This is an automatically translated article.
Tumor marker test is a method to support diagnosis, monitor treatment, predict the chance of cancer recovery and recurrence. The testing of tumor markers should strictly follow standard procedures to obtain quick and accurate results.
1. What is a tumor marker test?
Tumor marker (tumor marker) is a biomarker, produced, released into the bloodstream by cancer cells or healthy cells of the body in response to cancer cells or certain other benign (noncancerous) tumor conditions. These markers are found in blood, feces, urine, tumors, pleural fluid, abdominal fluid,... of cancer patients.
There are different types of tumor markers, each representing a specific disease. Some cancer markers are specific to only one type of cancer, but others tend to be elevated in many different types of cancer.
Tumor marker testing is a method of measuring certain cancer predictors, used to evaluate the presence of one or more types of cancer. However, there are many other causes of elevated cancer markers (leading to false-positive tests). Therefore, besides testing for tumor markers, it is necessary to rely on other methods, especially biopsy, to confirm the diagnosis of cancer.
Tế bào ung thư trong cơ thể
2. Indication for tumor marker test
Screening for some common cancers in people at high risk of the disease; Monitoring cancer patients after treatment; Diagnosis of specific tumors, especially brain tumors or similar tumors that cannot be biopsied; Confirm the diagnosis, check for characteristics such as size and invasiveness of the tumor, re-evaluate the effectiveness of therapy; Staging of some tumors; Prognosis treatment plan, help patients plan after surgical treatment; Predict the patient's response to treatment and chance of recovery; Predict the possibility of cancer recurrence after treatment, detect recurrence earlier than other tests.
3. Perform a tumor marker test
3.1 Procedure Wrap an elastic band around the arm to stop the flow of blood, making the veins under the band more visible, making it easier to insert the needle into the vein to draw blood; Disinfect the injection site; Insert the needle into the vein, fill the syringe with blood; Remove the bandage from the patient's arm when enough blood has been drawn; Place the gauze over the needle removal site, press against the injection site, and then cover; Bring the blood sample through the laboratory; Return results and answer patient questions.
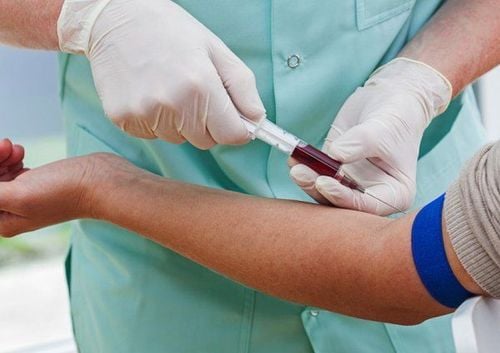
Thực hiện lấy mẫu máu xét nghiệm
3.2 Possible Complications and Management There are very few problems that can arise from having a venous blood sample taken for testing. Usually, the patient will have a small bruise at the site of the blood draw and the risk of bruising can be reduced by applying pressure at the site of the blood draw for a few minutes.
In rare cases, after a blood draw, the vein may swell (phlebitis). In this case, the patient should take a warm compress and apply it several times a day to the swollen area.
In addition, patients with coagulopathy taking anticoagulants may experience persistent bleeding after blood sampling. If you have problems with blood clotting or are taking anticoagulants, you should tell your doctor before taking a blood sample for testing.
4. Meaning of Tumor Marker Test Index
Cancer markers are currently commonly used to screen for cancer including:
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): Analysis from blood, used to diagnose liver cancer, monitor response to treatment; assessment of staging, prognosis and treatment response of germ cell tumors; Beta-2-microglobulin (B2M): Analysis from blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid, used to determine prognosis and monitor response to treatment of multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and lymphoma ,...; Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (Beta-hCG): Analysis from urine or blood, used to assess staging, prognosis and response to treatment of germ cell tumors, glioblastoma; CA-125: Evaluation and detection of ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, fallopian tube cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer and gastrointestinal cancers; Carcinoembryonic antigen: Evaluation and detection of gastrointestinal cancer, gastric cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, urinary tract cancer; CA19-9: Blood analysis, used to assess the response to treatment of gallbladder cancer, common bile duct cancer, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, and gastric cancer.

Một số xét nghiệm chất chỉ dấu khối u
The accuracy of each tumor marker test will vary. In particular, some tests give results for small changes in concentration or activity, requiring high accuracy. Meanwhile, some other tests give results that are large differences between normal and pathological values, so there is no need for high accuracy. Therefore, the accuracy of each test depends on the diagnostic purpose. Combining multiple tests may give more accurate results.
Note: Some limitations of tumor markers:
In addition to cancer, a number of other medical conditions can increase levels of tumor markers; Some tumor markers may be elevated in people without cancer; Tumor marker concentrations can change over time making definitive results difficult; Levels of a tumor marker may not change until the cancer is advanced, so tumor marker testing is not definitive for early detection, screening, or monitoring for recurrence. cancer; Some types of cancer do not make tumor markers in the blood. Tumor marker testing is used to detect, diagnose, monitor treatment, plan appropriate treatment, and detect some types of cancer that have recurred. Patients may be assigned to perform a tumor marker test in combination with other methods to confirm the diagnosis and have timely and effective treatment.

Khi xuất hiện các bất thường về sức khỏe, người bệnh nên đến cơ sở uy tín để được thăm khám
Vinmec's oncology department is one of the important specialties of the sub-specialty of surgery with the functions of cancer diagnosis, treatment and screening. Here, Vinmec will provide a full range of necessary medical care services for patients from cancer screening to treatment methods according to each stage of the disease. Advantages of oncology department at Vinmec with:
Team of experienced domestic and international doctors with high expertise Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals such as: Singapore, Japan, USA.... Comprehensive treatment and care for patients, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. There is a full range of specialized facilities for diagnosing the disease and staging it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, genetic - cytological testing. main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the Health System Vinmec nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
How does a biopsy of cancer cells take place? Normal and abnormal values of cancer marker CA 19-9 Is biopsy dangerous?