This is an automatically translated article.
Today, urinary obstruction is one of the risks that causes our body to damage the kidneys leading to many causes affecting the body.
1. Definition: Urinary tract obstruction
Urinary tract obstruction is a condition in which urine cannot flow (on one or both sides) of the ureters, so instead of flowing from the kidneys into the bladder, the urine flows back to the kidneys and can cause damage. injury to one or both kidneys.
Urinary tract obstruction can cause swelling and damage in one or both kidneys. Men and women of all ages are susceptible to this disease. Urinary tract obstruction can also be a serious problem for a fetus still in the womb.
2. Causes of urinary tract obstruction
Urinary tract obstruction can have many different causes. The cause of urinary tract obstruction is the compression caused by urine retention in the kidney which can damage the kidney and ureteral tubes.
Temporary or permanent obstruction of the urinary tract in the ureter can be caused by:
Trauma such as pelvic fracture Tumor metastases to the kidney, bladder, uterus or colon Gastrointestinal diseases Ureteral stones Fig. Central nervous system disorders can also cause urinary tract obstruction, which occurs when the nerves responsible for controlling bladder function fail to function properly. The use of nerve agents to control overactive bladder can also cause urinary tract obstruction in some cases.
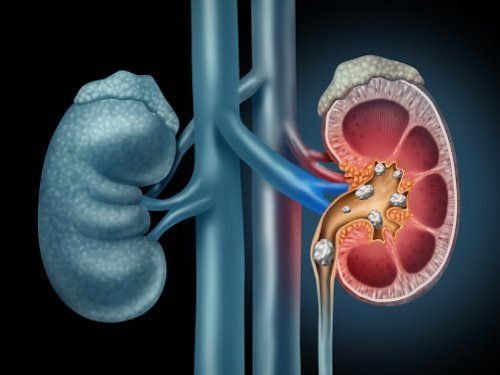
Sỏi niệu quản là nguyên nhân gây nghẽn đường tiết niệu
In men, urinary obstruction can be the result of an enlarged prostate. Pregnant women can also experience urine backflow due to pressure from the uterus on the bladder. However, urinary tract obstruction in pregnant women is relatively rare.
3. Symptoms of urinary obstruction
Urinary tract obstruction can be very rapid (acute) or gradual (chronic). You often feel pain in the middle of your back on one or both kidneys.
The extent and location of pain varies from person to person and also depends on if only one or both kidneys are affected. Fever, nausea, and vomiting are also common symptoms of urinary tract obstruction. The kidneys can become swollen and painful when urine flows back into the kidneys.
A change in urination habits can be a sign that you are suffering from a ureteral obstruction. Symptoms include:
Difficulty urinating Slow flow, leaking, dripping Feeling of needing to urinate all the time, especially at night Feeling the bladder is always full Reduce the amount of urine excreted Yes Yes blood in the urine If only one kidney is affected, the amount of urine excreted is reduced. If both kidneys are blocked, urine output will be severely reduced.
Subclinical manifestations:
Tests may show increased BUN and creatinine; If the obstruction is long enough, there may be evidence of interstitial duct disease (hyperkalemia, non-anion gap metabolic acidosis, mild hypernatremia). Urinalysis is mostly benign or has few cells; Severe proteinuria is rarely present. An obstructing stone can be seen on abdominal ultrasound or helical computed tomography with a 5-mm slice.
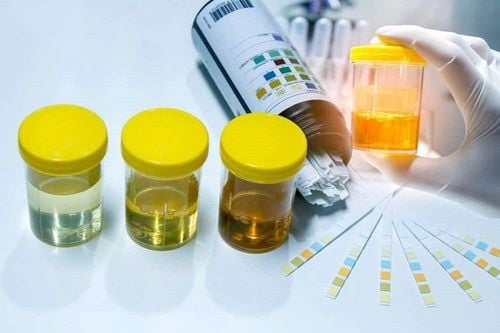
Xét nghiệm nước tiểu giúp chẩn đoán tình trạng nghẽn đường tiết niệu
4. Symptoms of urinary obstruction in the fetus
Complete urinary tract obstruction can happen to the fetus in the womb. One of the signs of urinary obstruction in the fetus is the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus is lower than normal.
Urine is one of the components of amniotic fluid. The fetus with urinary tract obstruction will not be able to excrete urine out of the body, leading to a decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid. This condition can be life-threatening to the unborn baby.
5. Diagnosis of urinary tract obstruction
Ultrasound can help doctors diagnose urinary tract obstruction. Ultrasound may be used to assess the degree of fluid retention and the integrity of the renal parenchyma; Computed tomography or intravenous urography may be used to locate the obstruction. Renal calyx dilatation is common; may not be seen with fulminant obstruction, superior occlusion by retroperitoneal tumor or fibrosis, or by retention of coral stones.
Image of retroperitoneal fibrosis with periarteritis showing the periarterial area, the posterior and lateral encapsulation of the intersecting aorta. Kidney size can indicate the duration of the blockage. It should be noted that unilateral occlusion can be long-lasting and severe (ultimately leading to loss of renal function on the occluded kidney), with no abnormal findings on physical examination and examination.
6. Treatment of Urinary Obstruction
The goal of treatment is to clear the blockage in the ureter so that urine can flow normally. Surgery: The doctor removes blockages such as tumors, polyps, or scar tissue that have formed in and around the ureter so that urine can flow back into the bladder. Stenting: A less invasive treatment method is to place a stent in the blocked ureter or kidney. A ureteral stent is a catheter placed inside the ureter to carry urine from the kidney to the bladder, which can be placed through the skin or through a cystoscope. The stent helps open the ureter and allows urine to drain. This method can be used in cases where the ureter becomes too narrow due to scar tissue formation or other causes.
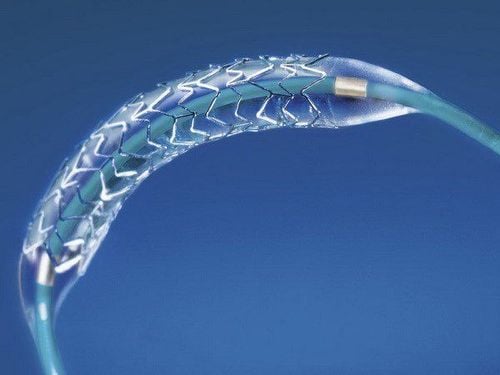
Đặt Stent là phương pháp điều trị hiệu quả, ít xâm lấn
In addition to ureteral stenting, patients with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis are often treated with immunosuppressants (Prednisone, Mycophenolate mofetil, and/or Tamoxifen).
Treatment of ureteral obstruction in the fetus: The doctor may place a catheter or urinary drainage system in the fetal bladder. The catheter will carry urine into the amniotic sac. Treatment is usually done when the fetus's kidneys show signs of irreversible damage. Usually, the doctor will treat to restore kidney function and clear the ureter after the baby is born. The package of Urology Screening - Stones at Vinmec Hospital was born with many utilities, including:
Being examined and consulted by urologists. Perform diagnostic X-ray and ultrasound services. Early detection of urinary diseases, stones and timely treatment advice. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.