This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Pham Lan Huong - Pediatric Center, Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Urinary tract infection is a common disease in children, occurring because pathogens (bacteria, viruses...) enter the urinary tract (kidneys, ureters, bladder...). Young children with urinary tract infections show fever, irritability, and fussiness; Older children present with fever, painful or frequent urination, or abdominal pain in the lower abdomen.
1. Signs of urinary tract infection in children
Most infections in the lower urinary tract including the bladder and urethra are called Cystitis . Symptoms of children may be as follows:
Painful, burning urination Urinating more often even though the amount of urine is very small Fever Waking up many times during the night Bedwetting, even though the child has been trained to urinate Abdominal pain in the bladder area (below the belly button) Foul, cloudy or bloody urine An infection that spreads from the ureters to the renal pelvis, called pyelonephritis , is often more dangerous. Symptoms can be similar to Cystitis, but children are often more tired, have a high fever that is persistent, and may be accompanied by chills with the fever, back pain, or vomiting a lot.

Trẻ xuất hiện triệu chứng sốt cao
2. Risk factors for urinary tract infections in children
Urinary tract infections are more common in girls because the urethra is short and close to the anus. Male children under one year of age with foreskin stenosis have a higher risk of developing the disease; The child has a defect or blockage somewhere in the urinary tract; Children have a reflux of urine from the bladder to the ureters, renal pelvis; Frequent urination or poor hygiene; Family history of urinary tract infections. Urinary tract infections can be treated simply, but early and correct detection is important. Undiagnosed and untreated urinary tract infections can lead to kidney damage.
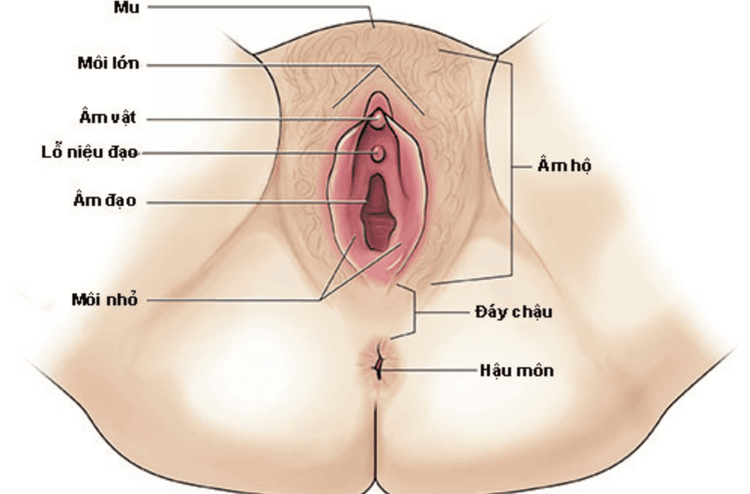
Cấu tạo cơ thể, niệu đạo gần hậu môn nên trẻ gái thường bị nhiễm khuẩn tiết niệu
3. Diagnosis of urinary tract infections
Diagnosing urinary tract infections in children, medical staff need to exploit the symptoms, examine to detect clinical signs and do urine and blood tests.
How the urine sample is collected depends on the age of the child. Older children can easily urinate and store it in a sterile container. For young children, the healthcare provider may place a drain from the urethra into the bladder to collect clean urine from the child.
The child's urine sample is tested for urinalysis (which is a method of looking at urine samples under a microscope to find bacteria or pus) or urine culture (which is a method of culturing a urine sample on a suitable medium). help to grow bacteria and identify the type of bacteria that causes disease). Identifying the type of bacteria that is causing the infection can help your doctor choose an antibiotic to treat.

Mẫu nước tiểu được đưa đi xét nghiệm
4. Treatment of urinary tract infections
Children with urinary tract infections are prescribed antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause the disease. After a few days, the child's urine sample is retested to see if the infection has cleared up.
In addition, children with symptoms of fever or pain when urinating will be given antipyretic and pain relievers. These signs usually improve after 2-3 days of treatment.
Children should be encouraged to drink plenty of water, but not coffee, soda or tea.
Children with severe urinary tract infections need to be hospitalized for intravenous antibiotics or injections. Including the following cases:
The child has a high fever continuously, is very tired or is diagnosed with Pyelonephritis; Children under 6 months old; bacteria spread from the urinary tract into the bloodstream (sepsis); The child is dehydrated, vomiting, or unable to take medicine. Children with vesicoureteral reflux need to see a doctor for treatment with medication or surgery (very rare).
5. Prevention of urinary tract infections
For young children using diapers, changing diapers often helps prevent the spread of bacteria that cause urinary tract infections.
Instructions for washing hands after using the toilet for children who have urinated on their own. For girls, wipe from front to back to limit the introduction of bacteria from the anus into the urethra.
Girls should not bathe with soapy soap to avoid scratching the urethra, and should wear cotton underwear instead of nylon.

Đưa trẻ đến gặp bác sĩ nhi khoa giúp cha mẹ yên tâm hơn
6. When to see a doctor?
The child has an unexplained fever with chills, especially if the child has back pain or pain when urinating.
In addition, the child has abnormal signs:
Bad smell when urinating, blood in urine; Pain in the back or lower abdomen; Fever over 38.3 degrees Celsius in young children or over 38 degrees Celsius (rectal measurement) in children; Newborns have fever, poor appetite, vomiting, or irritability. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE ALSO:
Caring for children with urinary tract infections Guidelines for care and detection of children with UTIs What you need to know about urinary tract infections