This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Van Thai - Ear - Nose - Throat Doctor - Department of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.1. Chronic otitis media
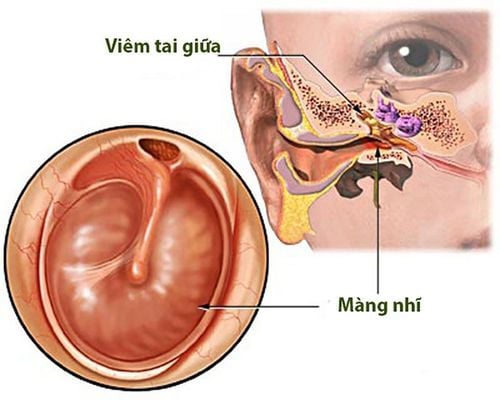
Chronic otitis media is the discharge of pus from the ear for more than 6 weeks, draining pus through the perforation of the eardrum. Patients often have the following symptoms: Purulent discharge, conductive hearing loss, no pain in the ear unless there is temporal bone inflammation, perforated eardrum... Middle ear infection can cause complications of encephalitis - meningoencephalitis. Ear polyps and other infections...Causes of chronic otitis media can be:
Arising from acute otitis media Eustachian tube obstruction Mechanical trauma Thermal, chemical burns Traumatic brain injury Causes after interventional catheterization Otitis media may be worse after an upper respiratory tract infection or water enters the middle ear through a hole in the eardrum while bathing or swimming. Infection usually occurs due to infection with Staphylococcus aureus or Gram-negative bacteria. The patient is painless but has pus and sometimes a rotten smell in the ear. Chronic otitis media can lead to structural changes in the middle ear such as osteonecrosis...
2. Diagnosis of chronic otitis media
2.1. Definite diagnosis 2.1.1 ClinicalChronic mucinous otitis media: Patient has intermittent purulent discharge. The pus that comes out is not rotten, slimy, sticky, and has not affected hearing much. Chronic purulent otitis media: Prolonged purulent ear discharge, solid green rot, may have cholesteatoma crystals. Hearing loss is increasing, and there may be a dull headache on the affected ear. Chronic otitis media with inflammation: The patient eats and sleeps poorly, is thin, has body weakness, has a high fever for a long time, and rots pus. For young children, there may be digestive disorders, high fever, convulsions... Because of damage to both the airways and bones, the ability to hear is worse. The patient has severe, intermittent ear pain, deep in the ear and radiating behind the mastoid region. Even spreading to the temples, leading to headaches, ringing in the ears and dizziness. 2.1.2 Subclinical
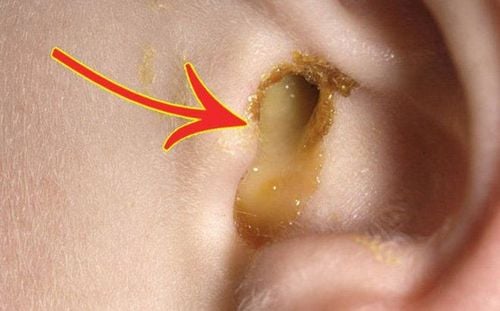
Ear examination: Persistent, thick and rotten purulent discharge from the ear. Cholesteatoma may appear yellow like fat, dropped into insoluble water. The tympanic membrane may be bulging, collapsing, or concave, or perforated, and the perforation margin is jagged, there may be polyps in the tympanic cavity, and the bottom of the tympanic cavity is dirty. Ear culture: Identify pathogenic bacteria and make an antibiotic map. CT scan of mastoid or head: Determine the extent of infection spreading outside the middle ear, Abscess brain - meninges, meningitis... Audiometric assessment of hearing.
Boils or inflammation of the outer ear canal: No symptoms of purulent ear discharge, ear pulling, painful pressure on the ear bottle, normal Schuller film often. Inflammation of connective tissue behind the ear or lymphadenitis: No hearing loss, no symptoms of purulent ear discharge, Jacques sign (-), Schuller film normal. Mastoid reaction: There is little hearing loss, ear pus does not have a rotten odor, and radiographs of the ear are normal. Pulmonary tuberculosis before otitis media: Differential diagnosis by chest X-ray,... Middle ear infection caused by spirochetes syphilis : Need to do specialized tests to diagnose...
3. Treatment regimen for chronic otitis media
3.1 Principles of treatment Principles of treatment of chronic otitis media:Control the infection Remove stagnant secretions in the middle ear such as mucus, pus... Surgery to restore hearing function Antibiotics should not be used This is not true because it may cause a loss of symptoms, making it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. Improper use of antibiotics can also turn acute into chronic, making the disease difficult to detect and complicate for a long time. Patients need to follow the treatment regimen of the otolaryngologist.

Removal of infectious secretions inside the ear: Instill physiological saline or hydrogen peroxide 6-10 units into the ear, aspirate, and then that dry the ear. Ear drops with antibiotic solutions such as: Polymyxin, Neomycin, Chloromycetin or Gentamycin. For anti-inflammatory effects can be combined with steroids. A 1.5% acetic acid solution may be used if Pseudomonas is present. Ear drops 2-4 times/day. Systemic antibiotics: Usually indicated for the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic otitis media. However, it is important to limit the risk of antibiotic resistance. Treatment of accompanying diseases in the nose, throat,... During the treatment period, the patient tries to avoid getting water into the ear when swimming, washing hair... 3.3 Surgical treatment Surgical treatment surgical removal For patients with tympanic polyps protruding into the ear canal, or granulomatous tissue, it is more effective to use the drug. However, when removed because these polyps can grow from the VII nerve, the lining of the stapes or the transverse semicircular canal. Because that can lead to complications of labyrinthitis after surgery or facial paralysis.
Reconstructive surgery: With or without tympanic membrane patching, tympanic membrane patching alone, and epiglottitis. The mastoidectomy is performed by 2 methods: Lowering the posterior wall of the ear canal and keeping the posterior wall of the ear canal intact.
Treating related diseases such as tooth decay, nasopharyngitis,... This is the cause of acute otitis media. When you have acute otitis media, you must be treated with the right regimen and continue to monitor If you have chronic otitis media, you need to continue to monitor and promptly detect complications for timely intervention. Communication on prevention of otitis media for people in the community. In summary, chronic otitis media is a persistent purulent discharge from the ear and can lead to dangerous complications if not treated such as: facial paralysis due to nerve damage VII, perforated tympanic membrane that does not heal, epidural abscess,... The treatment regimen for chronic otitis media is medical or surgical treatment, depending on each patient.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a team of experienced otolaryngologists, equipped with modern medical equipment such as endoscopes, specialized surgical microscopes is a prestigious address for examination and treatment. treatment of ENT pathology and head and neck surgery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.