edema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the patient should immediately discontinue amoxicillin therapy, receive emergency treatment with adrenaline, breathe gene oxygen. , intravenous corticosteroid therapy, ventilation (including intubation), no further penicillin or cephalosporin treatment.
In case of pseudomembranous colitis, if mild, stop the drug, if severe (possibly due to Clostridium difficile), restore water and electrolytes, use anti-clostridium antibiotics such as vancomycin or metronidazol.
5. Be careful when taking Clamogentin
Some notes patients need to remember before and while using Clamogentin include:
Avoid using Clamogentin in pregnant women, especially in the first 3 months, unless the doctor prescribes it; During breastfeeding, women can use Clamogentin if approved by their doctor; When using Clamogentin, if there are symptoms such as dizziness, headache, the patient should not drive or operate machinery; Attention should be paid to the elderly, patients with a history of jaundice or liver dysfunction due to the use of Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid because Clavulanic Acid increases the risk of intrahepatic cholestasis. Symptoms of cholestatic jaundice are rare with the use of the drug, but can be aggravated. However, these symptoms are usually reversible, disappearing after 6 weeks of stopping treatment; Serious hypersensitivity reactions may occur in patients with a history of allergy to penicillins or other allergens. Therefore, before initiating treatment with Amoxicillin, the patient should be carefully evaluated for a history of allergy to penicillins, cephalosporins or other allergens; Patients with moderate or severe renal impairment should pay attention to adjust the dose; Amoxicillin users sometimes experience redness with fever and lymphadenopathy; Prolonged use of Clamogentin sometimes leads to the development of resistant bacteria; It is recommended to periodically check hematological indicators, kidney and liver function during treatment with Clamogentin; A differential diagnosis should be performed to detect Clostridium difficile diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis; Patients with infectious mononucleosis are at high risk of developing a rash when taking Clamogentin; When intravenous injection of Clamogentin drug in high doses, it is necessary to maintain a balance in the amount of fluid in and out to minimize the phenomenon of urinary stones. Bladder catheters should be checked regularly to avoid occlusive precipitates if high concentrations of the preparation are present in the urine; Patients with renal failure or taking high doses of Clamogentin may experience convulsions; The use of Clamogentin may cause a false-positive reaction in the Coombs test.
6. Clamogentin drug interactions
Some Clamogentin drug interactions include:
Clamogentin may prolong bleeding and clotting time, so caution should be exercised in patients taking anticoagulants (warfarin); Clamogentin can reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, so the doctor should inform the patient to choose the right contraceptive method; Patients with hyperuricemia when using Allopurinol together with Amoxicillin may increase the possibility of Amoxicillin rash; There may be antagonism between bactericidal Amoxicillin and bacteriostatic agents such as fusidic acid, tetracycline, chloramphenicol; Amoxicillin reduces the excretion of methotrexate, increases toxicity on the gastrointestinal tract and on the hematopoietic system; When taking Probenecid immediately before or simultaneously with Amoxicillin will reduce Amoxicillin elimination, increase Amoxicillin blood concentration. However, Probenecid did not affect the half-life, maximum blood concentrations and AUC for Clavulanic Acid; Co-administration of Clamogentin with mycophenolate mofetil may reduce the therapeutic effect of mycophenolate. Above are the uses of Clamogentin medicine. When prescribed Clamogentin, patients should coordinate with all instructions of their doctor to ensure effective treatment and reduce the risk of unpredictable events.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.