This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, there is no cure for generalized scleroderma, so it is mainly symptomatic treatment, in order to control the progression of the disease and limit complications.1. How long does scleroderma live?
To date, there have been no studies to accurately estimate how long scleroderma lives. Although there is no cure for this disease, patients can still live with the disease if they adhere to the treatment regimen. If treated properly, the disease will not significantly affect the quality of life, does not pose a threat to life, and the patient can still prolong life.Generalized scleroderma is a lifelong disease. Therefore, patients need to stay optimistic and fight until the end of the disease. The disease usually has a chronic course, accompanied by exacerbations of the disease. Patients with scleroderma with only skin lesions generally have a better prognosis than generalized scleroderma patients with visceral lesions.
In general, how long scleroderma survives depends heavily on the early diagnosis and treatment of the disease and the progression of organ damage such as pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, and heart failure. kidney . If patiently and well adhere to the generalized scleroderma treatment regimen, the patient's life expectancy can be extended over 10 years (accounting for about 50 - 60%).
2. Non-drug treatment of systemic scleroderma

Sử dụng kem làm mềm da, xoa bóp da thường xuyên
Health education for patients, making patients fully aware of generalized scleroderma and drugs to treat it. ensure compliance with the drug regimen; Management of Raynaud's: Have the patient dress warm, use gloves, and wear socks. In addition, the patient must not smoke and must not use vasoconstrictor drugs (amphetamine, ergotamine...); Use emollient creams, massage the skin regularly. Do not abuse cosmetics used on the skin. Do not use soaps that dry the skin; Control gastroesophageal reflux disease: Should divide into many small meals, do not eat too full, lie with your head elevated, do not lie down immediately after eating. In addition, avoid the abuse of coffee, tobacco and other stimulants; Instructing exercises suitable for health status, breathing exercises and full body massage regularly.
3. Symptomatic treatment of systemic scleroderma
For skin symptoms (such as skin calcification, skin sclerosis): use drugs such as d-penicillamine, colchicine, interferon gamma, histamine H1 inhibitors, skin moisturizing creams.To limit the symptoms of bone and joint problems: Use physical therapy and movement therapy (therapeutic methods of extremity, mud soak or mineral soak in the scleroderma), a combination of pain relievers, drugs non-steroidal anti-inflammatory. Note the side effects of the drug on the digestive system.
To treat vascular syndrome (Raynaud's), patients need to keep their extremities warm, physiotherapy, peripheral vasodilators, and calcium channel blockers.
Prevent organ damage (gastroesophageal syndrome, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis...) with corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, proton pump inhibitors.
If medical treatment is not effective, the doctor will consider surgical treatment to remove the necrotic limb.
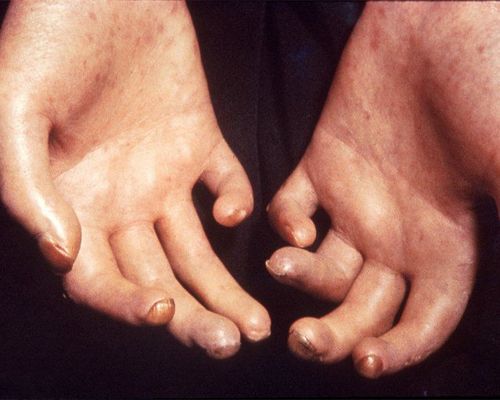
Nếu điều trị nội khoa không hiệu quả, bác sĩ sẽ cân nhắc điều trị ngoại khoa cắt bỏ phần chi hoại tử
4. Monitoring during treatment of generalized scleroderma
Patients treated with generalized scleroderma are monitored and managed as outpatients, periodically re-examined every 1-3 months depending on the specific disease status and progress of each patient. Patients should be examined and evaluated for clinical symptoms such as: skin sclerosis, Raynaud's syndrome, degree of extremity necrosis, esophageal motility disorder, dyspnoea symptoms, and infection.Patients need to be diagnosed early, promptly treat symptoms, long-term monitoring and combined with reasonable rest, while waiting for scientists to find a solution to treat scleroderma. could be more efficient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.