This is an automatically translated article.
Tracheobronchial trauma is a serious, potentially life-threatening condition. The principle of treatment of laryngeal trauma is to ensure breathing, and at the same time restore the maximum anatomical structure and respiratory physiology, pronunciation of the laryngeal system.
1. What is laryngeal trauma?
Tracheobronchial trauma is damage to the structure and components of the larynx due to mechanical impact from inside or outside the larynx. Although rare, trauma to the larynx is a very serious condition that can obstruct the airways causing respiratory failure, which is life-threatening. The majority of patients with severe laryngeal trauma die before receiving medical care.
The most common causes of laryngeal trauma are:
The patient is traumatized by being stabbed by something directly in the neck and chest area. The patient suffered a closed neck injury due to being beaten or strangled too hard. Patients with thoracic trauma due to strong compression of the sternum against the spine or from a rebound. Wounds caused by weapons of war, by inhalation of gaseous or liquid poisons.
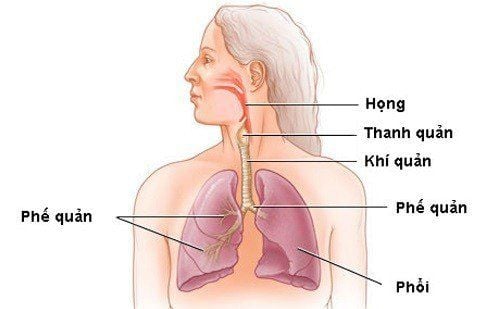
Chấn thương khí quản có thể gây nguy hiểm đến tính mạng người bệnh
2. Symptoms of laryngeal trauma
Symptoms of tracheal trauma vary widely depending on the severity of the injury. Some common signs and symptoms are:
Dyspnea : dyspnea in both phases, the degree of dyspnea can be mild to moderate or severe and gradually increasing. Severe dyspnea if there is swelling, discharge, or excessive blood flow into the airways causing airway obstruction. Air or blood spurts out from the wound with the rhythm of breathing. Subcutaneous pneumothorax: due to the opening of the larynx shaft, it can spread and cause deformation of the neck, chin, face, and chest. Subcutaneous pneumothorax is often severe in wounds that have small openings and are obstructed by external planes. Pneumothorax can worsen breathing difficulties, even causing cardiac tamponade leading to death. Cough: Cough is severe, may choke, pain increases when coughing, shortness of breath is cyanotic. Hoarseness or loss of voice due to damage to the vocal cords, laryngeal nerve, or cricoid joint.
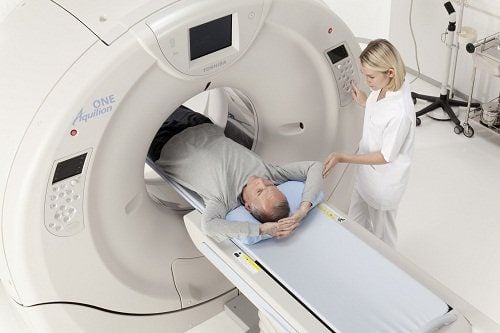
Chụp cắt lớp vi tính là một chẩn đoán hình ảnh cho phép phát hiện các triệu chứng của bệnh
In addition to clinical examination to detect the characteristic symptoms of the disease, to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a number of paraclinical techniques such as:
X-ray: helping to see the image of the overflow. pneumothorax, the degree of pneumothorax in the neck or chest area, but difficult to identify the affected area. Endoscopy: helps to determine the exact location and nature of the lesion, but caution should be exercised because it can aggravate the injury. Computed tomography of the larynx: shows specifically broken images of cartilage structures of the larynx, images of soft tissue damage such as mucosal hematoma, cricothyroid membrane tear, tracheobronchial membrane tear, images pneumothorax, funnel cartilage dislocation, cricothyroid joint,... In general, computed tomography of the larynx shows a relatively complete and comprehensive tracheal trauma, helping to guide treatment.
3. How to treat laryngeal trauma?
Principles of treatment of laryngeal trauma is to ensure breathing in cases of severe, life-threatening trauma, while restoring the maximum anatomical structure and respiratory physiology, pronunciation of the patient. tracheal system.
Specific laryngeal trauma treatment measures include:
3.1. Emergency treatment
Emergency tracheostomy is performed when the patient has a perforation, tear, or rupture of the tracheal cartilage, the patient has severe shortness of breath, and a life-threatening obvious pneumothorax. Difficulty opening the trachea, the doctor will open far from the wound to maintain ventilation of the breathing tube. At the same time, take measures to prevent shock and bleeding.
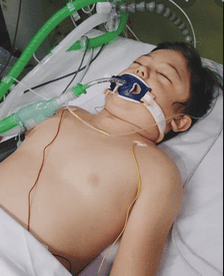
Bệnh nhân bị rách khí quản cần tiến hành mở khí quản cấp cứu
3.2. Surgical treatment
Rehabilitation treatment by surgical methods as follows:
Interventional laparoscopic surgery: laparoscopic surgery helps to fully assess the damage and conduct intervention. If there is a mucosal tear, the doctor will use a microsurgery tool to suture, fix the ring joint if there is damage,... Orthopedic surgery according to the usual outer line: Approaching the lesion through the neck incision corresponds to the cricoid membrane. Sutures restore mucosal tears. Broken cartilage is fixed with steel thread, non-absorbable thread or screw brace. If part of the cricoid cartilage is lost, the subungual fascia is sutured into the defect to reconstruct it. External orthopedic surgery combined with dilatation: the approach to the lesion is similar to that of conventional external orthopedic surgery. Materials placed as dilators can be endotracheal tubes, Abouker tubes, Montgomery tubes. The dilator is placed from the prosthetic vocal cords to the first tracheal cartilage ring and secured with non-absorbable sutures. The time to remove the dilatation ranges from 2 to 6 weeks. End-to-end tracheal anastomosis: performed in cases where the tracheal ring is separated.
Phẫu thuật nội soi giúp điều trị phục hồi chức năng chấn thương thanh khí quản
3.3. Internally medical treatment
Medical treatment of tracheal trauma is indicated in cases of lesions only in the superficial mucosa, without severe dyspnea and without structural changes of the larynx.
Medical treatment measures include:
Give the patient bed rest, lie down with the head elevated, limit changes in head position, give oxygen support. Cool and humidify the air to prevent exudation, suggest patient not speak for several days to reduce edema and hematoma. Administer corticosteroids to patients early to prevent edema and adhesions. Antibiotics are used to fight infection. Take an H2-antagonist or a proton-pump inhibitor to prevent acid reflux. Nursing the patient through the intravenous route. Get tetanus vaccine to prevent tetanus in sick people (if needed).
Người bệnh có thể cần tiến hành tiêm vắc-xin uốn ván
4. Prognosis after treatment
Patients with mild lesions, not difficult to endoscopy, have a positive prognosis. After medical treatment 1-2 days, the patient will be reassessed airway, if stable, will be discharged.
Cases of complicated trauma to the larynx, rupture of cartilage and mucosa structures have a severe prognosis and need to be closely monitored. After removing the breathing tube, the patient will be periodically monitored for the next several months to detect early symptoms of laryngeal stenosis, warts, and strictures.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.