This is an automatically translated article.
Acymess medicine has the main ingredient Acyclovir, a drug used to fight viruses, used by injection to treat viral infections and prevent the risk of re-infection.
1. What is Acymess?
What is Acymess drug? Acymess medicine has the main ingredient Acyclovir 250mg, prepared in the form of lyophilized powder for injection. Acyclovir when entering the body will be phosphorylated to the active form Acyclovir Triphosphate, this active ingredient inhibits DNA synthesis and inhibits viral replication by inhibiting DNA polymerase enzyme as well as binding into viral DNA, without affecting normal cellular metabolism. Some of the drug's effects on viruses such as:
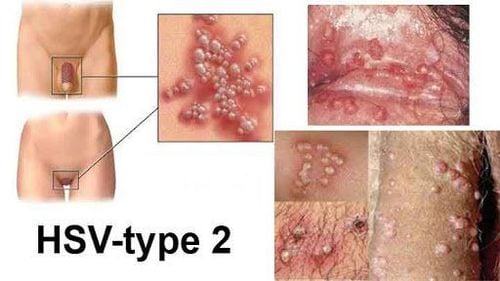
Acyclovir's anti-Epstein-Barr virus activity may be due to the viral DNA polymerase's increased susceptibility to inhibition to low concentrations of Acyclovir triphosphate (produced by cellular enzymes. phosphorylated cells). Anti-cytomegalovirus activity in humans may be due to inhibition of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. The effect of Acyclovir is strongest on Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and less effective on Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), Varicella zoster virus. The drug showed no effect on other latent viruses.
2. Indications and contraindications of the drug Acymess
2.1.Indications Indications of Acyclovir in the following cases:
Treatment in cases of Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection (types 1 and 2) for the first time and relapse in mucous membranes, skin; encephalitis - meningitis, in the eye causes keratitis. Prophylaxis of HSV infections in mucous membranes and skin, in the eyes or in cases of ocular surgery. Varicella Zoster virus infection. Treatment of shingles and prevention of eye complications caused by shingles. Chickenpox in pregnancy ; Neonatal chickenpox; Severe chickenpox in children under 1 year of age; Chickenpox has complications, especially pneumonia caused by chickenpox. 2.2. Contraindications Acymess is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to Acyclovir or to other components of the drug.
3. Usage and dosage of Acymess
3.1 Administration Treatment with Acyclovir must be started as soon as possible at the onset of signs and symptoms of the disease. When mixing the drug, it is necessary to ensure a sterile environment, because the drug does not have anti-infective agents and if the drug is not used up after dilution, it should be discarded. The drug is administered by intravenous infusion, administered by medical personnel within 1 hour to avoid precipitation of acyclovir in the kidneys. 3.2 Dosage Adults:
HSV infection in immunocompromised people, severe initial genital herpes or prophylaxis of HSV infection in immunocompromised people: dose 5 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours . Treat for 5-7 days. HSV encephalitis: Dose by injection 10 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours. Treatment for 10 days. VZV infection: In people with normal immune system, use 5 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours; In immunocompromised patients, use 10 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours. Children:
Children from 3 months to 12 years: Doses are usually calculated according to body area. A course of treatment usually lasts from 5 to 10 days.
HSV infection (except in cases of encephalitis - meningitis) and VZV in children with normal immune system: 250mg/m2, every 8 hours (equivalent to about 10mg/kg/time, every 8 hours/time) ). HSV encephalitis or severe VZV infection in immunocompromised children: Use 500 mg/m2, every 8 hours (about 20 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours). Newborn up to 3 months old:
HSV infection: 10 mg/kg/time every 8 hours. Treat for 7-10 days. Disseminated HSV infection: 20 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours, for 14 days. If there is nerve damage, last up to 21 days. VZV infection: Use with 20 mg/kg/time, every 8 hours. Treat for at least 7 days. Other subjects:
Elderly: Dosage reduction is required in geriatric patients with mild renal impairment. Renal Impairment: Dosage and frequency of administration must be varied according to the degree of kidney damage. Obese: Doses are based on ideal body weight to avoid overdose. In pregnant women infected with VZV: Inject at a dose of 15mg/kg/time, 8 hours apart/time. 3.3 Overdose and missed dose of Acymess Overdose: Symptoms of overdose in patients with renal failure when receiving too high a dose of Acyclovir intravenously have seen changes in consciousness from confusion, hallucinations to coma. Progress is usually good after drug discontinuation and hemodialysis. How to handle overdose patients need to undergo hemodialysis until kidney function recovers, stop taking the drug for fluid and electrolyte transfusion. Missed dose: Injections are administered at a medical facility, so missed doses can be avoided.
4. Side effects of Acymess
When taking Acymess medicine can cause some side effects such as:
Common: Headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, erythema multiforme, rash, photosensitivity . Uncommon: Usually due to the unfortunate injection of the drug out of the vein, causing inflammation and tissue necrosis. Neurological or psychiatric reactions such as lethargy, tremors, confusion, hallucinations, seizures. Rare: Anorexia , digestive disorders; Anemia, causing leukopenia, lymphadenitis, decreased platelet count, thrombocytopenic purpura; hemolytic syndrome; uremia, which can sometimes lead to death, has occurred in immunocompromised patients receiving high doses of acyclovir, headache, dizziness, agitated behavior; Rash, pruritus, urticaria, fever, pain, elevated liver enzymes, hepatitis, jaundice, muscle aches, angioedema, hair loss. The drug can cause renal tubular precipitation when administered intravenously, leading to acute renal failure. No frequencies specified: Abnormal visual function, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
5. Notes when using Acymess
In the course of using Acymess, patients should note:
Be careful when using with people with renal failure, the dose must be adjusted according to the creatinine clearance. Slow intravenous infusion, with a duration of at least 1 hour to avoid precipitation of acyclovir in the kidney. Avoid rapid injection or injection with a large amount, need to give enough water to infuse within 1 hour. The risk of renal failure is increased, if concomitantly with nephrotoxic drugs. Therefore, caution should be exercised when co-administering these drugs; if these drugs must be combined, renal function should be assessed. Intravenous treatment with high doses may cause reversible increases in serum creatinine, especially in dehydrated patients, which may increase the precipitation of acyclovir in the renal tubules. Intravenous administration of acyclovir can also cause manifestations of encephalopathy. Care must be taken when administering to people with diseases of the nervous system, liver and kidney disease, electrolyte disturbances, hypoxia. Caution should be exercised when administering to patients who have experienced a neurological reaction to cytotoxic drugs or have received intracanal methotrexate or interferon. Caution for pregnant women: Acyclovir should be used during pregnancy when the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. Lactation: Acyclovir is excreted in human milk; however, no adverse effects have been reported in the nursing infant while the mother is taking acyclovir. Caution should be exercised when administering the drug to nursing mothers.
6. Drug interactions
Interactions of Acymess with other drugs include:
Probenecid increases the plasma half-life of Acyclovir, reduces urinary excretion and clearance of Acyclovir. Concomitant use of zidovudine and acyclovir may cause lethargy and drowsiness. Close monitoring is required if the patient must be coordinated. Interferon enhances the anti-HSV-1 effect of acyclovir. However, these interactions in clinical practice are still unclear. Amphotericin B and Ketoconazole potentiate the antiviral potency of Acyclovir. Parenteral acyclovir such as Acymess must be used with extreme caution in patients who have received methotrexate into the spinal canal. Acymess is an injectable antiviral drug that should be used under the direction of a doctor. During the course of taking the drug, if you have unusual symptoms, you need to talk to your doctor for specific advice.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.