This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Doctor of Urology Department, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Ureteral stones cause severe pain for patients, seriously affecting quality of life. There are many treatment methods for ureteral stones such as: extracorporeal lithotripsy, endoscopic retrograde ureteral lithotripsy, percutaneous stone removal, laparoscopic lithotripsy, open surgery to remove stones.
1. Characteristics of ureteral stones
Renal calculi (SNQ) form when a kidney stone moves down and stops at any location in the ureter, usually at sites of natural narrowing of the ureter such as the junction of the renal pelvis and ureter. The ureter crosses the pelvic blood vessel or the ureter drains into the bladder. Early SNQ affects kidney function if it is blocked for a long time. Most SNQs less than 5mm in size will be expelled spontaneously in the urine stream.
An important predictor of the likelihood of stones moving down the bladder is the size and location of the stone. The closer the SNQ is to the bladder, the easier it is to move out. Most of the SNQ will move down into the bladder within 4–6 weeks. Therefore, stones ≤ 5mm in size are usually treated medically, otherwise, active stone removal is required.
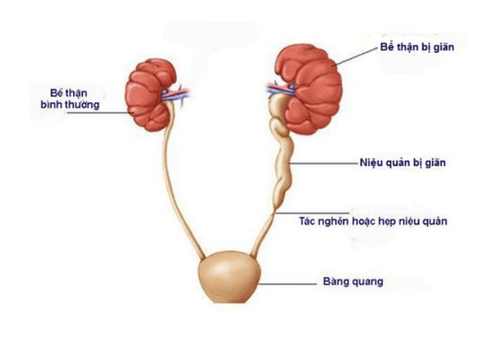
Sỏi niệu quản là nguyên nhân gây tức nghẽn đường tiết niệu
2. Symptoms
The typical symptom of SNQ is renal colic due to the stone moving in the ureter, blocking the flow of urine from the kidney to the ureter, the sudden increase in pressure in the renal pelvis will trigger the pain. The pain is severe, the hip area spreads to the lower abdomen, the intensity gradually increases and there is no pain relief posture. The pain is often accompanied by a feeling of nausea or vomiting. Other possible symptoms include: hematuria, urinary frequency, and painful urination.Fever or cloudy urine is a sign of a urinary tract infection. This condition requires urgent treatment because of the risk of serious infection and serious damage to kidney function.
Sometimes the patient does not see anything unusual, except for a feeling of back pain when doing heavy work.
3. Diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis is based on the patient's pain characteristics: typical hip pain or renal colic.
Ultrasound: is the initial means to suggest the diagnosis of ureteral stones with signs of hydronephrosis and dilated ureters. Ultrasound often shows SNQ in the upper and lower 1/3 of the ureter. X-ray of the urinary system (KUB): can detect SNQ in about 60-80% of cases, except for non-contrast stones such as uric acid and cysteine stones. Computed tomography (MSCT): is the best means of diagnosing SNQ, helping to determine the location, size, contrast, and degree of obstruction with an accuracy of up to 96%.
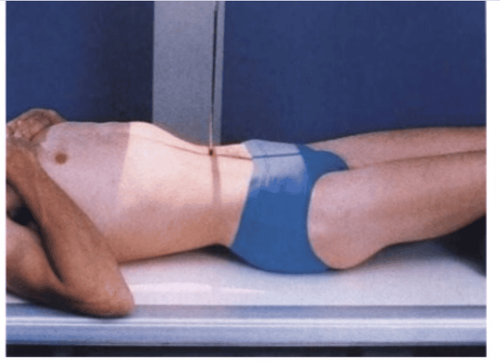
X-quang hệ tiết niệu cho phép chẩn đoán bệnh sỏi thận tiết niệu
4. Methods of treating ureteral stones
Factors related to the decision of medical treatment or active stone removal intervention include:
Stone size: stones < 5mm can all move out naturally; Clinical pain level; Degree of obstruction and kidney function; Infection status.
4.1. Emergency treatment
SNQ causes acute pyelonephritis, patients with low back pain accompanied by fever and chills need to resolve the obstruction urgently with percutaneous nephrostomy or ureteral catheterization and in combination with appropriate antibiotic therapy. When the infection is resolved, then intervention to remove the stone.
In addition, emergency indication is also performed in the case of ureteral stones causing obstruction with acute kidney damage (decreased renal function).
Treatment of renal colic: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the drugs of first choice. May be combined with other pain relievers such as paracetamol or morphine for better pain control.
Thuốc NSAID giúp điều trị các cơn đau quặn thận
4.2 Medical treatment
Indications for medical treatment when the stones are small, ≤ 10mm in diameter, smooth stones, clear margins, normal kidney function, able to closely monitor the patient. The follow-up time for medical treatment ranges from 4-6 weeks.
The principle of treatment is to facilitate the movement of stones out by controlling pain with analgesics, antispasmodics. In addition, the patient needs to drink a lot of water on average about 3L per day. Infusion when the patient has a lot of vomiting or severe infection.
Treatment of stone expulsion with alpha-blockers or nifedipine in the case of stones in the lower third of the ureter.
4.3 Surgical treatment
Indications for surgical intervention when:
Ureteral stones > 1cm; SNQ with urinary tract infection; Unresponsive to pain relief; Medical treatment failed; Affects renal function (renal failure, nephrolithiasis/unique kidney, bilateral ureteral stone).
4.3.1 Extracorporeal lithotripsy
The doctor will control the lithotripsy machine, which emits vibrations from outside the patient's body, locates it by X-ray or ultrasound towards the location of the stone in the kidney. These shock waves break the stone into small pieces and travel with the urine out of the body. Extracorporeal lithotripsy is effective with not too hard (<1000 HU) and the stone is located in the upper segment of the ureter.
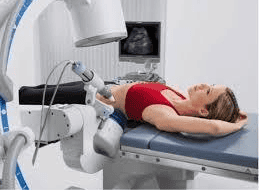
Hình ảnh tán sỏi ngoài cơ thể
The advantage of this method is that there is no pain, no kidney damage, no need to stay in the hospital, the stone clearance rate is up to >80%.
4.3.2 Retrograde ureteroscopy with lithotripsy
The ureteroscope with a laser head is inserted into the ureter through the urinary tract. The ureteral stone is seen on the screen and laser energy is used to break the stone into small pieces and remove it.
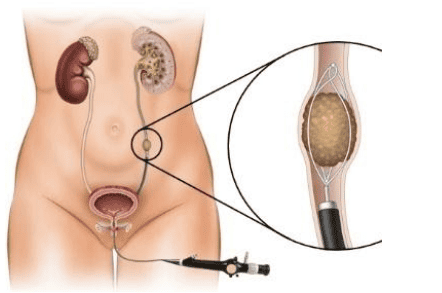
Nội soi niệu quản ngược dòng tán sỏi là một phương pháp điều trị sỏi tiết niệu
The advantages of this method are no pain, little damage, discharge within 24 hours, no incision, high stone removal efficiency > 90%. Surgery is safe, but there are also some complications such as urinary tract infection, hematuria, ureteral stricture.
4.3.3 Laparoscopic stone removal surgery
The surgeon inserts the endoscopic instrument into the body through 3 small holes on the patient's hip and back to remove the stone. Laparoscopic stone removal surgery is often used when there are large stones in the ureter.
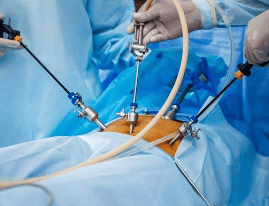
Phẫu thuật nội soi lấy sỏi làm tăng tỷ lệ sạch sỏi
The advantage is high stone clearance rate > 95%, less damage.
Patients have to stay in the hospital for 1-2 days, there may be some complications such as wound infection, incision bleeding, bloody urine, urine leakage.
4.3.4 Percutaneous stone removal
The doctor inserts a needle from the skin into the kidney under ultrasound or X-ray guidance. According to this puncture, the doctor uses a set of tools to widen the tunnel into the kidney and use a small nephroscope to observe, dissolve the stone and remove it from the body. This method is often used for patients with large stones in the upper third of the ureter.
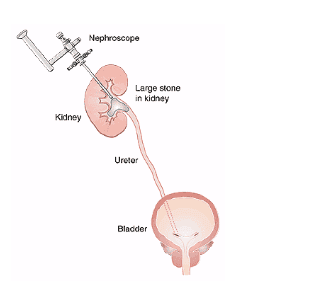
Phương pháp lấy sỏi qua da có thể gây tổn thương các cơ quan lân cận
Advantages: less incision pain and high stone clearance rate.
Patients may experience complications such as: infection, bleeding, fluid accumulation around the kidney, damage to nearby organs...
4.3.5 Open surgery to remove stones
This method is currently rarely used due to the long incision, the pain of the incision, the long recovery time, applied to complicated ureteral stones or failure of other treatments.
5. Preventing recurrence of stones
| Lượng nước nhập |
Lượng nước nhập: 2,5 – 3,0 lít / ngày Uống mỗi 2 – 4 giờ Đi tiểu: 2,0 – 2,5 lít/ngày Thức uống có pH trung tính |
| Chế độ ăn |
Ăn kiêng (tránh tiêu thụ lượng lớn vitamin). Ăn nhiều rau và chất xơ. Lượng calcium: 1000 – 1200 mg/ngày Hạn chế muối: 4 – 5g/ngày Hạn chế protein động vật 0,8 – 1,0g/kg/ngày. |
| Lối sống |
BMI: 18 – 25 kg/m2 Hoạt động thể lực, cân bằng lượng nước mất |
To detect ureteral stones early, you should check your general health regularly. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general Vip Standard general health checkup package Patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.