This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Tien Dat - Emergency Medicine - Cardiology - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 12 years of experience in the field of emergency resuscitation - cardiology.1. The process of developing atherosclerosis
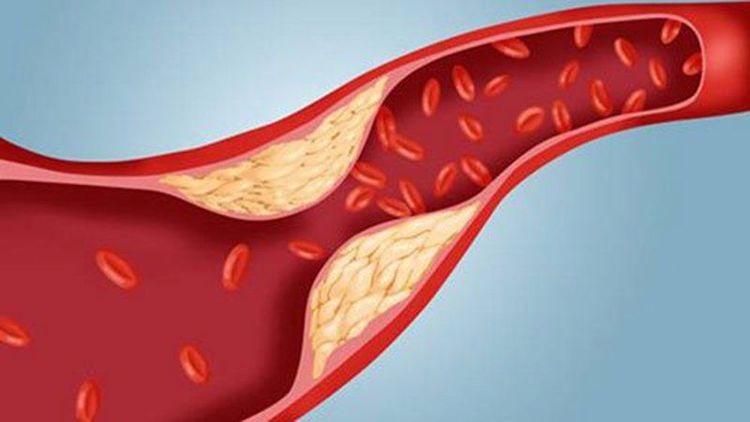
Endothelial cells have a role in regulating cell adhesion molecules, preventing vasoconstriction, balancing between thrombolysis and thrombolysis, preventing lipoprotein oxidation, and reducing vascular permeability to lipids. . Atherosclerosis begins with dysfunction of endothelial cells.The function of the omentum is disturbed due to the effect of flow in the bifurcated arterial segments, the curvature of the arteries leading to these arterial segments are more susceptible to lipid permeation, and the response of endothelial cells to The tearing force of the flow will attract monocytes to penetrate into the vessel wall to create atheroma.
After infiltrating the vascular wall, the monocytes will pull in macrophages to eat lipids to form foam cells, expose cytokines to form the extracellular matrix, create fibrosis and migrate smooth muscle cells into the endothelium.
Hyperlipidemia is the main factor causing endothelial dysfunction in addition to other risk factors such as: hypertension, diabetes, smoking... Hyperlipidemia causes endothelial dysfunction and cell damage. The endothelium loses its ability to block lipid infiltration and LDL oxidation, increasing lipid accumulation. When oxidized LDL can cause inflammation, making the plaque more fragile. Meanwhile, HDL enhances endothelial function, has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant effects, thereby helping to prevent atherosclerosis and help transport cholesterol back to the liver.
2. Recommendations on guidelines for the treatment of dyslipidemia in stroke and ischemic stroke patients
Statins are used in patients with stroke, ischemic stroke, or transient ischemic attack with an LDL-C level ≥100 mg/dL (2.5 mmol/L), to reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiac events. pulse (Group I recommendation B).Use of statins in patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack with LDL-C levels <100 mg/dL (2.5 mmol/L), to reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiac events circuit (Group I recommendation C).
Patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack with concomitant atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease should be treated according to the 2013 ACC/AHA cholesterol guidelines, including including lifestyle changes, diet, and medication recommendations (Class I recommendation A).
The treatment of dyslipidemia is an important part of the strategy to reduce the risk of stroke recurrence for patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack.
3. Statins with lipid-modifying drugs
There are 3 main classes of drugs that regulate blood lipids: Resins, Fibrates and Statins. Statins are a group that have been shown to be effective in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, both coronary and cerebrovascular diseases. Statins inhibit the enzyme HCM-CoA reductase, reduce cholesterol synthesis in hepatocytes, reduce intracellular cholesterol, increase the number of LDL-C receptors in hepatocytes, increase the capture of LDL-C into the liver, and decrease LDL concentrations. in blood. Statins help:Stabilize atheroma, anti-inflammatory. Inhibits the activation and proliferation of smooth muscle cells. Restores endothelial function, normalizes muscle tone, reduces hemodynamic stress. Restore balance between thrombolysis and formation of 6 statins approved by the FDA: Simvastatin, Lovastatin, Pravastatin, Fluvastatin, Atorvastatin, and Rosuvastatin. The efficacy of these statins to lower LDL-C and other lipid components was not the same, in which the efficacy of Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin was found to be superior to other Statins in both lowering LDL-C, lowering triglycerides, and increasing HDL-C. .
4. Studying the role of statins in the treatment of cerebral ischemia
Statins in addition to regulating blood lipids also have many other effects through stabilizing endothelial function, stabilizing atheroma, anti-inflammatory... providing important protective effects on cerebral blood vessels. Case studies with Statins in cerebral ischemia.The CARE (Cholesterol and Recurrent Event) study showed an effective reduction in vascular events, it is worth noting that the clinical trials using Statins all reduced the frequency of ischemic events while not increasing the frequency of vascular events. This is different from previous epidemiological studies that have shown that low cholesterol levels increase bleeding in the brain. The SPARCL (Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Level trial) study examined 4731 patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack within 6 months without a history of coronary heart disease, comparing high-dose Atorvastatin 80 mg/day with placebo, the mean follow-up was 5 years. Results Atorvastatin 80mg reduced the risk of stroke by 16%, reduced major coronary events by 35%, and reduced major cardiovascular events by 20%. Based on these results, the American Heart Association and the American Stroke Association recommend high-dose statin therapy for patients with ischemic stroke and ischemic attack in patients without a history of coronary artery disease. ASTEROID (A Study evaluate the effect of Rosuvastatin On Intravascular ultrasound-Derived coronary atheroma burden) study: Rosuvastatin 40mg effectively reduced the size of coronary atherosclerotic plaques, as assessed by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and angiography dosing ring. The METEOR study showed that Rosuvastatin 40mg reduced carotid endocardial thickness.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.