This is an automatically translated article.
Hydrocele is a swelling in the scrotum that occurs when fluid collects in the thin membrane surrounding the testicle. Hydroceles are common in newborns and go away on their own without treatment after 1 year of age. Boys and adults can develop hydroceles from infection or trauma to the scrotum.1. Symptoms of hydrocele
Scrotal swelling on one or both sides of the scrotum. Hydroceles are usually painless. Hydroceles in adults can be uncomfortable from the heaviness of the swollen scrotum. Pain may increase with the degree of inflammation. In some cases, the degree of swelling of the scrotum may decrease in the morning and increase at the end of the day.2. Causes of hydrocele
Usually the result of an injury or infection inside the scrotum. Infection usually occurs in the testicles or epididymis. The infection can be transmitted through trauma or through sex. Testicular cancer3. Complications of hydrocele
Hydroceles are usually not dangerous and do not usually affect fertility. However, hydroceles can be caused by other underlying causes from the testicles that will cause serious complications, including:Orchitis or testicular cancer: Both cause reduced sperm-forming function Inguinal hernia: Complications of inguinal hernia can cause intestinal obstruction due to intestinal strangulation, if not promptly treated, can be life-threatening.
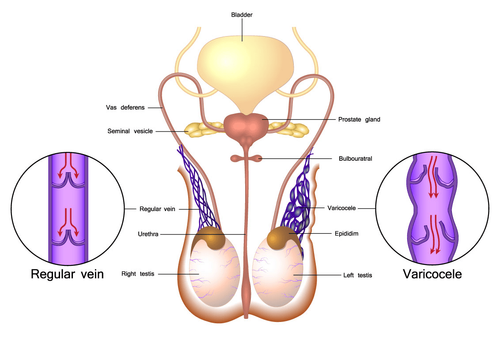
Tràn dịch màng tinh hoàn có thể gây biến chứng nguy hiểm như ung thư tinh hoàn
4. Diagnosis of hydrocele
4.1 Physical examination Assess the degree of effusion and pain Apply pressure to the abdominal wall and scrotum to check for inguinal hernia, if present Shine through the scrotum: Get a better look at the fluid around the testicles. 4.2 Subclinical After a physical examination, the doctor may order a number of tests:Blood and urine tests: Help identify infection (eg epididymitis) Ultrasound helps detect drainage inguinal gastritis, testicular tumor...
5. Treatment of hydrocele
Có thể điều trị tràn dịch tinh hoàn bằng phương pháp phẫu thuật
5.1 Hydrocele surgery Indicated if hydroceles are large or cause discomfort. The doctor will make a very small incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen, the fluid is drained out of the testicle, then the passage between the abdomen and the scrotum will be tightened so that the fluid cannot re-establish in the future. Hydroceles may recur after surgery.
5.2 Drainage of the epididymis Testicular fluid can be drained with a needle. However, effusions can recur for several months.
5.3 Sclerotherapy Injects fibrous agent to prevent hydroceles from reoccurring after hydrocele has been drained.
Currently, the sacral anesthetic technique is one of the techniques applied before surgery to treat hydrocele at Vinmec International Hospital and is directly performed by a team of specialists. .
This is a regional anesthetic technique that is performed by introducing local anesthetic into the epidural space through the sacral cleft and sacral canal. Helps relieve pain during and after surgery for almost all surgical interventions on the lower abdomen and lower extremities such as: Surgery of undescended testicle, inguinal hernia, hydrocele. Therefore, sacral anesthesia is also known as transsacral epidural.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.