This is an automatically translated article.
The article is consulted by the Master. Doctor Nguyen Quang Duc - Doctor of Nuclear Medicine - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
The parathyroid gland is a small endocrine gland, but the function of the parathyroid gland is very important. Parathyroid adenoma is a common disease, especially in elderly women. The simplest method to detect parathyroid tumors is ultrasound.
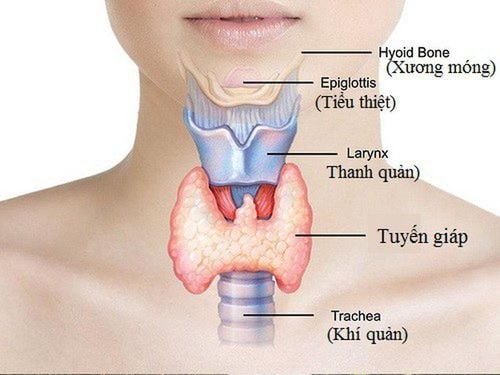
1. Anatomy and function of the parathyroid gland
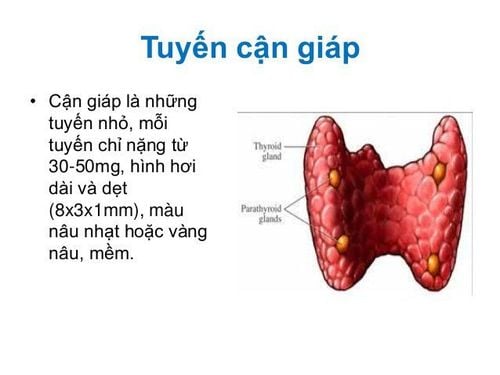
The parathyroid gland is a small endocrine gland, about 6x4x2mm in size, consisting of 4 glands, each weighing about 30-50mg, slightly elongated and flattened, soft, brown or yellow-brown. The normal person has 4 parathyroid glands: 2 superior parathyroid glands located behind the thyroid gland and 2 inferior parathyroid glands located behind the lower pole of the thyroid lobe. Sometimes some people have 5 to 6 parathyroid glands or, rarely, 3 parathyroid glands.
The function of the parathyroid gland is to secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH). Once secreted from the parathyroid glands, the half-life of PTH is very short, only about 10 minutes. The role of PTH on cell membranes is to make it easier and more active for calcium to enter cells. The effects of PTH mainly take place in the bones, kidneys and intestines.
In the bone: The effect of accelerating bone replacement, in which the osteoclast effect predominates with an increase in the distribution of calcium and phosphorus into the blood causing hypercalcemia. In the kidney: PTH creates favorable conditions to enhance the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules after glomerular filtration. PTH reduces phosphorus reabsorption in the renal tubules. Intestinal: Increases absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestine. Therefore, the main function of the parathyroid gland is to regulate the concentration of calcium and phosphorus in the blood, this is a very important function for the body, because calcium participates in the functioning of the neuromuscular system.
2. Ultrasound in parathyroid tumors
Parathyroid tumor is a disease that can occur at any age, but mainly occurs in people aged 50-70 years, women are 3 times more likely to have parathyroid tumors than men.
Some clinical signs may be seen often due to adenoma causing hyperparathyroidism . Common manifestations such as:
In the kidney: Patients with hyperparathyroidism often have kidney stones. The rate of patients with parathyroid tumor has kidney stones about 80%. In bones: Pain occurs in the long bones, spine, pelvis. There may be natural fractures, long healing times, premature tooth loss. Bone deformity occurs later. This phenomenon is due to increased levels of PTH increase bone resorption. On nerves and muscles: May have moderate or severe muscle weakness causing difficulty with movement, possibly causing muscle atrophy. Most patients feel very tired, anxious, have memory loss, and are prone to stress. Digestive: Anorexia, nausea, epigastric pain, constipation, possibly gastric and duodenal ulcers. In addition to the above clinical signs, it is necessary to combine with subclinical signs to diagnose the disease. Among them, ultrasound is one of the first imaging methods used with parathyroid tumors. Especially more effective in cases of tumors with hyperplasia, increased parathyroid gland size.
Ultrasound is a method of using ultrasound waves to probe organs in the body, the advantage is that it is quick and cheap, it can specifically evaluate the parathyroid gland, see the state of increased angiogenesis, the branches of the vessels. feed.
Ultrasound images of parathyroid tumors can be seen on conventional ultrasound, including:
Usually, the image of the adenoma is a solid, hypoechoic, relatively homogeneous mass, located behind the thyroid gland. However, there are also some cases of parathyroid adenomas that have fluid-filled cysts. The shell of the tumor can be clearly seen, dividing the mass separate from the thyroid gland. Assess surrounding organizations: Infiltration can be seen.
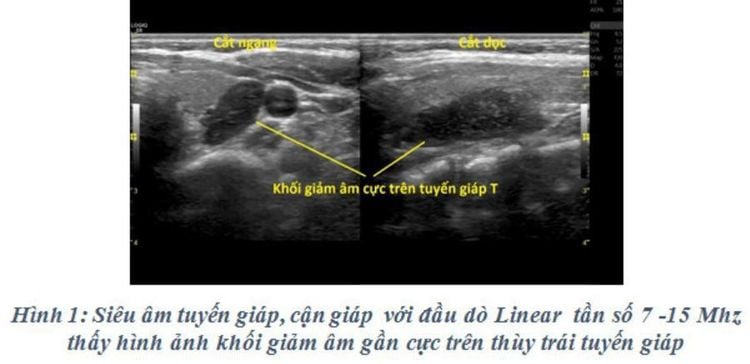
On Doppler ultrasound:
There is an increased angiogenesis in both the periphery and the center of the mass, but mainly the angiogenesis is in the periphery. A branching of the feeding vessel can be seen from the inferior thyroid artery, entering one pole of the mass. Image of the artery that feeds the branching gland that runs in the periphery before going deep into the center. On the elastography ultrasound:
The tumor of the parathyroid gland is found to have a relatively low hardness, almost much lower than that of a benign thyroid tumor.
Thus, ultrasound is a method to make the diagnosis of parathyroid tumors simpler. In addition to this measure, in cases in combination with abnormal tests and suspected disease, it can be combined with other laboratory methods such as scintigraphy, ...
Parathyroid tumor is a very rare condition. common, may be discovered incidentally on ultrasound or blood tests. The disease has a serious impact on health, so when you see the body showing unusual signs, especially osteoporosis in young people, you should go to medical facilities for examination and early diagnosis.
Besides, patients should choose good quality medical units for accurate examination and timely intervention.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a routine of screening and screening for parathyroid diseases effectively, helping to check the function, screening and early detection of parathyroid diseases.
The examination is always performed by a team of doctors, experts with many years of experience in the profession combined with a system of modern equipment and machines to make the treatment more effective and shorten the hospital stay. hospital for the sick.
Therefore, the hospital is a reliable medical care address and always receives high praise from both professionals and customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.