This is an automatically translated article.
Tuberculosis is a dangerous disease with high contagiousness. To determine if a person has the disease requires a variety of diagnostic methods, including a subcutaneous test for tuberculosis.
1. Importance of TB testing
Tuberculosis is a disease caused by bacteria. When TB germs enter a certain organ in the body, multiply and grow out of control of the body, it will cause tuberculosis. Of the various types of tuberculosis, pulmonary tuberculosis is the most common. The rate of patients dying from TB is second only to HIV/AIDS. The reason is because in the beginning, the disease has no obvious symptoms, mainly a cough, which is easily confused with common diseases. By the time the disease has clear symptoms, it has entered the final stage, making it difficult to treat. Therefore, the diagnosis and implementation of tests for early detection of tuberculosis greatly assist in the treatment of the disease.
2. What is the subcutaneous test for TB?
The TB subcutaneous injection test (also known as the Mantoux test) is a technique done to check if a patient has been previously exposed to the tuberculosis bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis). This is a test that measures the immune system's response to the bacteria that cause tuberculosis. This test is done by: Injecting a small amount of tuberculin of the TB bacteria (antigen) into the patient's arm. If you have ever been exposed to TB bacteria, your skin will react to the antigen with a red bump at the injection site within 2 days.
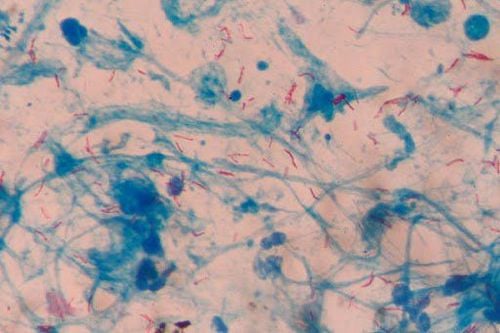
Hình ảnh vi khuẩn gây bệnh lao
Subcutaneous TB test for TB is one of the most effective tests for detecting TB infection. This test is usually done when symptoms or other diagnostic methods suggest that a person may have TB. However, this test cannot tell the duration of the TB infection, whether the TB infection is active or inactive, whether it can be passed on to others,...
3. When does subcutaneous injection confirm tuberculosis?
Subjects to be tested for Mantoux include:
Surrounding people with tuberculosis; Persons working in the healthcare sector; People with weakened immune systems due to the use of certain drugs, cancer, HIV/AIDS, etc.
Đối tượng làm việc trong lĩnh vực chăm sóc sức khỏe nên định kỳ kiểm tra sức khỏe
4. Perform a subcutaneous test for TB
4.1 Preparation Patients should notify their physician if they ever have a positive Mantoux test. In this case, the patient does not need to be tested again, except in unusual cases; Patients should inform their doctor if they are sick, any medications they are taking; The patient tells the doctor if he has ever been vaccinated against tuberculosis, when he was vaccinated. 4.2 Procedure The patient should sit in the correct posture, raise the arms; Clean and dry the area to be tested; Inject purified Tuberculin antigen or PPD subcutaneously. This substance can form a small bump on the skin. The area around the skin can be circled by the doctor with a pen to mark; The doctor did not bandage the needle, but left it open to monitor the injection area within 2-3 days.
4.3 Attention after the test Do not use gauze, bandages on the injected area; Do not scratch or scratch the injection area because this will make the test area red and give false results; If the injection site is very itchy, the patient can cover it with a cold towel; Can wash the injection area, dry gently after washing; The patient visits the doctor 2-3 days after the test to check the results.

Thực hiện xét nghiệm dưới da xác định bệnh lao
5. Meaning of subcutaneous injection index
Based on the size of the bump measured 2 - 3 days after the test to determine the result. After observing the tested skin area, the doctor will assess the patient's risk of contracting tuberculosis.
A red rash at the test site means you don't have a TB infection. If the red rash is hard, it may be that the patient has been exposed to TB bacteria before or has been vaccinated against TB before. The test results obtained will depend on the individual's risk of tuberculosis. Specifically, if you are in a high-risk group, a small bump on the skin is also a sign of TB infection. If you are in a low-risk group, a large bump is diagnosed as TB.
At-risk groups include:
High-risk group: People with HIV, people who have been in contact with someone with active TB recently, people with TB symptoms, X-ray detected TB, kidney failure terminal stage, liver transplant, long-term use of corticosteroids,... Moderate risk group: People who recently traveled to a country with a high rate of tuberculosis, drug users injecting drugs, nursing home residents, healthcare workers, children, the homeless, people in contact with people at high risk for TB, people who are too thin, have kidney failure, diabetes , cancer , had surgery to remove part of the stomach, leukemia,...; Low-risk group: Those who have not had any exposure to TB bacteria listed in the 2 groups above.
Người sử dụng ma túy bằng cách tiêm chích thuộc nhóm nguy cơ trung bình
Normal results (negative): no hard swellings are detected in the test area or there is a swelling less than 5mm in size.
Abnormal (positive) result:
5mm hard bump: Tuberculosis infection in people in high-risk group; 10mm hard bump: TB infection in the middle-risk group; Hard bump 15mm: Tuberculosis infection in low-risk group. Those who test positive are still followed up for about 1 week.
*Note:
Mantoux test results cannot conclude TB infection is active or inactive; When a subcutaneous test is positive for TB, other diagnostic tests such as X-rays, sputum smears, and sputum cultures should be performed to confirm whether the TB form is dormant or active. . A person who tests positive but has no symptoms is considered to have TB infection but has not passed it on to others (latent TB); For hospital staff or routine subcutaneous testers, a second test performed within a few weeks of the initial negative test may result in a positive result even though the person is not contagious. infected in the period between 2 tests. This result may indicate that the person has had a long-term previous TB infection or a previous BCG vaccination; Some people do not respond to a subcutaneous test for TB even when they are infected.
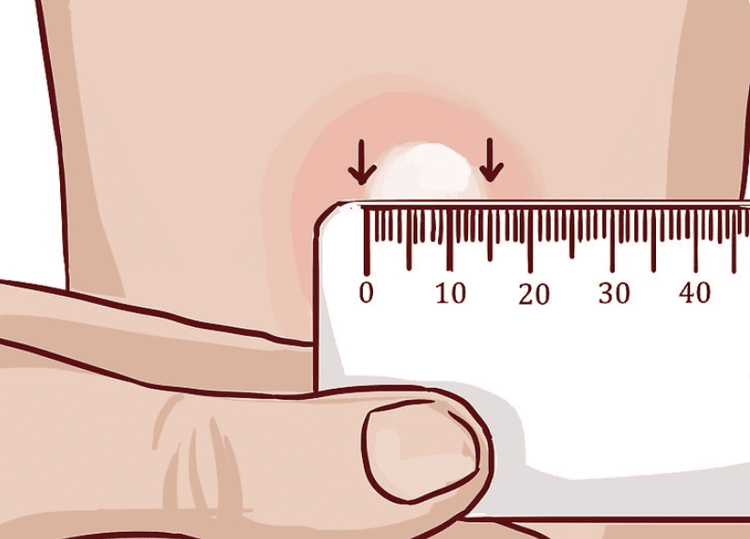
Cách kiểm tra kết quả xét nghiệm dưới da xác định bệnh lao
When a subcutaneous test is indicated for tuberculosis, the patient needs to follow the doctor's instructions to obtain the most accurate results and have an appropriate and effective treatment.
To register for a visit at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
SEE MORE
What is the difference between lymph node tuberculosis and pulmonary tuberculosis? Pregnant women are susceptible to tuberculosis, why? How do I know if I have tuberculosis?