This is an automatically translated article.
A lymph node biopsy is a procedure that helps check for signs or shows how advanced some disease is, such as cancer. The doctor will remove a small piece of lymph node and send it to a lab to look at under a microscope.
1. What is a lymph node biopsy?
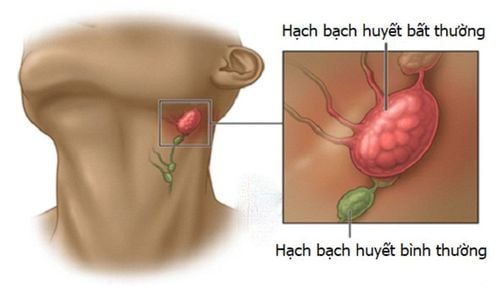
Lymph nodes are a part of the body, but most people are unaware of the existence of these small organs. There are hundreds of small lymph nodes distributed throughout the body (about 500-600), which play a major role in recognizing and filtering out harmful substances, including germs. Some lymph nodes are palpable in the neck, armpit, and groin.
A lymph node biopsy, also called a lymph node biopsy, helps diagnose cancer or see if malignant cells have spread to another area. This test also helps detect infections and explains why you are experiencing certain symptoms, such as swollen lymph nodes. Specifically, lymph node biopsy is often indicated in the following cases:
Inflammatory lymph nodes, at risk of infection; Infected lymph nodes, parasites; Malignant lymphadenopathy, acute leukemia ; Cancer metastasis. From the biopsy results, your doctor will decide what further tests to do, as well as the next treatment.
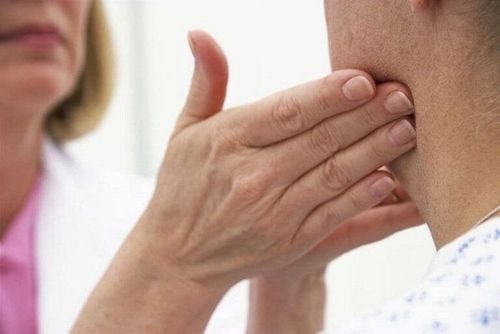
2. Types of lymph node biopsies
Before performing a biopsy, you need to do routine tests, do imaging tests and listen to the doctor's advice, answer questions, as well as sign a consent form for the procedure.
If you are taking anticoagulants or aspirin, your doctor may ask you to stop taking them for a while or change to a short-acting medication a few days before the biopsy.
You need to tell the medical staff if you have ever had an allergic reaction to anesthetic before. In addition, you can eat and drink normally before the procedure. A lymph node biopsy done by a doctor in a hospital procedure room includes several types of the following:
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về hạch bạch huyết
Hạch bạch huyết có vai trò quan trọng trong hệ miễn dịch của cơ thể. Bài trắc nghiệm dưới đây giúp bạn hiểu phần nào vai trò và chức năng của hạch bạch huyết.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2.1. sentinel lymph node biopsy
Your doctor may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to determine if your cancer, such as melanoma or breast cancer cells, has spread to new areas.
The sentinel lymph nodes are the first place cancer cells travel when they spread. If there aren't any cancer cells in the sentinel node, that means the tumor is probably still in its original location.
The first step to performing this type of biopsy is to find the sentinel lymph nodes. The doctor will inject radioactive material and/or a blue dye into the area near the tumor. The lymphatic system - a network of tubes and nodes that fight germs - sends dye or radioactive material to the sentinel nodes. Your doctor will use a device that looks for radiation or dye to find out the location of the sentinel lymph nodes.
Next, these sentinel nodes will be removed. You will not feel any pain during the procedure because you are under general anesthesia. Most people can go home the same day after the biopsy is completed.
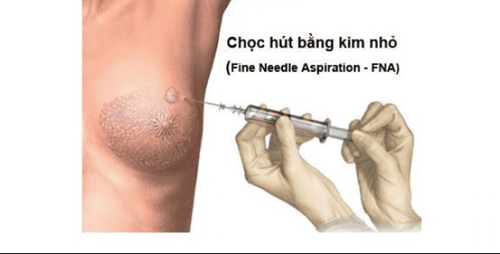
2.2. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
This type of biopsy is very similar to a blood sample, except that the doctor will use a thinner needle with a hollow tube in the middle.
The doctor will put a needle in one of the lymph nodes to collect fluid and cells, and then bring the sample for testing. You may be given a local anesthetic so you don't feel any pain at the site of the procedure.
People can usually go home the same day after the biopsy. But if your doctor doesn't take enough lymph samples to make a diagnosis, you may have other tests.
2.3. Tissue extraction with a large needle
This procedure is essentially the same as fine needle aspiration (FNA), but the doctor will use a needle with a larger hollow center. This large needle can remove a small mass of tissue, which provides more diagnostic information than liquids and cells from a fine needle. You also usually receive a local anesthetic during the procedure.
With both types of needle biopsies, the doctor may have to insert the needle several times into the skin to get enough sample to test. However, the whole procedure only takes about 15-30 minutes.
2.4. Open biopsy
This procedure closely resembles surgery. The doctor will make an incision in the skin to remove all or part of the lymph node.
You are usually given a local anesthetic, but sometimes your doctor also recommends general anesthesia. People need stitches after the procedure, but most will leave no scars.
In general, a lymph node biopsy is generally very safe, although there may be some bleeding and pain after the anesthetic wears off. You can take pain relievers such as paracetamol or anti-inflammatory drugs. Fine-needle aspiration takes the least amount of recovery time. You can leave the hospital and return to normal activities immediately. If your doctor has used anesthesia, you will need to rest before returning to your activities. Note, should keep the biopsy area dry and clean for 2 days afterward.
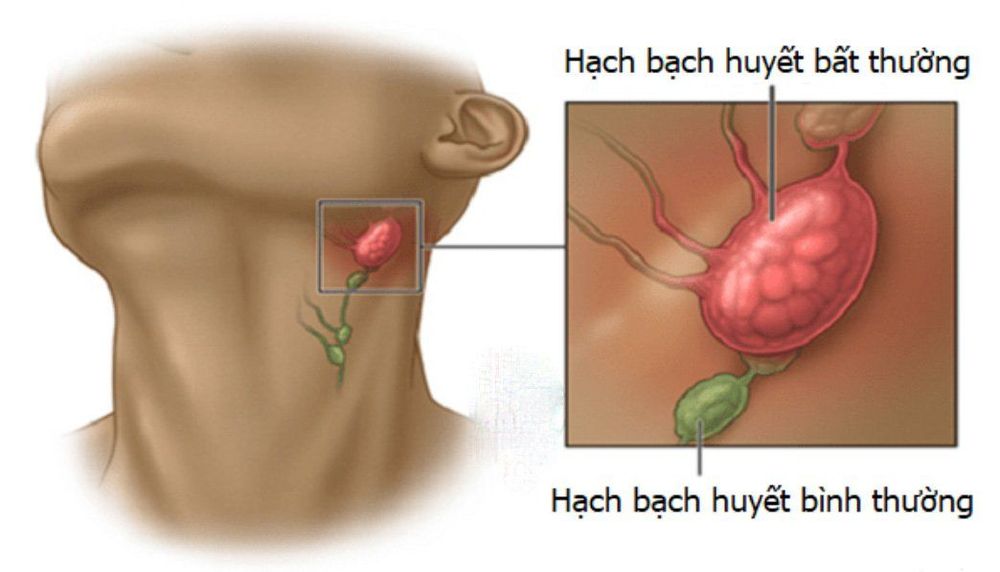
3. Lymph node biopsy results
After the biopsy is done, the doctor will send the lymph node sample to the pathology room. The tissue sample will be placed on a slide and examined under a microscope to see if it is normal, or if any cancerous cells are present.
The time it takes to get the results of the biopsy will vary by type. If you've had a sentinel lymph node biopsy, your doctor will also sometimes check for signs of cancer during the procedure. If malignant cells are found, more lymph nodes will be removed and you do not need to go back for another test.
With fine needle aspiration, you can get results on the same day. For large needles and open biopsies, you will need to wait a little longer depending on other tests you need to do. If no further tests are needed, you may receive your results 2 - 3 days after the procedure. In case more tests are needed, you may have to wait 7-10 days or even longer.
In general, you will receive your lymph node biopsy results at your next follow-up visit, or sooner if needed. In case the biopsy lymph node sample cannot conclude the medical condition, the doctor will explain and order a repeat biopsy or do other tests. If you have any other questions regarding a lymph node biopsy, you should visit the clinic to be directly answered and advised by your doctor.
Lymph node biopsies help doctors detect many serious diseases, which in turn will help patients have an early direction for examination and timely treatment. However, patients need to choose reputable examination sites, because this technique requires highly skilled operators and modern machinery to give the most accurate biopsy results.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a hospital famous for its quality of modern medical services, with a full range of machines for examination, diagnosis and treatment of diseases, including lymph node biopsy procedure.
Lymph node biopsy procedure at Vinmec is carried out in accordance with the correct and methodical procedure under the direction of a team of experienced and qualified medical doctors, which will bring the most accurate results, from which timely treatment, comprehensive health protection for customers.
Vinmec International General Hospital gathers a team of highly qualified, well-trained and experienced doctors and nurses at home and abroad. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com