This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.When the triglyceride index is high, people can face the risk of acute pancreatitis. Although this possibility accounts for only about 5% of all cases in general, the complications of acute pancreatitis due to elevated triglycerides are not mild.
1. What is acute pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia?
Acute pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia usually occurs in patients when triglyceride levels reach above 20 mmol/l. On the other hand, when triglycerides are mildly and moderately elevated, they play a major role in the initial phase of the inflammatory process in the pancreas. In fact, the triglyceride index can increase very quickly after a high-fat meal, so about 10% of patients are diagnosed with acute pancreatitis when testing triglyceride levels above 20mmol/l, but the concentration is above 20mmol/l. This again decreased very quickly after about 72 hours of treatment. Therefore, the test can help detect the cause of acute pancreatitis due to high triglycerides and have timely treatment.Until now, the mechanism of causing acute pancreatitis due to elevated triglycerides has not been elucidated. Some studies have shown that chylous granules (which will begin to appear in the blood of patients when triglyceride levels rise above 10mmol/l) contain lipoprotein molecules that are rich in triglycerides, which is the main cause. cause inflammation in the pancreas. When the body works according to the circulatory system to the pancreas, the largest chylous particles will cause blockage of the pancreatic capillaries, causing the pancreatic acinars in the ischemic areas to rupture and the cholymicrons will come into direct contact with pancreatic lipase, further damaging the acinar and microvascular parenchyma of the pancreas.
2. Causes of acute pancreatitis due to increased triglycerides
There are many causes of acute pancreatitis, in addition to the leading causes of alcoholism and gallstone disease, it is also due to hypertriglyceridemia. This cause often goes unnoticed or overlooked at the time of diagnosis (only discovered during testing and no other cause can be found).
In adults, severe hypertriglyceridemia is often the result of a combination of primary and secondary causes. When conducting a study in 123 patients with triglyceride levels > 2,000 mg/dL, it was found that all patients had a primary metabolic defect and up to 110/123 patients had both primary and secondary causes. secondary. In fact, inherited disorders of lipoprotein metabolism often develop insidiously until there is a secondary cause of elevated triglyceride levels and severe hypertriglyceridemia syndromes.
The degree of hypertriglyceridemia will be proportional to the degree of acute pancreatitis. At the same time, a number of factors also influence the status of acute pancreatitis including: pancreatic lipase activity, previous pancreatic damage or efficiency of fatty acid removal from the pancreas. serous....
3. Pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis due to increased triglycerides
Acute pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia usually occurs when triglyceride levels exceed 1000 mg/dl, they work by two main mechanisms:Due to an increase in the concentration of chylomicrons in the patient's blood:
Chylomicrons are substances form after about 1 to 2 hours when eaten and peak after 4-5 hours, within 8 hours they will be cleared. However, when there is an abnormality in lipoprotein structure and lipoprotein lipase enzyme in the body, the concentration of Chylomicrons will increase in the blood. Until the elevated triglyceride levels exceed 1000 mg/dL, chylomicrons will appear frequently in the capillaries, their very large size can block the pancreatic capillaries and lead to anemia causing necrosis and acidosis. . In the acidic environment, free fatty acids cause trypsinogen activation, which will lead to autodigestion of pancreatic tissue and cause acute pancreatitis.
Decomposition of triglycerides into free fatty acids:
When the concentration of chylomicrons is high, triglycerides will contact the pancreatic lipase enzyme around the pancreas and form free fatty acids in high concentrations, causing infectious lesions. Pancreatic cytotoxicity and local injury, as well as increased inflammatory mediators and free radicals, then manifested externally by signs of acute pancreatitis.
4. Symptoms of acute pancreatitis caused by triglycerides
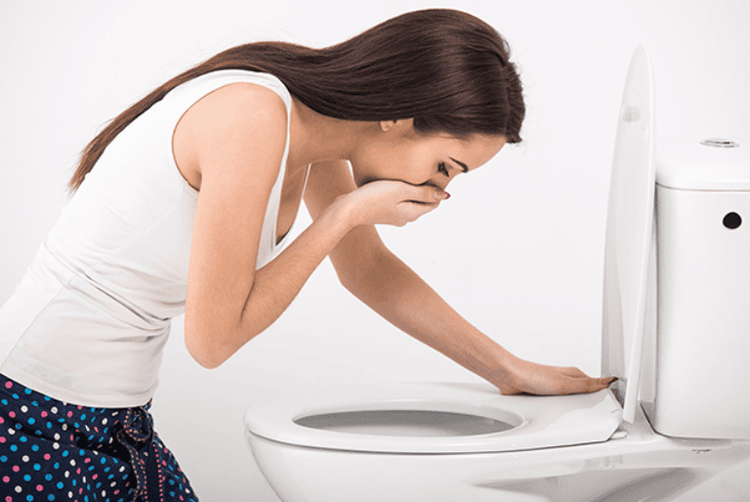
Acute pancreatitis due to increased triglycerides has clinical symptoms similar to acute pancreatitis due to other causes, patients will have:Severe abdominal pain, abdominal distention, bowel obstruction; Nausea, vomiting;

5. Treatment of acute pancreatitis due to high triglycerides
The treatment plan for acute pancreatitis due to elevated triglycerides is the same as for acute pancreatitis caused by other causes such as fluid rehydration, intravenous nutrition, electrolytes, antibiotics if there is infection, acid-base balance. , intensive resuscitation for critically ill patients with organ failure....In the case of acute pancreatitis caused by too high triglycerides, the treatment method is plasma exchange to remove the amount of cholymicrons. too high in the blood. This is an effective and safe measure that helps prevent inflammation in the pancreatic parenchyma and is affordable for many patients.
Patients after stable treatment of acute pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia need to find out the cause of the increase in triglycerides to eliminate and use drugs to reduce the concentration of this substance in the blood to avoid recurrence of acute pancreatitis.
With nearly 20 years of working at Da Nang General Hospital in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy - hepatobiliary disease, every year, Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang participates in endoscopy more than 1500 cases including: endoscopic diagnosis of diseases stomach, colon such as: detecting inflammation, ulcers, polyps, cancer, finding HP bacteria, detecting cancer early in the digestive tract...; Endoscopic treatment such as: Hemostasis in gastrointestinal bleeding, esophageal varices ligation in cirrhosis, endoscopic gastrointestinal polypectomy...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.