This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
1. What is Crohn's disease?
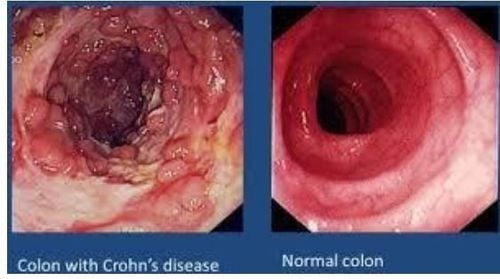
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes ulcers to form in the digestive tract anywhere from the mouth to the anus.
Crohn's disease causes intermittent ulcers anywhere from the mouth to the anus
Symptoms include abdominal pain, intermittent cramping, diarrhea, and bloody urine. Other symptoms include weight loss, pain in the stomach, joint pain, and fatigue. Some patients with Crohn's disease have severe symptoms, while in others, symptoms are less severe. Some people with the disease go a long time without symptoms, even without treatment, while others have a serious illness that requires long-term treatment or even surgery.
1. Diagnosis of Crohn's disease
Diagnosis of Crohn's is mainly based on clinical features when taking history and physical examination with the support of blood test results, imaging, endoscopic features and histopathology:
Clinical symptoms (symptoms must persist for at least 4-6 weeks): Diarrhea, colored and/or mucoid stools, nocturnal diarrhea, bleeding from the rectum, abdominal pain, weight loss, growth retardation , delayed puberty in children, extra-gastrointestinal symptoms, and family history of IBD. On examination, abdominal mass may be seen, signs of perianal disease (fissure, perianal abscess), signs of other organs (joint pain, swelling, erythema nodosum, red eyes).
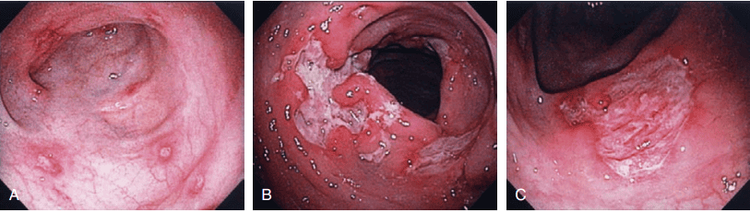
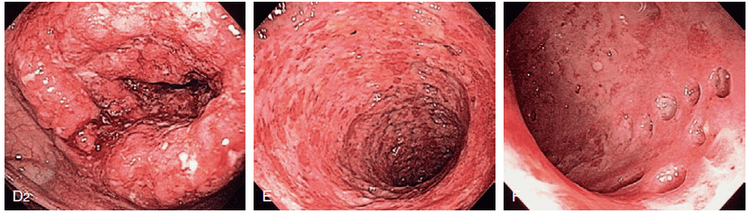
Laboratory tests: Iron or vitamin B12 deficiency anemia may be seen, anemia, decreased albumin, increased fecal calprotectin, some positive antibodies (ASCA, anti-glycoprotein-2). Microbiological tests should be done to rule out gastrointestinal infection On imaging modalities (ultra-abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging): Intestinal wall thickening, edema, especially small bowel loops. Deep ulcers or strictures, fistulas, fatty infiltrates around bowel loops can be seen or images of abscesses and mesenteric nodes can be seen. Endoscopy: Intermittent, segmental inflammatory lesions in the gastrointestinal tract with small aphrodisiac ulcers or deep, long ulcers, mucosal "pebble" appearance, fistula lesions or strictures may be seen. Histopathology (at least 2 biopsies of each segment and at least 5 different segments of colon, including terminal ileum): Focal inflammatory lesion with transmural inflammatory lesion, slittal structure change , granuloma formation unrelated to glandular lesions, increased lymphocytes in the epithelial layer.
3.Principles of treatment of Crohn's disease
For Crohn's, the choice of treatment modality depends on the location, severity, complications of the lesion as well as the patient's prognosis. The individualization of treatment is based on the degree of response demonstrated by symptom relief as well as the patient's tolerability.
During the acute-onset phase, treatment to control symptoms to achieve clinical remission” is necessary before entering the maintenance phase to stabilize the disease. When treatment to achieve remission, time can be from 2-4 weeks in most patients, however, in some cases, this period must last from 12-16 weeks. Patients who achieve a remission response will continue on maintenance therapy. Patients who are still symptomatic will have to choose another treatment modality.
>> See more: Treatment of high-risk Crohn's patients - Article by Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
4.Evaluate the patient before treatment
Evaluation of patients in the acute phase will depend on clinical symptoms, mucosal lesions on imaging or endoscopic means, biomarkers such as CRP, fecal calprotectin.
To facilitate the selection of treatment modality, Crohn's patients are usually divided into three groups: low-risk group with mild to moderate disease severity, high-risk group with severe disease severity. from moderate to strong and the third group is the very heavy, extreme group. Patients in the high-risk group include complications such as fistula, stricture, at risk of intestinal obstruction, even intra-abdominal infection. Risk factors for severe progression include young age of onset, ileal involvement, multiple segment lesions, severe perianal or rectal disease, and fistula or stricture.
Low-risk group with mild to moderate disease activity: CDAI score of 150-220, usually responds to oral medications, and has no symptoms of dehydration, intoxication, pain, or Abdominal mass, intestinal obstruction, or weight loss >10% of body weight. The lesions on endoscopic examination of these patients are also not severe. High-risk group with moderate to severe disease activity: CDAI score from 220-450, not responding to treatment like low-risk group, often high fever, thin weight loss, abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea a lot (no evidence of bowel obstruction), severe anemia. The lesions on endoscopy range from moderate to severe. Very severe, fulminant group: CDAI score > 450, patients with persistent symptoms even after using corticosteroids or probiotics, presenting with high fever, persistent vomiting, evidence of intestinal obstruction or formation in an abscess or surgical sign. Endoscopic images show severe mucosal damage.
The assessment of the severity of lesions on endoscopy is based on the scale of SES-CD, CDEIS presented in the section on endoscopic characteristics of Crohn's. During treatment, monitoring response and side effects is very important, especially when deciding to use biological products. When patients do not respond to this class of drugs, blood levels should be measured and antibodies to these biologics should be determined. Among the therapeutic drug groups, it is important to understand that some drugs with local action such as sulfasalazine, mesalamine, budesonide are broken down in the intestine while corticosteroids, mercaptopurine, azathioprine, methotrexate, biological products, cyclosporine A, tacrolimus have affects the entire gastrointestinal tract.
5.Assessment of response to treatment
To evaluate response to treatment, can be based on remission on histopathology, endoscopic images or clinical symptoms. In terms of clinical symptoms, a CDAI score < 150 or patients without signs of an acute inflammatory episode were considered to be in remission. Patients who consistently require corticosteroids to achieve clinical stability are considered “steroid dependent.” With the goal of rapidly controlling inflammation and preventing complications in Crohn's patients, the following classes of drugs are used. Uses include: 5-aminosalicylates (5-ASA), antibiotics, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologics (anti-TNF drugs such as infliximab, adalimunab, certolizumab pegol, drugs that affect metabolism) leukocyte chemotaxis such as velodizumab, natalizumab, anti-p40 (anti IL12/23), ustekinumab).
6. Treatment for low-risk groups
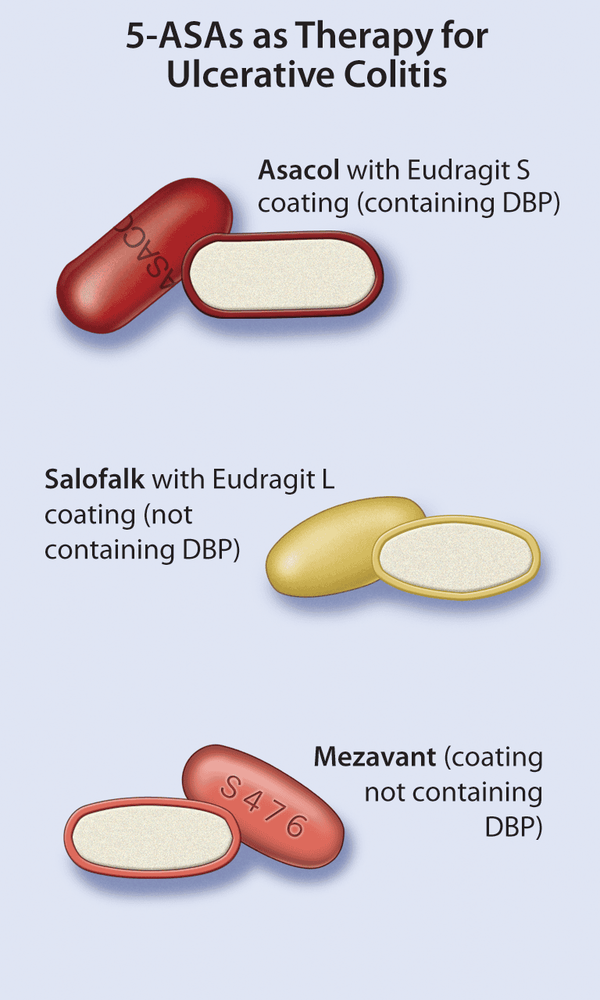
a.Mesalamine
5-ASA plays a role in local anti-inflammatory, widely used in ARIs. For Crohn's, oral mesalamine has not been shown to be more effective than placebo in relieving symptoms and healing intestinal mucosal damage, especially in active disease. Sulfasalazine has a combination formula of sulfapyridine with 5-ASA in which the role of sulfapyridine is to transport 5-ASA to the colon. Sulfasalazine at a dose of 3 - 6 g/day is effective in symptomatic treatment in Crohn's patients with mild to moderate active colon and/or ileal involvement. However, the drug did not prove to be effective in cases with only small bowel lesions and did not help heal mucosal lesions compared with placebo.
For lesions of the sigmoid colon and rectum in UC, 5-ASA enemas or suppositories provide symptomatic relief and maintain stability, however, a local role in Crohn's disease has not been proven.
b. Corticosteroids
Traditional corticosteroids are effective in rapidly reducing symptoms during an exacerbation in patients with moderate to severe disease and often requiring systemic administration. Oral form for 8 weeks. In cases of acute exacerbations, the 8-week course may be repeated.

However, metronidazole did not demonstrate a remission effect when compared with placebo. Ciprofloxacin demonstrated similar efficacy to mesalamine in advanced Crohn's but was also no more effective than placebo. Neither of these antibiotics had any effect on the healing of intestinal mucosal lesions. Due to the lack of evidence regarding benefit, antibiotic use is not recommended as an effective option for achieving remission and wound healing in Crohn's. Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be indicated only in the presence of infection-related complications such as intra-abdominal abscess formation or in the short term to prevent postoperative recurrence when combined with azathioprine.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic techniques for digestive diseases, diseases that cause chronic diarrhea, Crohn's disease... Along with that, at Vinmec Hospital, screening for gastric cancer and gastric polyps is done through gastroscopy with Olympus CV 190 endoscope, with NBI (Narrow Banding Imaging) function for The imaging results of mucosal pathology analysis are clearer than conventional endoscopy, detecting ulcerative colitis lesions, early gastrointestinal cancer lesions... Vinmec Hospital with facilities Quality and modern equipment and a team of experienced experts, always dedicated to medical examination and treatment, customers can rest assured with gastroscopy and esophagogastroduodenoscopy at Vinmec International General Hospital. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.