This is an automatically translated article.
Varicocele is a common disease in men, occurring in all age groups, especially after puberty. It is responsible for 15-25% of primary infertility cases and 75-81% of secondary infertility cases.1. What is varicocele?
Varicocele is a dilatation of the vas deferens (including the internal seminal veins, the scrotal veins, and the posterior vas deferens). The cause of this condition is due to a problem with the venous valve system, causing blood to flow backward from the abdomen into the scrotum (instead of flowing one way from the testicles to the abdomen as usual), disturbing the development environment. sperm development.
The testicles are where sperm are produced. The seminal vesicles are the place to bring secretions and CO2 out, and at the same time dissipate heat for the testicles. When the testicular veins are dilated, the secretions and CO2 are stagnant, which will increase the temperature of the testicles, affecting the sperm production function. People with varicocele can have a decrease in the quantity and quality of sperm, even no sperm in the semen, causing infertility.
2. Things to do when examining varicocele
In the early stages, varicocele often has no symptoms. Most of the patients were discovered by chance during a reproductive health check-up. When going to the infertility clinic, the patient will have a clinical examination, combined with semen analysis, male sex hormone and scrotal ultrasound to determine if the cause is abnormal in quantity and quality. , sperm shape,... is it caused by dilatation of the seminal vasculature? After being diagnosed with varicocele, combined with abnormal semen analysis, the patient will be advised to treat the disease according to the best plan.
2.1 Diagnosis by clinical examination
The doctor will base on the symptoms that the patient is experiencing (testicular pain, heaviness in the scrotum), combined with clinical examination: look, feel the varicose veins in the scrotum, .. . to diagnose disease.
During clinical examination, it is necessary to keep the patient upright and facilitate relaxation of the scrotal dartosmus for a more accurate assessment of the seminal veins. The doctor carefully examines the scrotum, using the index and middle fingers to check the spermatic cord. In typical cases, the doctor can easily see varicose veins above and behind the testicle.
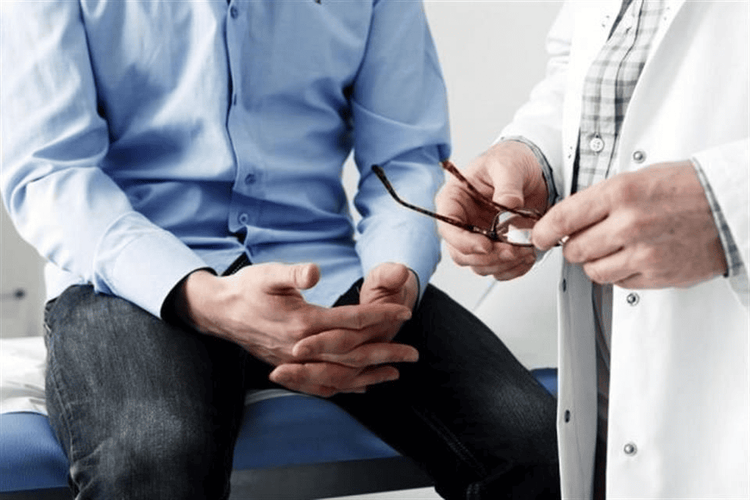

Thăm khám lâm sàng chẩn đoán giãn tĩnh mạch thừng tinh
For a more accurate check, the doctor may have the patient do the Valsalva maneuver (stress test). This procedure does the following: have the patient take a deep breath, hold the breath, and push while the doctor examines the scrotum above the testicle.
Clinically, varicocele is divided into 5 levels:
Grade 0: not clinically detected, diagnosed only on ultrasound, angiography or other diagnostic means. Grade 1: palpable dilated varicocele during Valsalva maneuver. Grade 2: palpable varicose veins when the patient is in an upright position. Grade 3: visible varicose veins when the patient is in an upright position. Grade 4: Visible varicose veins under the skin of the scrotum even when the patient stands or lies.
2.2 Subclinical diagnosis - Doppler ultrasound
Doppler ultrasound of testicular blood vessels is a method to help doctors accurately assess the degree of varicocele. Normally, the diameter of the vas deferens should not exceed 2mm. If, on ultrasound, at least one vein in the venous plexus is more than 2 mm in diameter, and there is reflux that becomes larger when the patient stands up or performs the Valsalva maneuver, it is defined as a varicocele.
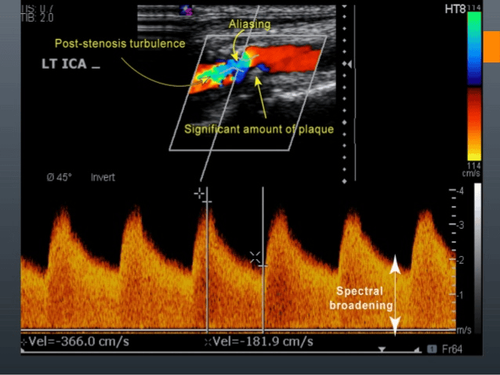
Siêu âm Doppler chẩn đoán giãn hệ thống tĩnh mạch tinh
In addition, ultrasound and computed tomography of the abdomen may also be indicated for patients with confirmed varicocele. This is to rule out cases of varicocele secondary to retroperitoneal or pelvic compression. Tests of reproductive hormone LH (luteinizing hormone), FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), testosterone are also applied when varicocele is diagnosed to check if the patient has endocrine disorders, ..
On ultrasound examination, varicocele is divided into 5 levels:
Grade 1: no varicocele in the scrotum, there is reflux of the spermatic plexus in the spermatic cord in the inguinal canal when disease person performing the Valsalva maneuver. Grade 2: no varicocele in the supine position. When the patient is moved to standing, perform the Valsalva maneuver: there is varicose veins and focal reflux in the superior testicle. Grade 3: no varicocele in the supine position. When the patient is moved to standing and performs the Valsalva maneuver: there is varicose veins and diffuse reflux in both the upper and lower poles of the testicle. Grade 4: varicocele, with reflux when performing the Valsalva maneuver in the supine position. Grade 5: varicocele, with reflux even without the Valsalva maneuver. Where to check varicocele? With the current conditions in Vietnam, hospitals from the provincial level and male study centers can perform clinical and subclinical diagnosis. Semen analysis is indicated in cases of infertility to assess the impact of varicocele on male fertility.
There are many treatment methods for varicocele, including medical and surgical. If you suspect you have a disease, you should go to a reputable hospital, specializing in male gynecology, for timely examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.