This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Dr., Dr. Tran Nhu Tu - Dean and Master, Doctor Lam Thi Kim Chi - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International HospitalUltrasound is often chosen as the first diagnostic tool in soft tissue lesions of the head, face and neck, including inflammation of the salivary glands. The test has a diagnostic role in determining the disease and provides information to help differentiate salivary gland inflammation from other diseases.
1. Ultrasound diagnosis of salivary gland inflammation
1.1 Ultrasound diagnosis of acute salivary gland inflammation Through ultrasound images, in acute inflammation, the salivary glands are larger than normal in size and hypoechoic. The hypoechoic region is not uniform, small oval. Color ultrasound can observe increased blood flow to the inflamed area. In acute salivary gland inflammation, lymph nodes increase in size.
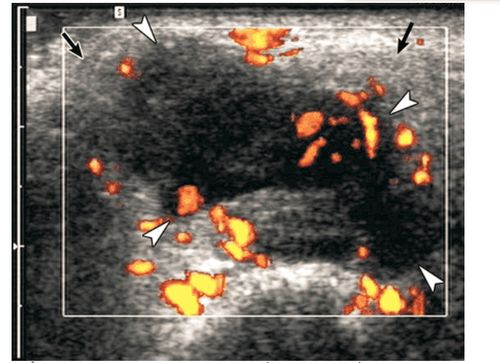
1.2 Ultrasound diagnosis of chronic salivary gland inflammation Ultrasonography of chronic salivary gland inflammation often shows the salivary glands to be normal or small in size, hypoechoic, heterogeneous, and usually without an increase in superior vascular flow. Doppler ultrasound. The hypoechoic area is small round, oval, distributed throughout the glandular parenchyma.
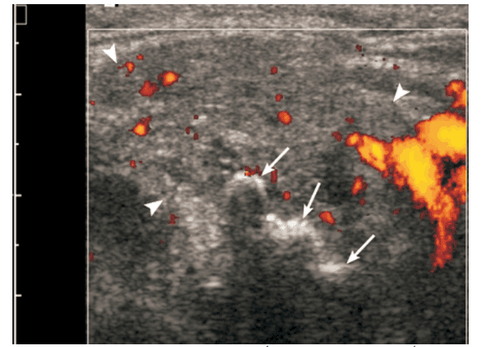
Viêm tuyến nước bọt mạn trên siêu âm
1.3 Ultrasound diagnosis of abscess - abscess in acute salivary gland inflammation On sonographic images, the abscess is a hypoechoic lesion or an acoustic drum with posterior echogenicity and indistinct margins. The central region of liquefaction can be detected as an avascular region or as mobile deposits. Hyperechoic dots are visible inside the abscess. In addition, the hyperechoic region surrounding the abscess can be detected. Ultrasound is used to perform the drainage procedure.
1.4 Ultrasonographic diagnosis of chronic sclerosing salivary gland inflammation In chronic sclerosing salivary gland inflammation, diffuse Küttner tumors can be observed with multiple small hypoechoic dots scattered in a glandular background. Heterogeneous.
In the local case, the hypoechoic lesion is heterogeneous, observed mainly within a normally shaped gland. Suspected cases of chronic sclerosing salivary gland inflammation should be aspirated, biopsied to diagnose the disease.
1.5 Ultrasound diagnosis of granulomatous salivary gland inflammation On ultrasound, granulomatous granulomatosis has a nonspecific picture. In the salivary glands, there are one or more hypoechoic areas, normal size or enlarged salivary glands, diffuse hypoechoic. Blood vessels may have increased flow.
For tuberculosis of the salivary glands, under ultrasound, large salivary glands can be observed. The valvula is localized almost acoustically in the parotid gland, possibly with many internal cavities and cavities. The pituitary necrosis caverns are hypoechoic, without blood vessels. In mycosis, the salivary gland is observed as a malignant, hypoechoic mass with indistinct margins.
Khối u chia thùy múi, không đồng nhất
1.6 Ultrasonography for the diagnosis of salivary stone disease Ultrasound is a non-invasive method that is well used in all cases of suspected salivary gland stones and is often used as the first diagnostic tool.
In salivary gland calculi, ultrasound imaging shows strongly echogenic bands or spots with distal echogenicity. If there are symptoms of tube blockage, the dilated tubes are clearly visible.
When submandibular gland stones are suspected, ultrasound imaging may reveal stones located in the glandular parenchyma or in the Wharton duct. Determining the location of the stone helps to choose the appropriate treatment.
Ultrasound imaging of chronic ductal calculi is often more difficult to detect. At this point, the stones lying in the tube are not dilated. Stones located near the foramen or midway of the Wharton tube may be better revealed by intraoral pressure on sonography.
In about half of patients, salivary gland stones coexist with inflammation. Hyperechoic bubbles of gas mixed with saliva may mimic stones in the Wharton tube leading to misdiagnosis.
1.7 Diagnostic Ultrasound of Sialosis Sialosis is a recurrent, painless, non-inflammatory, tumorless swelling of the salivary glands that is usually bilateral and involves the parotid gland. Sialosis often occurs with endocrine diseases, poor nutrition, cirrhosis, alcoholism, or other deficiencies such as vitamin deficiency.
Ultrasonography in salpingopathy reveals enlarged, hyperechoic salivary glands with indistinct deep lobes, without focal lesions or increased vascular flow.
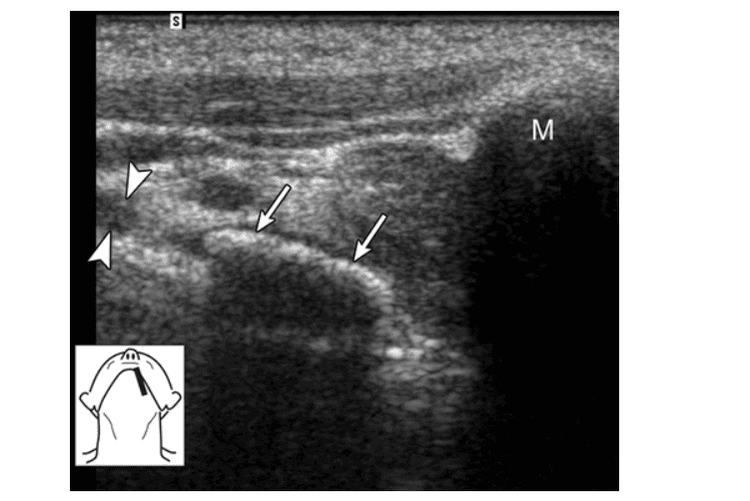
Ảnh siêu âm cho thấy một sỏi (các mũi tên) nằm gần lỗ ở gần mào lưỡi
1.8 Diagnostic ultrasound of Sjögren's syndrome Sjögren's syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disease occurring mainly in women over 40 years of age, characterized by aggressive plasma and lymphocytic infiltration, which destroys the salivary glands. and lacrimal gland, the clinical manifestation of which is dry mouth and eyes.
Ultrasound has a diagnostic effect in the advanced stage of the disease through examination of the parotid and submandibular glands. Ultrasound imaging shows heterogeneous structures of the salivary glands with scattered areas of hypoechoic or small oval-shaped drums, often with well-defined limits and increased flow of blood vessels. Areas of hypoechoic or anechoic voiding are thought to arise from infiltrating lymphoid cells, damaged glandular parenchyma, and dilated ducts.
Sjögren's syndrome is often associated with lymphoproliferative disease. Therefore, ultrasound also has the effect of early detection of changes in lymphocytes. Biopsy is recommended for lesions exceeding 2 cm or rapidly growing lesions.
On sonographic imaging, non-Hodgkin lymphoma presents as multiple scattered nodules with vascular proliferation in the salivary glands. Furthermore, bilateral (non-calculous) inflammation, granulomatous disease (such as sarcoidosis), hematogenous metastases, and benign lymphoid epithelial lesions in HIV-positive patients should be considered in these settings. The presence of many scattered hypoechoic areas in the parenchyma of the salivary glands.
In inflammatory diseases of the salivary glands, in addition to using ultrasound, other imaging methods are also used in combination to diagnose the disease, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and CT scan.
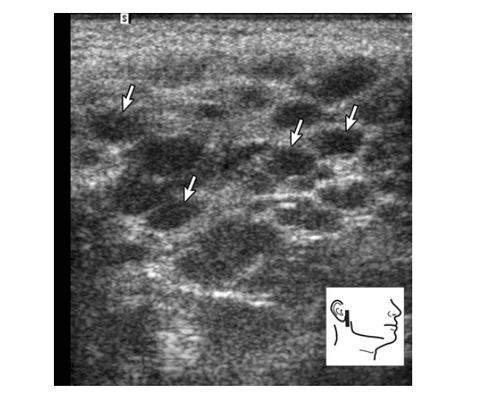
Hội chứng Sjögren giai đoạn tiến triển ở tuyến mang tai
2. Clinical diagnosis of salivary gland inflammation
Clinical symptoms are the first step, helping the doctor to suspect the disease and give diagnostic tests. Some typical symptoms of salivary gland inflammation include:
Unusual or foul odor in the mouth, pus in the mouth, dry mouth The salivary glands in the parotid or under the jaw are enlarged, sometimes causing disfigurement. Facial form The skin of the parotid gland is swollen, glossy, hot to the touch, not red, not concave (for viral salivary gland inflammation) and red, concave (for bacterial salivary gland inflammation) Small, thick saliva Inflamed, red or pus-filled Stenon duct oozing when stroked along the duct (for bacterial salivary gland inflammation) Swollen lymph nodes at the angle of the jaw Infection signs such as fever or chills Pain throat, jaw pain when opening the mouth, chewing, swallowing, pain spreading to the ears, headache, fatigue.

Người bệnh xuất hiện tình trạng đau họng
3. Treatment of salivary gland inflammation
Treatments for salivary gland inflammation vary depending on the severity of the infection, the underlying cause, and the extent of symptoms. In which, there are 2 methods used mainly: antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial infections, pus or fever, and a vacuum cleaner used to suck the abscess.
In addition, the patient also needs to apply home remedies for inflammation of the salivary glands such as:
Drink 8-10 glasses of water a day with lemon to stimulate the salivary glands and keep the salivary glands clean. Inflamed salivary glands Apply warm water to the inflamed glands Gargle with warm salt water Soak in sugar-free tomatoes or lemon candies to stimulate saliva production and reduce swelling Most infections, inflammation of the salivary glands are not resort to surgery. However, in cases of chronic or recurrent infections, you may need surgery.

Chanh giúp hỗ trợ điều trị viêm tuyến nước bọt
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
MORE:
Is salivary gland inflammation contagious? Ultrasound of parotid salivary gland inflammation Complications and treatment of salivary gland inflammation