This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Tran Truong Giang - Intensive Care Unit - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
To be able to treat delirium, in addition to the responsibility of the resuscitator, the remaining medical staff and the patient's relatives also need to be fully equipped with detailed knowledge about this disease.
1. What is the treatment for alcohol delirium?
Delirium is very difficult to treat, the disease does not directly endanger life, but indirectly and causes many severe impacts to patients, relatives, the environment and society. To be able to treat delirium, in addition to the responsibility of the resuscitator, the remaining medical staff and the patient's relatives also need to be fully equipped with detailed knowledge about this disease.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) can occur when an individual stops or significantly reduces alcohol consumption after a long period of use.
2. Pathogenesis
A complex, controversial mechanism, currently explained through neurotransmitters: Alcohol functions as a neurotransmitter through the GABA and NMDA systems. When stopping alcohol suddenly -> Sudden decrease in GABA system activity (CNS depressant system). The body reacts by compensatingly increasing NMDA system activity through glutamate transmitters, leading to increased release of noradrenalin, increased sympathetic stimulation: Fast pulse, sweating, tremors,...
Endocrine Mechanisms : Stop drinking suddenly -> Disturbance of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis -> Increased secretion of cortisol.
3.Clinical manifestations of alcohol delirium

Người bệnh thấy run, tay ẩm,lo lắng sau khi ngưng uống rượu từ 6-12 giờ
On average, about 6 - 48 hours, clinical signs will appear if not treated -> worsen according to 4 stages of the disease.
Stage 1 Usually in the early morning (6-12 hours after the last cup of wine): The patient feels tremors, wet hands, anxiety and restlessness.
Stage 2: 24 - 48 hours after stopping drinking:
Heavy sweating Tremor: Hands, lips, eyelids – Muscle tremors Nausea, vomiting Epigastric pain, diarrhea Insomnia, nightmares Stage stage 3: Pre-eclampsia tremor
Symptoms like stage 1, 2 but more severe Diffuse tremor Profuse sweating (drops) Very nervous, anorexia, insomnia Occurrence of neurological symptoms: Hypertonia muscle , disorientation in space and time , hallucinations , whole body collapse Stage 4: Delirium - Tremens
Clearly manifested with 2 severe signs of delirium and tremor
Whole-body, continuous tremor Risk of seizures Confusion, hallucinations Persistent irritation Difficulty speaking, ataxia, swallowing disorders High fever, sweating, dehydration
4.Factors initiating delirium

Tai biến mạch máu não là một trong các yếu tố khởi phát cơn sảng rượu
Infection Trauma, surgery Cerebrovascular accident Gastrointestinal bleeding Forced not to drink, quit drinking
5.Diagnosis of alcohol delirium
Brain injury Acute meningitis Hypoglycaemia, hyponatremia Patient has used stimulant drugs in combination 5.2 Diagnosis of severity
Based on CIWA (Clinical Institute Withdrawal assessment) scale
8 points: Very mild (Goal) during treatment) 8-15 points: Moderate 15-26 points: Severe > 26 points: Very severe
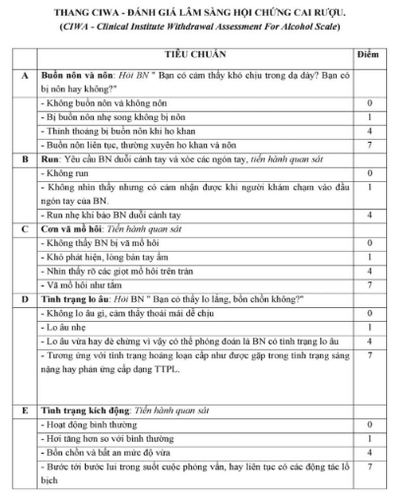
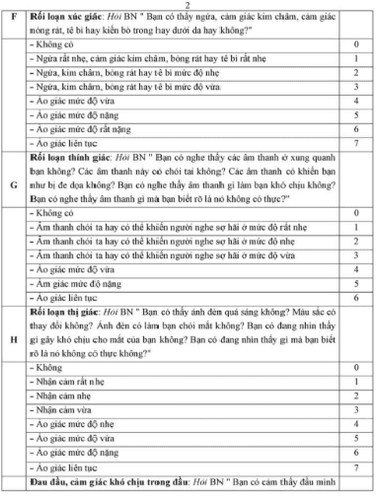
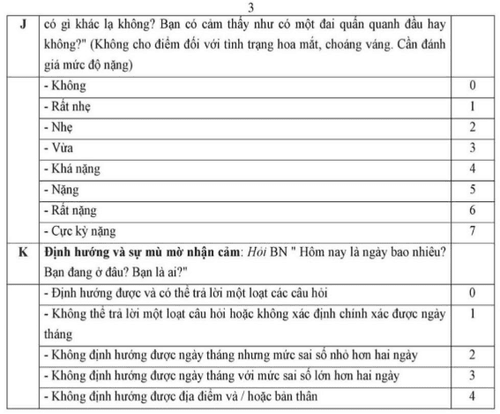
6. Complications of alcohol delirium
Associated with thiamine deficiency
Wernicke's syndrome with triad: Confusion, optic nerve disorder, difficulty in muscle coordination Korsakoff's syndrome: A late complication of Wernicke's, dementia, memory loss
7.Treatment of alcohol delirium

Sủ dụng thuốc để điều trị sảng rượu
7.1 Sedative treatment
Benzodiazepines are the first-choice group of drugs because of their antagonism, drugs that act on multiple nerve conduction systems, preventing complications. Drugs:
Diazepam: In severe cases, the dose can be 500 mg/24h (50 ampoules) Chlordiazepoxide Lorazepam: Usually used in delirium patients with severe liver damage Combination:
Phenobarbital Haldoperidol: Combination when symptoms of the disorder decompensated thinking such as schizophrenia. When combined, attention should be paid to the QT prolongation effect and the td to reduce the seizure threshold:
Alpha 2 agonist: Dexmedetomidine, clonidine Beta blocker 7.2 Treatment of seizures in alcoholics
Use of maintenance anticonvulsants has no role Is Self-limited convulsions 7.3 Supportive nutritional therapy :
Vitamin deficiency, especially Vitamin B1 :
Vitamin B1 is essential for alcohol metabolism through 2 enzymes Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase. Vitamin B1 participates in G metabolism through the pentose phosphate cycle. Therefore, when supplementing with Vitamin B1 it should be before or at the same time as G infusion. Add electrolytes: Magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, other trace elements,.. This is A very practical note to daily life, because most alcoholics eat very little, especially rice, and do not pay attention to vitamins.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
LEARN MORE
Drunkenness: A dangerous disease Drinking alcohol properly: Things to note The effect of alcohol on pregnancy