This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Master, Doctor Le Hong Chien - Doctor of Radiology - Intervention - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Ultrasound is a method of imaging common bile duct stones with many advantages, without affecting the patient's health, with high accuracy. The method of diagnosing common bile duct stones on ultrasound will determine the location and size of the common bile duct stones with an accuracy of 95%.
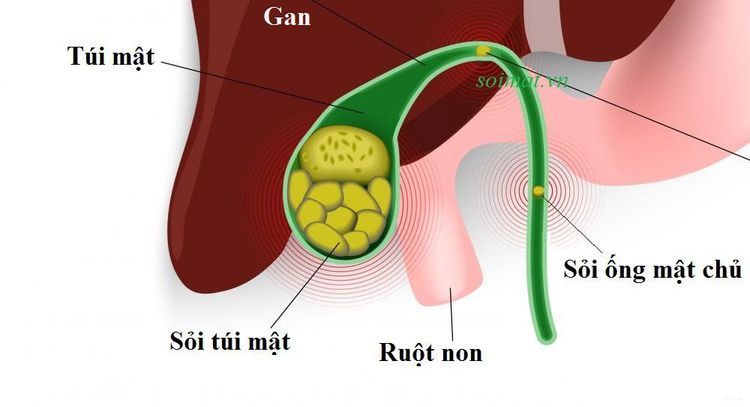
1. What are common bile duct stones?
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of at least one gallstone in the main extrahepatic biliary tract. Stones can be from bile pigments or calcium and cholesterol salts. People with a history of gallstones, gallbladder disease will have a high rate of common bile duct stones. Some of the following other factors increase the risk of developing common bile duct stones such as:Obesity, a diet high in fat, low in fiber, high in calories, prolonged fasting Pregnant women Losing weight quickly but lack of physical activity If a family member has had common bile duct stones, you are at risk. Common bile duct stones, if not detected early and treated promptly, can lead to many dangerous complications such as:
Obstruction of the bile ducts: Gallstones can block the bile ducts, causing jaundice and biliary tract infection. Peritoneal bile infiltration: Because bile stagnates above the obstruction of the common bile duct, seeps through the wall of the bile duct. Biliary peritonitis: Caused by rupture of the gallbladder or perforation of the common bile duct, bile and bacteria enter the abdomen causing peritonitis. Purulent cholangitis and hepatobiliary tract abscess: Due to bile stasis and infection, pyelonephritis causes cholangitis. Subsequently, many small abscesses were formed scattered around the liver. Biliary tract bleeding: Bleeding in the bile ducts in the case of stones and abscesses causes ulceration of the bile duct wall, causing the bile duct to communicate with blood vessels in the liver. Septic shock of biliary tract: patients with high fever, biliary obstruction syndrome, low blood pressure, blood cultures with bacteria. Pancreatic duct obstruction – pancreatitis: The tube leading from the pancreas to the common bile duct that helps the body digest food. Gallstones can obstruct the pancreatic duct leading to acute pancreatitis, which requires prompt treatment to avoid dangerous complications. Cholecystitis: Gallstones in the neck of the gallbladder can cause cholecystitis and may require cholecystectomy when the gallbladder becomes inflamed again and again, losing function. Gallbladder cancer: Patients with gallstones have a high risk of gallbladder cancer, but the incidence is very small.
2. Symptoms to recognize common bile duct stones
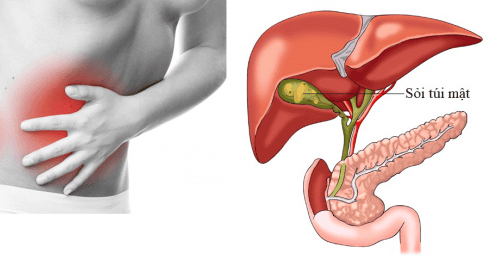
Common bile duct stones cause dangerous complications as above, so recognizing the signs and symptoms of the disease is very important for timely treatment. Symptoms of common bile duct stones include:Pain in the right lower quadrant: The patient will have severe pain, pain spreading to the right shoulder or back, the pain is worse after eating and the pain lasts. Fever: Symptoms of fever usually occur simultaneously or a few hours after pain, high fever 39-40oC accompanied by chills and sweating. In addition, the patient may have dry lips, fatigue; thin people, rapid pulse Jaundice and eye mucosa: This is the main symptom, appearing later, at first only mild yellow in sclera, then dark yellow in both skin and mucous membranes. Gallbladder distention: When the gallbladder is distended, it may emerge below the right costal margin, palpable, round, smooth, even, tender, and mobile. In some cases the liver is enlarged below the costal margin. Other symptoms: Vomiting symptoms are often accompanied by pain, and the urine is small and dark like water. Occasionally, discolored stools due to complete biliary obstruction and skin pruritus due to bile salt toxicity are present.
3. Image of common bile duct stones on ultrasound
Ultrasound is a method of imaging common bile duct stones with many advantages such as simplicity, low cost, no effect on patient's health, high accuracy. The method of diagnosing common bile duct stones on ultrasound brings high value as follows:Determine the location and size of common bile duct stones on ultrasound with accurate results up to 95%. Ultrasound is widely used to aid in the diagnosis of hepatobiliary diseases. The image of common bile duct stones on ultrasound is usually an echogenic structure with shadow and is located in the common bile duct. Similarly, gallstones will show a dark shadow in the gallbladder.
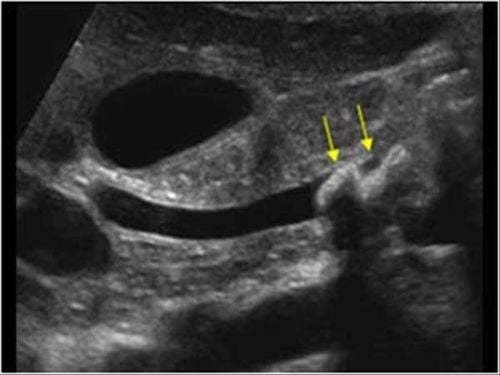
Difficulty in surveying the biliary tract in obese people Stones in the lower part of the common bile duct are more difficult due to gas in the duodenum - the transverse colon, the patient has old surgical scars, thick abdominal wall... Therefore, in addition to the ultrasound method of common bile duct stones, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can be used in the diagnosis of suspected stone cases. which cannot be confirmed by ultrasound.
4. Treatment of common bile duct stones
After diagnosing the condition of common bile duct stones in the patient, the treatment is an indispensable measure to prevent complications.Non-surgical treatment:
Temporary medical treatment of infectious biliary obstruction in acute biliary obstruction is always accompanied by infection or biliary obstruction causing bile stagnation, making bacteria active and growing; or there is an infection of the biliary tract with swelling and hugging the stone obstructing the flow of bile; The main treatment is antibiotics against Gram (-) bacteria, smooth muscle relaxants. This method temporarily treats symptoms to limit complications caused by stones.
Use chemicals to dissolve gallstones such as:
Use chemicals to dissolve gallstones such as giving oral chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic. Mixture of MTBE (Methyl - Tertiary - Butyl - Ether) is injected into the biliary tract through endoscopy. Currently, there are many advanced methods to treat common bile duct stones with minimally invasive techniques that have been widely applied:
Endoscopy through the duodenum, sphincterotomy to remove stones (ERCP). Percutaneous lithotripsy, endoscopic biliary lithotripsy. Extracorporeal lithotripsy: Currently, many countries around the world apply OMC lithotripsy outside the body, the results are quite successful. Surgical treatment:
Surgical treatment is a surgical method to remove stones, create bile-intestinal circulation and drain the infection of the biliary tract. Before surgery, it is necessary to have medical treatment first such as antibiotics, choleretics, biliary smooth muscle relaxants, fluids, and electrolytes. Indications for surgery when:
Emergency surgery: Indicated in cases of biliary peritonitis and peritoneal biliary infiltration. Indications for delayed emergency surgery: In case of biliary tract bleeding due to stones, biliary abscess due to stones, acute pancreatitis due to gallstones. In case of septic shock of the biliary tract, acute nephritis caused by gallstones must be resuscitated well, then surgery early and with minimal intervention. Steps of common bile duct stone surgery include:
Step 1: Prepare surgical instruments to ensure sterile, endotracheal anesthesia Step 2: Cut the middle white line above the umbilicus, if necessary, pull further below the navel 1- 2 cm. The doctor examines the liver, gallbladder, determines the stone and the location of the stone in the common bile duct. Step 3: Open the common bile duct in the upper duodenum to remove stones and foreign bodies, then wash the biliary tract with serum, pump out the intrahepatic bile ducts to remove the stones in the liver. Step 4: Check the circulation of the common bile duct with the duodenum with a Benique catheter and intraoperative cholangiography. Step 5: Drain the biliary tract by Kehr tube to drain the infected bile, then check the biliary tract through Kehr after surgery. If the gallbladder is necrotic or gallstones are present, the gallbladder must be removed. If there are stones in the liver combined, it is necessary to carry out the removal of the stones in the liver by instruments or lithotripsy. In some cases, the common bile duct can be sutured closed if intraoperative cholangioscopy has confirmed all stones and good biliary drainage into the duodenum.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.







![[Video] Don't be subjective with gallstone disease](/static/uploads/small_20191104_030711_425223_soi_omc_max_1800x1800_jpg_2e7a54defa.jpg)



