This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with MSc.BS Nguyen Huy Nhat - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.1. Pleural lavage
Pleural lavage is a technique to introduce 0.9% sodium chloride solution into the pleural cavity in the treatment of pleural effusions with the aim of removing pus, blood and residues remaining in the pleural cavity.Pleural lavage will be performed for diseases with pus, blood in the pleural cavity such as: hemothorax, empyema,...
2. Indications and contraindications
2.1 Indications for pleural lavage Pleural lavage is indicated in the following cases:Empyema has been aspirated repeatedly without clinical improvement. Pleural effusion in septal exudate or localization Obtain specimen Test to diagnose the cause Used to treat local antibiotics in some cases 2.2 Contraindications Contraindicated pleural lavage in cases such as:
Bronchial fistula Cardiovascular emergency Effusion has occurred have a solid wall Hemodynamic disorders Coagulation disorders Hemostasis
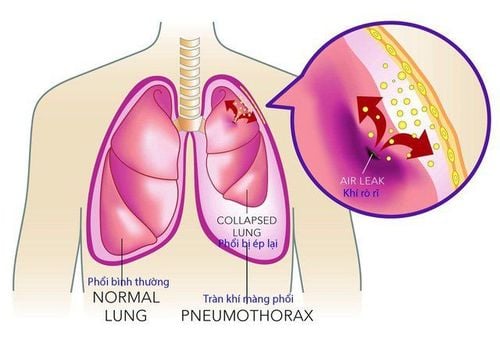
3. Perform pleural lavage
3.1 Preparation The person performing the pleural lavage is a respiratory specialist. In addition, it is necessary to prepare some tools including:Troca and a barrel with a diameter of 1mm. The diameter catheter fits the troca barrel. 3-prong lock or transmission set with fork. Pumps of all kinds. Transmission lines translate in and out. Ambu ball and oxygen Wash solution: NaCl 0.9% X 1000ml. Antibiotic solution: Noxylex, Rifocin, Strepto-kinase, Chymotrypsin. Xylocaine 2%, 5 ampoules. Depersolon 30mg, 5 ampoules. Adrenaline 10 mg, 5 ampoules. Atropine 1/4mg, 5 ampoules. For the patient, he will be prescribed a sedative from the day before, and the medical staff will explain the purpose of the procedure so that the patient cooperates.
3.2 Procedures Place the patient in a sitting or lying position such as thoracentesis, arms raised above the head Examine the patient again before the procedure View X-ray film to select the aspiration path, Avoid the wrong side Disinfect the puncture area with 1.5% iodide alcohol, then with 70 degrees alcohol Anesthetize the puncture area usually in the intercostal space 5 mid-axillary or intercostal 2 mid-clavicular lines After inserting a catheter with a catheter pleural, retract the barrel, and push the catheter in. Insert the 3-prong buckle onto the cannula-head. Install the cord attached to the wash solution bottle to one branch of the 3-prong buckle. The other fork is connected to the pleural fluid drainer. First, drain to remove 200-300ml of pleural solution, then slowly add the washing fluid into the pleural space for 10-15 minutes. Wait for the patient to breathe for 4-8 breaths, then remove the washing solution. Wash until the water is clear, then stop. Put the solution with antibiotic mixed in. Immerse in the pleural space and withdraw the troca. Compression or clamping with agraf or with a suture.
Shock due to xylocaine Slow pulse: inject atropine 1⁄4 mg Shock due to pain: need to stop the procedure, give the patient oxygen and anti-shock Acute pulmonary edema Pleural effusion Hemothorax In summary, pleural lavage is a procedure that cleans the pleura, removing blood, pus, and debris from the pleural space. After pleural lavage, some complications may occur, so the patient should be monitored for vital signs regularly. If you see symptoms such as difficulty breathing, vomiting, ... or any unusual signs, you should immediately notify a medical staff for timely treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.