This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Do Nguyen Thuy Doan Trang - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Purulent pericarditis is a common disease in our country, encountered about 30-50% in pericarditis in children. Children with empyema can lead to cardiac tamponade and death if not diagnosed and treated early.
1. What is purulent pericarditis?
Purulent pericarditis is inflammation caused by pyogenic bacteria in the pericardial cavity. Purulent pericarditis is common at a young age, the average age of illness is 6-7 years old. The disease ranks first in pericardial diseases and second in congenital heart diseases.2. Causes of purulent pericarditis in children
Primary cause of pyelonephritis in children is rare, usually due to infection in other organs such as acute respiratory infection superinfection, empyema, osteomyelitis, purulent meningitis, external boils skin and soft tissue. The most common pathogenic bacteria are Staphylococcus aureus, Hemophilus Influenza, streptococcus, pneumococcus, meningococcal... Bacteria are usually carried in the bloodstream from primary infection sites such as pneumonia, empyema, pleural effusion. , osteomyelitis ... sometimes followed by endocarditis .Purulent pericarditis in children often develops on the basis of an organism with reduced resistance. Common after children have viral diseases such as measles, chickenpox. Other causes such as empyema of the pericardium such as direct infection from the outside through the wound, liver abscess burst through the diaphragm into the pericardium, commonly left lobe liver abscess.
3. Diagnosis of empyema in children
3.1 Clinical symptoms
Fever: An elevated, fluctuating temperature is the first clinical symptom, indicative of an infection. The duration of the fever lasts for weeks. Shortness of breath: After about 1-2 weeks of high fever, the child begins to feel short of breath. Edema: Manifestation of heart failure, usually occurs after dyspnea and begins with edema of the lower extremities, or occult edema of eyelids Precardiac pain (for older children) occurs in 15-80% of cases, characteristics Chest pain often comes on suddenly, when coughing, taking a deep breath, or changing position. Chest pain often radiates to the back because the lower third of the pericardium contains the phrenic nerve. Cardiac examination: distant heart sound, pericardial rub Other symptoms: dyspnea, edema, hepatomegaly, tachycardia, jugular venous distension, and when there are signs of cardiac compression, the child shows signs of paradoxical pulse when measured. blood pressure, systolic blood pressure decreased by ≥ 10 mmHg during inspiration compared with expiration.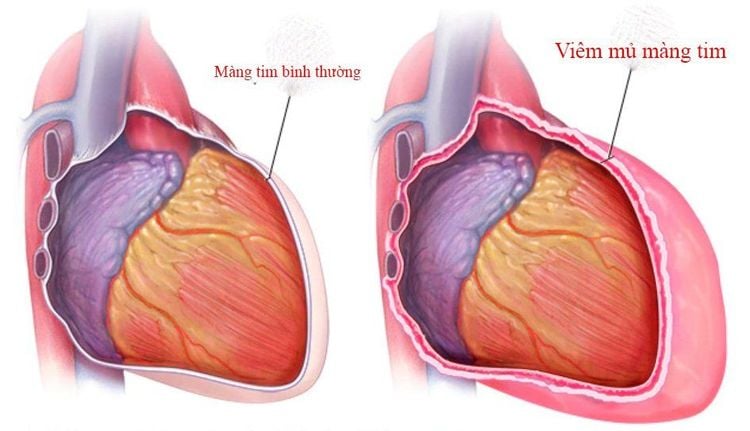
3.2 Subclinical
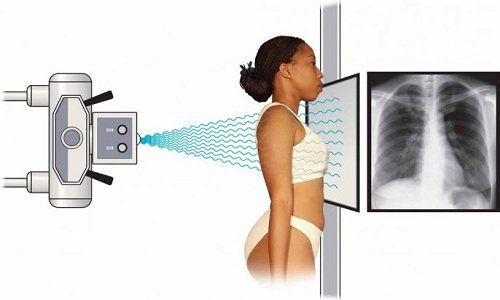
Cardiopulmonary x-ray: Large, raft heart shape, the cardiac arcs are not clear, the heart peduncle is short, making the heart round like a gourd, the diaphragmatic center angle is blurred, the border is obtuse, the diaphragm is less mobile and pushed down. The pleural effusion can be seen on both sides. Two lung fields, the hilar area is dark due to stagnation. Electrocardiogram: Repolarization disorder with ST segment and T wave changes in peripheral and precordial transitions. Echocardiography: Determine the volume of fluid in the pericardium, there is an increase in the sound of the fluid and fibrinization, signs of cardiac tamponade. Blood tests: white blood cell count increased, erythrocyte sedimentation rate increased, white blood cell count turned left. Blood culture Pericardial aspiration, pus culture in the pericardial cavity can find evidence of pathogenic bacteria CT scan: A test that should be done along with echocardiography, to help confirm the thickness of the pericardial effusion, evaluate pericardial thickening and also help identify other abnormalities.4. Treatment of pericarditis in children
4.1 Principles of treatment
Antibiotic according to the antibiogram, when there is no antibiogram, the appropriate antibiotic should be selected based on the clinical characteristics. Antibiotic treatment when cultured blood or pericardial cavity fluid according to pathogenic bacteria. The duration of antibiotic treatment is usually 2 to 4 weeks. Treat purulent, bacterial pericardial infection by techniques such as pericardial aspiration, drainage or surgery. Cardiac support: when there are signs of heart failure Diuretic: when there are signs of heart failure or cardiac tamponade.4.2 Techniques to clean pericardial pus
These techniques will be considered depending on the patient's situation, the patient's condition as well as the availability of necessary facilities and the skill of the surgeon. Accordingly, common surgical procedures to remove pus in the pericardial cavity include local aspiration or drainage of the pericardium, opening a "window" on the pericardium, or surgical removal of the pericardium.Regardless of the method chosen, the goal to be achieved is to completely resolve the pus-filled cavity, avoid the infection from spreading to the whole body as well as prevent complications of constrictive pericarditis later for the child.
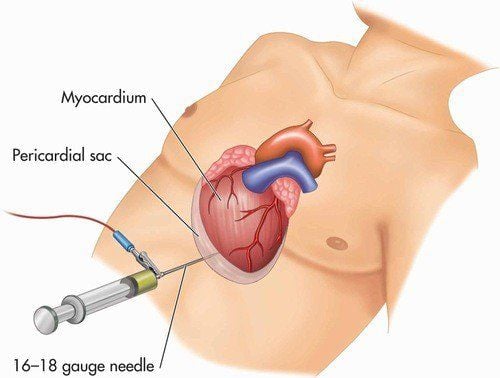
Pericardial puncture is indicated for cases of acute purulent pericarditis, severe dyspnea, severe heart failure, not allowing other procedures, threatening cardiac arrest due to cardiac tamponade. The results of this method are often not very good, leaving sequelae because of not being able to thoroughly aspirate, after a period of time, heart failure still does not decrease, the infection still does not decrease, it may still be serious and dangerous. endanger the patient's life. If there is help, it will also progress to constrictive pericarditis. Pericardial empyema is indicated for cases where aspiration is unsuccessful or the results are not good. The patient's general condition improved and allowed the procedure to be performed. This technique gives better results, but the treatment time is still prolonged (5-7 days drainage). Pericardectomy (Laparoscopic or open surgery): Indications for surgery must choose a good time, wait for the patient to get out of the dangerous stage, then a few days of recovery will improve with indications for resection. remove the pericardium. Open pericardial resection as soon as possible. When empyema has progressed to constrictive pericarditis, the outcome is not better and the technique is more difficult. To help patients determine the cause, complications and grade of pericarditis, Vinmec International Hospital currently has a Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination, for the following subjects: Cold limbs; heart palpitations; Rapidly breath; Anxiety, insomnia; Shoulder, wrist pain; Unexplained fatigue; Sweating, indigestion; Swollen feet; Frequent migraines; There is a feeling of tightness when walking; Family with heart disease...
Advantages of cardiovascular examination at Vinmec International General Hospital include:
Medical team - doctors are leading experts, highly qualified, dedicated devoted and wholeheartedly for the benefit of the patient, bringing high efficiency in medical examination and treatment; Comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services; System of modern equipment, supporting effective diagnosis and treatment; Modern, civilized, luxurious and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.