This is an automatically translated article.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is a pathological condition in the platelets that leads to coagulation disorders and affects the hemostatic function. Some questions arise as to whether idiopathic thrombocytopenia is curable?
1. What is idiopathic thrombocytopenia?
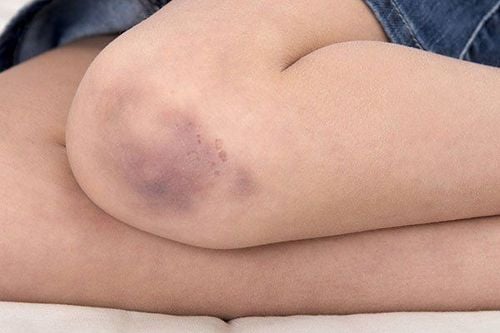
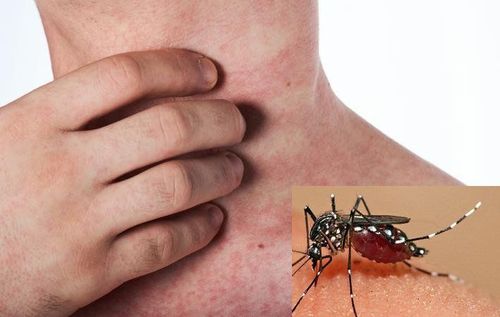
Platelets are one of the three main components of blood, they are produced in the bone marrow and play an important role in performing the hemostatic function to help maintain a stable blood volume for the body. When there is a wound on the body, the platelets will be activated and brought to the site of the injury to combine together to limit the amount of blood loss. If the platelet count drops too low, blood clotting slows down and leads to bleeding under the skin, either internally or externally.Patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura have symptoms characterized by many bruises all over the body or bleeding inside the mouth. There is also bleeding under the skin in the form of large patches or tiny dots like rashes.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura can occur in both children and adults of various ages. For young people, the proportion of women is higher, in contrast to the elderly, the disease is more common in men. Children who get this disease can get sick from an illness caused by certain viruses, such as chickenpox, mumps, or measles. All of these diseases are associated with thrombocytopenia bleeding.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is divided into two main categories including acute and chronic. In children, the acute form is common and lasts less than 6 months. In contrast, the chronic form lasts longer than 6 months and occurs in adults.

Bệnh giảm tiểu cầu vô căn với những vết bầm tím ở khắp cơ thể
2. Causes of idiopathic thrombocytopenia
"Idiopathic" here means that the cause is unknown because this was a disease that scientists still could not understand the cause. Until now, the pathogenic mechanism has been gradually elucidated, in which the immune system plays a key role in the progression of the disease. Therefore, the medical literature now calls this disease immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
The cause of the disease is that the body's immune system produces antibodies against platelets, causing them to be destroyed in the spleen, leading to a decrease in number. In addition, when the immune system is disturbed, it will affect the cells that produce platelets, thereby reducing the number in the blood.
In young patients, thrombocytopenic purpura tends to occur after an episode of viral illness, whereas in adults it can occur at any time.
3. Symptoms of thrombocytopenic purpura
Some common symptoms commonly seen in patients include:
Bruises, petechiae, hemorrhagic plaques in the lower region of the diagnosis Patients often have nosebleeds Bleeding from the roots of the teeth that persists after performing dental procedures Urinary tract or gastrointestinal bleeding protracted Menorrhagia Heavy bleeding during surgery However, there are still some cases where patients have the disease but do not have any symptoms.
4. Diagnosis of thrombocytopenic purpura
Doctors will conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient's symptoms, medical history and medications that the patient is taking (if any). Especially indispensable are the paraclinical tests including blood count, peripheral blood smear and myelogram.
Bone marrow analysis is essential for the diagnosis of hematological diseases. The doctor inserts a large needle into the patient's pelvis and pulls out some bone marrow fluid to look at the blood cells under a microscope. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient does not feel any pain.
In addition, a number of other tests can be performed to find the cause of the disease:
Microbiological tests include serological diagnosis of H.Pylory, HBsAg, anti HIV, anti HCV,... Linkage test Immunological related: TSH, ANA, FT4, Anti DsDNA, ANA 8 profile, LE cell, FT3,... Hematological tests with anemia: Billirubin, Reticulocytes, haptoglobin, direct Coombs test, iron Serum, Ferritin, LDH, ...

Một số xét nghiệm có thể giúp chẩn đoán bệnh giảm tiểu cầu vô căn
5. Treatment of thrombocytopenia bleeding
Treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenia is based on the patient's platelet count and extent of bleeding. Therefore, in some cases treatment is not really necessary. Children with acute thrombocytopenic purpura recover in less than 6 months without the need for treatment.
In adults, mild cases sometimes do not need to be treated. However, it is necessary to monitor the platelet count regularly to avoid abnormal developments to ensure the safety of the patient's health.
Adults with mild thrombocytopenic purpura sometimes do not need treatment, however, it is necessary to monitor the platelet count regularly to detect abnormalities in time to avoid bad situations for the patient. When the platelet count is too low, there is a risk of bleeding in the brain and other organs.
Some common drug groups used to treat thrombocytopenia bleeding such as:
Corticosteroid group: Drugs such as prednisolone, methylprednisolone have the effect of suppressing the immune process to make platelet count. Intravenous Globulin (IVIg): For patients with severe bleeding, immunoglobulins are injected into the body to increase platelets quickly, helping to reduce the maximum amount of blood loss. Anti D imunolgobulin : This drug works to increase platelet count quickly, but can bring many side effects to the patient. Therefore, it is only indicated for patients with Rh (+) blood group. Rituximab: This is a monoclonal antibody produced to destroy antiplatelet cells. They bind to immune B cells to destroy and reduce the amount of antibodies in the blood. However, the benefits of this approach have so far not been known whether there are long-term benefits or not. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists: Includes Eltrombopag (promacta) and Romiplostim (nplatc) that work to increase bone marrow production to increase platelets, helping to limit bleeding and bruising. These are two drugs that have been approved by the US Drug Administration to treat patients with thrombocytopenia bleeding. In addition, the doctor may prescribe other drugs such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate in severe cases because they can bring many side effects. Antibiotics: In some cases, patients with thrombocytopenia bleeding are caused by peptic ulcer disease caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria. Therefore, using antibiotics to treat it can be effective in some cases. Splenectomy: When a patient has severe thrombocytopenia that does not improve even with medication. Your doctor may recommend a splenectomy to reduce the amount of platelets being destroyed here. However, this surgery is not indicated in children because of the high risk of recurrence and increased risk of infection later in life. Emergency cases : When thrombocytopenic purpura requires urgent treatment, the doctor may prescribe platelet transfusion, intravenous methyprednisolone or imunoglobulin anti D Reasonable lifestyle changes: Limit overuse of drugs affect platelets such as warfarin, ibuprofen, aspirin. Do not use alcohol as it can reduce clotting factors. Pregnancy thrombocytopenia bleeding: In case the pregnant woman has a mild disease, there is no need for treatment, just go to the doctor periodically to have a blood test to monitor the platelet count. If the platelet count is too low at the end of pregnancy, the patient is at risk of losing a lot of blood during and after delivery. At that time, the doctor will make a reasonable treatment plan to ensure stable platelet levels for both mother and baby. In most cases, babies born to mothers with this disease will not be affected. If a baby is born with a low platelet count, it should be treated aggressively.

Bác sĩ sẽ đưa ra phác đồ diều trị bệnh giảm tiểu cầu vô căn sau khi thăm khám
6. Progression and complications of thrombocytopenic purpura
6.1. Complications The most dangerous complication of thrombocytopenia bleeding is prolonged bleeding, especially cerebral hemorrhage, internal bleeding.
When using drugs to treat thrombocytopenia bleeding, patients may experience side effects of the drug. Prolonged use of corticosteroids can lead to osteoporosis, an increased risk of infections due to a suppressed immune system, diabetes. Therefore, if you detect any strange reactions of the body, you should immediately notify the doctor for a reasonable adjustment of the drug.
6.2. Progression Most cases will not be so severe that it is life-threatening. In children, it usually resolves on its own within 6 months without treatment. For the chronic form, it can last for several years. Many patients can still live and function normally for decades with this disease if their condition is well managed and a healthy lifestyle is followed. Therefore, the disease usually has no complications related to life expectancy.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is a limited and curable disease if detected in time. When you have the above symptoms, you need to immediately go to a specialized medical facility for early diagnosis and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.