This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Mai Anh - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Thi Mai Anh has nearly 10 years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially in imaging breast and thyroid cancer.Bladder tumor is a common tumor in patients with urinary tract cancer. Bladder ultrasound helps to identify abnormalities, morphological features of the bladder. So how is this method done, what is the image of bladder tumor on ultrasound? The article will help readers better understand the ultrasound method to diagnose bladder diseases.
1. What is a bladder tumor?
Bladder tumor is the most common type of cancerous tumor of the urinary tract. This is the type of tumor that accounts for the highest percentage of urinary tract tumors and the second most common among urogenital - genitourinary tumors.According to statistics, in the world bladder tumor is the second disease after prostate cancer.
2. Causes of bladder tumor
According to research, bladder tumors are caused by many causes, including the following main causes:Genetics:
Due to an abnormal change in the replication process from DNA to RNA leading to changes in protein synthesis.
Smoking:
Smoking is a major factor in the development of bladder tumors and the development of bladder cancer if malignant. According to statistics, it is estimated that one-third of bladder cancer patients are related to smoking, the proportion of smokers with the risk of bladder cancer is four times higher than that of the general population. equivalent in both sexes.
Statistics show that 50% of male bladder tumor patients smoke and 35% of female patients.
Due to occupation, exposure environment:
Working environment related to printing, chemical, dyeing, rubber, petroleum, and tanning industries has a high risk of disease. Caused by substances: benzidine, beta-naphthylamine and 4-aminobiphenyl, which are potentially pathogenic. The exact mechanism by which these chemicals induce tumors is unknown, but it appears to be a multistep process and involves the activation of oncogenes and the suppression or complete destruction of the tumor. whole gene that inhibits cancer.
Due to fluke:
The type of fluke that causes bladder tumors often appears in African countries due to a blood fluke with the scientific name Schistosoma.

Thuốc lá là một trong các nguyên nhân chính gây u bàng quang
3. Symptoms of bladder tumor
Clinical symptomsBlood in the urine: This symptom occurs in 85-90% of patients. Unexplained hematuria, which may be gross or microscopic hematuria, hematuria, or recurrence. In addition to blood in the urine, accompanied by symptoms of dysuria, painful urination.
There may be bone pain if bone metastases, low back pain if metastases into the retroperitoneal space or compression of the ureter.
Subclinical symptoms
Ultrasound:
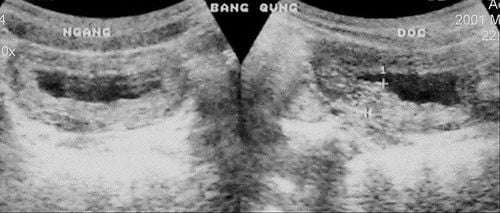
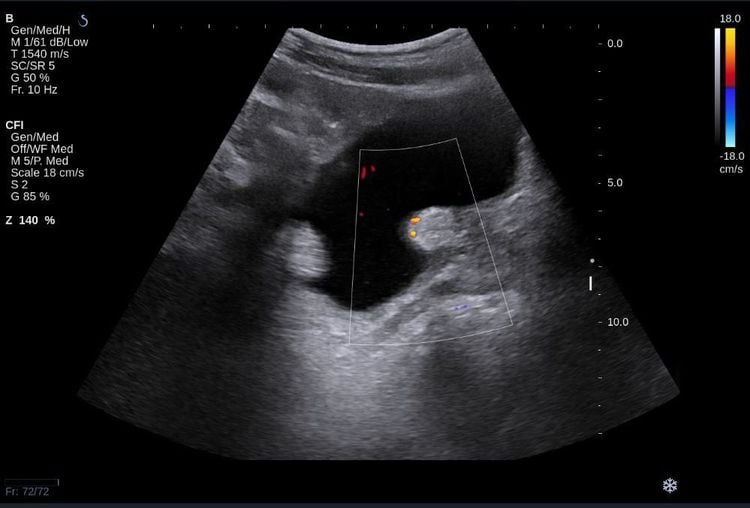
Ultrasound is a convenient, fast, highly accurate test that helps the doctor to see the image of the entire bladder lumen and bladder wall, thereby One or more tumors can be seen, sometimes even tumor infiltrates.
Ultrasound is also a means of monitoring recurrence after endoscopic treatment of superficial bladder tumors. In addition, images of the kidneys, renal pelvis, prostate gland,...
can also be seen.
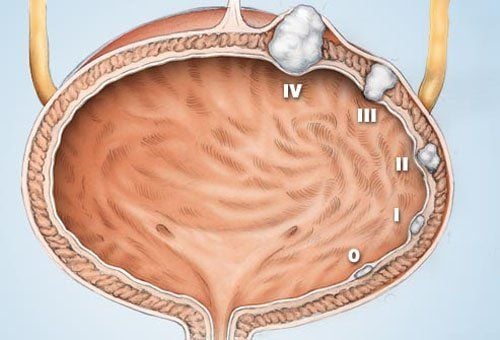
4. Image of bladder tumor on ultrasound
Bladder pathology has many different signs, from which the ultrasound image is also different. Common bladder diseases:Diffuse bladder wall thickening:
There are 2 main causes of diffuse bladder wall thickening:
Neurogenic bladder. On ultrasound, the bladder wall is thickened, with a "waist" appearance in cross-section. Many such knots form the shape of a pine tree.
Tuberculosis cystitis. The bladder is thick-walled and small in volume. The patient feels the bladder is full when this ultrasound image is taken.
Focal bladder wall thickening:
Causes of focal bladder wall thickening:
Transitional cell carcinoma – this is the most common cause. Very variable shape, possibly with calcified crust on the surface.
Schistosomiasis is common in the late stages, but is often focal thickening.
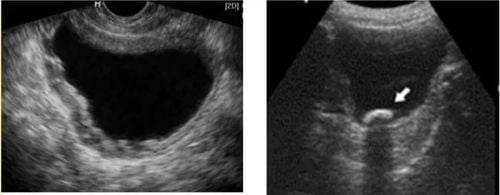
Hình ảnh u bàng quang trên siêu âm
Stones with typical crescent-shaped, shadowy hyperechoic surface. Move in patient position
Urine catheter
Blood clot May move or stick to the bladder wall. Disappear spontaneously or with washing.
Transitional cell carcinoma Convex polypoid
Cystoid lesions associated with bladder wall:
Hernia of the ureter: Usually triangular but can be ectopic. Size changes according to ureteral peristalsis
Bladder diverticulum when ultrasound shows thin wall protruding outside the bladder. Change in size when the bladder is full or after urination
Urinary cysts appear between the bladder and the navel
Muller duct cysts Not communicating with the bladder
Ultrasound technique to diagnose bladder diseases is a safe method , and cause few complications, so doctors often choose to perform. Therefore, if the body has abnormal manifestations, the patient should go to the doctor for diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of facilities, modern medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can completely rest assured to visit and treat. treat.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.