This is an automatically translated article.
Inguinal hernia can cause many complications if not detected early and treated promptly. The disease can make surgery more difficult, the risk of recurrence is high, and the mortality rate is increased due to organ necrosis, infection, toxicity, etc. Therefore, patients should not be subjective and disregard this condition. .
1. What is an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernia is a condition in which an organ in the intestine (omentum, intestine, ...) is not located in the usual position but protrudes out of a point on the abdominal wall in the groin. Inguinal hernia can cause dangerous complications if there is strangulation - that is, the herniated organ cannot return to the abdomen, causing edema leading to ischemia, necrosis and infection.
About 2 - 3% of male infants have inguinal hernia, the rate in female infants is less than 1%. Older people also often suffer from direct inguinal hernias because the fascia of the abdominal wall weakens with age. In addition, there are several factors that increase the risk of inguinal hernia: heredity, cough, chronic constipation, pregnant women, smoking, premature babies, trauma to the inguinal region,...
Patients with inguinal hernia have symptoms such as:
A bulge in the groin area The size of this mass increases when standing for a long time, coughing or straining when defecating The bulge disappears when lying down Pain when coughing, exercising , bending over There is a burning, burning or heaviness sensation in the groin Men with swelling of the scrotum However, these symptoms can be similar to some diseases of the genital organs (hydrocele, testicular torsion, testicular torsion, etc.) ,...) so patients need to be examined, diagnosed and treated early.
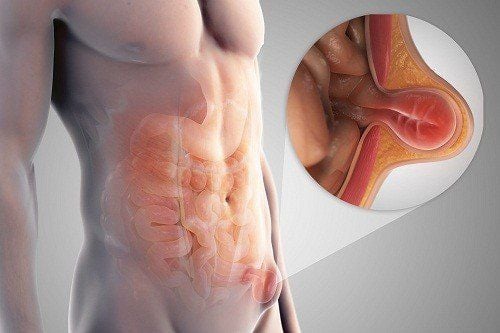
Thoát vị bẹn với triệu chứng xuất hiện khối phồng vùng bẹn
2. Complications of inguinal hernia
If the inguinal hernia is not treated in time, mild cases will cause pain in the groin area, affecting psychology, living and quality of life of the patient. If left untreated for a long time, the herniated viscera often protrudes out, it may stick to the surrounding tissue, unable to return to the abdomen (trapped hernia). At this time, the patient has more discomfort, there is a risk of injury to the herniated organ.
If the patient has complications of strangulation (herniated viscera cannot get back into the abdomen), it will cause edema, leading to ischemia, necrosis and infection. If the herniated organ is the intestine, it can cause intestinal obstruction (symptoms of nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, inability to defecate,...). If surgery is not promptly performed within 4-6 hours of onset, the bowel may become necrotic, threatening the patient's life. The surgery to repair inguinal hernia at this time is also more complicated, it is necessary to remove the intestine, it may not be able to place the reinforcing mesh in the groin area, increasing the risk of recurrence.
3. How to treat inguinal hernia?
When there are warning signs of inguinal hernia, the patient should go to the doctor to be examined by a doctor while standing, coughing or pushing. In case the clinical examination is not clear, the doctor may assign the patient to perform ultrasound, CT scan or MRI to diagnose.
Regarding the treatment of inguinal hernia, surgery is still the main option. Surgery is highly effective for patients. The principle of surgery is: Remove the hernia sac, restore the abdominal wall to enhance the endurance of the abdominal wall.
The doctor can choose open surgery or laparoscopic surgery depending on specific situations:
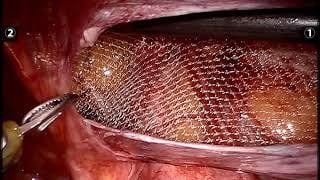
Open surgery: The doctor uses a surgical knife to make a large incision in the patient's groin area to bring the organs to the correct position in the socket. abdomen, then use a muscle scale or an artificial mesh to reinforce the abdominal wall in the groin area. This is the traditional method of surgery, performed after anesthesia or sedation; Laparoscopic surgery: The doctor makes several small incisions on the patient's abdomen, using a laparoscope (the head has a camera) and specialized tools to strengthen the groin area. This method of inguinal hernia treatment has the advantage of being less invasive, small scars, quick recovery, and early discharge from the hospital. The conservative treatment method (wearing tight pants, using a hernia bag band, ...) is only done for children under 6 years old due to less strangulation, the peritoneal tube can be closed or applied to the disease. The elderly and frail have many comorbidities.
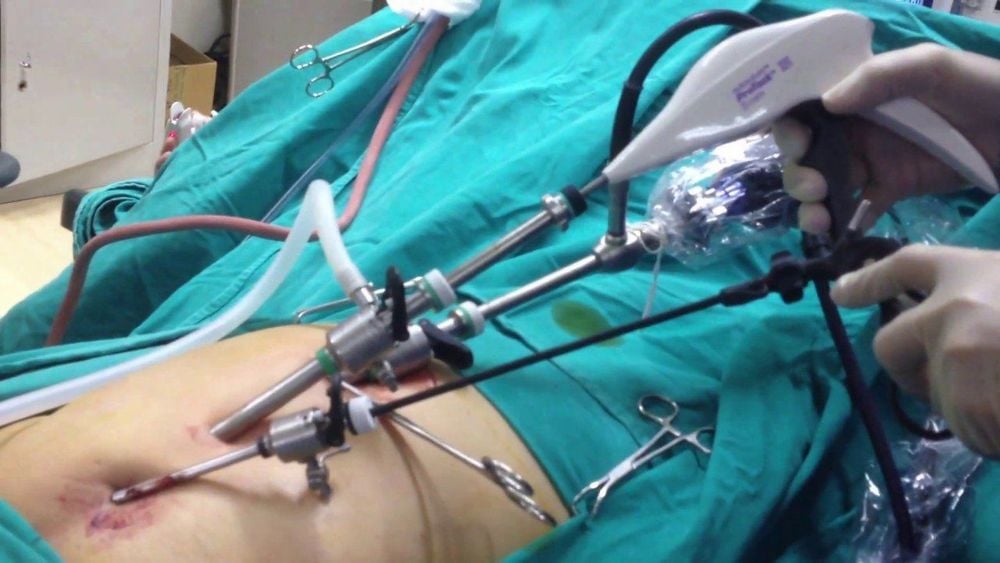
Phương pháp phẫu thuật nội soi được ứng dụng trong điều trị thoát vị bẹn
4. How to prevent inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernia has genetic factors, age, sex, certain diseases (prolonged cough, chronic constipation,...). Therefore, depending on the cause of the disease, each person can prevent inguinal hernia by:
Build a diet rich in fiber, fruits, green vegetables, drink enough water every day; limit hot spicy foods, difficult to digest to avoid the risk of constipation; Avoid using tobacco, alcohol or stimulants; Avoid activities that can put a lot of pressure on the abdomen; Thoroughly treat the causes of persistent cough symptoms; Periodic medical examination and specialist examination if inguinal hernia is suspected. Inguinal hernia is a benign disease, usually only causing discomfort to the patient, but if left untreated, it can lead to intestinal necrosis, very dangerous peritonitis. Therefore, if you suspect that you have the disease, you should see a doctor and treat an inguinal hernia as soon as possible.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.