This is an automatically translated article.
Blood thinners are medicines that prevent blood clots from forming. It works by helping to prevent existing blood clots from becoming larger. Blood clots in the arteries, veins, and heart can cause heart attacks, strokes, and blockages in blood vessels, and the use of blood thinners should be followed by a doctor's prescription for effective treatment. sick.
1. What are blood thinners?
Blood thinners are drugs that help blood flow smoothly through veins and arteries by keeping blood clots from forming or getting bigger. It is one of the main classes of drugs used to treat certain types of heart disease and heart defects, as well as other conditions that can increase your risk of dangerous blood clots.
While blood thinners can protect people from heart attacks and strokes, they also come with risks. For example, medication may cause a person to bleed more than usual during an injury. However, because the life-saving benefits of these drugs often outweigh the potential risks, the indications for use should be made when necessary and the possible risks involved. At the same time, it is important that the patient also learn about the type of blood-thinning medication being used as well as possible side effects, unusual signs to watch for.
2. Indications of blood thinners
Doctors need to prescribe blood thinners if a person has certain heart or blood vessel conditions:
Abnormal heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation Heart valve replacement Risk of blood clots after surgery Congenital heart defects There are two main types of blood thinners, including anticoagulants such as heparin or warfarin (also called Coumadin) that slow the body's process of making blood clots, and antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin, which prevent blood clots. blocks blood cells called platelets from clumping together to form blood clots.
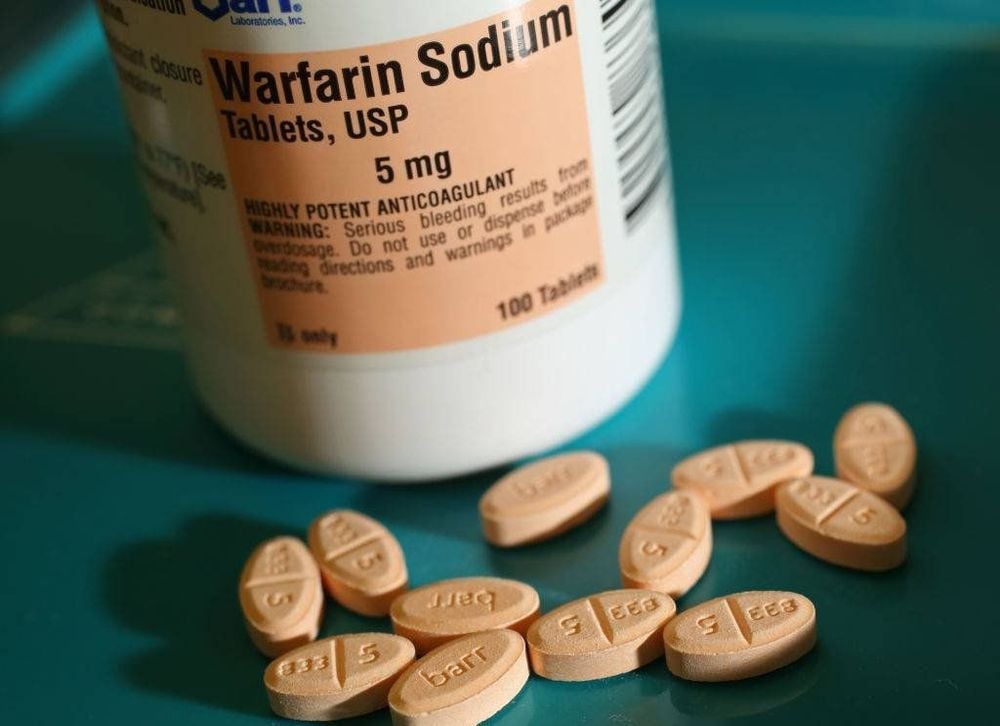
Thuốc chống đông máu warfarin giúp làm chậm quá trình tạo cục máu đông trong cơ thể
When a person is prescribed blood thinners, follow the instructions carefully. Blood thinners can interact with certain foods, medications, vitamins, and alcohol. Therefore, the doctor needs to know all the medications and supplements the patient is taking while taking blood thinners. At the same time, you will likely need regular blood tests to check how well your blood clots. It is important to make sure that the person is taking enough medication to prevent blood clots, but not so much that it causes bleeding, especially in cases of severe bleeding that can be life-threatening.
3. Mechanism of action of blood thinners
Blood thinners do not actually make the blood thinner nor can they break up blood clots. But they keep the blood from forming new clots. They can also slow the growth of existing blood clots.
Vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants do this by competing with vitamin K from the liver. The body needs vitamin K to produce proteins called clotting factors, which help blood cells and platelets easily bind together.
Antiplatelet drugs keep platelets from sticking to each other and to the walls of blood vessels. These drugs are weaker than anticoagulants because their target is platelets.
4. Side effects of blood thinners
Possible side effects during blood thinner treatment include:
Uncontrolled internal bleeding such as bleeding in the brain, abdomen, joints Bruising skin and rash Urine turns dark red or dark brown Stools turn red, dark brown, or black Bleeding more than usual during periods Coughing up blood Bleeding gums or nose bleeds that don't stop Severe headache or stomach pain thickening does not improve Feeling sick, weak, faint, or dizzy Skin with lots of bruising or blood blisters Cuts on the body that do not stop bleeding Internal bleeding, or bleeding, is an emergency get timely medical care.

Sử dụng thuốc làm loãng máu có thể gây tình trạng ho ra máu ở người bệnh
In summary, blood thinners are prescribed for patients who have had blood clots or are at risk of future blood clots or who have had a heart attack or stroke. At this time, blood thinners will both reduce the risk of a second disease as well as prevent this risk from happening. However, because of the opposite risk of causing bleeding, blood thinners when prescribed need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions as well as know how to recognize the signs of side effects of the drug in order to intervene. timely.
Blood thinners are prescription drugs, so before using, patients should consult pharmacists, professional doctors. Avoid self-medication that can pose many health risks.
Vinmec International General Hospital has a team of leading doctors and experts specializing in examination and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Patients can register for an examination to receive in-depth advice on medication use as well as treatment directions to help improve their health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com