This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Toan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Acute ethanol poisoning is when a patient drinks a lot or has complications such as trauma, hypoglycemia, ... When ethanol poisoning can lead to coma, respiratory failure and even death.
1. What is acute ethanol poisoning?
Alcohol is the most commonly abused drink in the world. Acute alcohol poisoning can cause coma, respiratory failure, and death. Severe cases are often due to heavy drinking or complications such as trauma, hypoglycemia,.... It is necessary to distinguish ethanol poisoning (C2H5OH) from other alcohols, especially Methanol (CH3OH) and Ethylene Glycol. (C2H6O2).In alcohol contains ingredients Ethanol and many other substances. After the body tolerates alcohol, the concentration of Ethanol will gradually increase in the blood and at this time, Ethanol will inhibit the central nervous system. Ethanol blood levels have little correlation with the degree of intoxication because tolerability depends on the individual's body condition and the amount of alcohol consumed. On average, nonalcoholics metabolize Ethanol at a rate of 20 mg/dL/hr, while chronic alcoholics metabolize ethanol at a rate of 30 mg/dL/hr.
When drinking a lot of alcohol, the drinker will get drunk and show signs of behavior disorder, then the patient goes into a state of depression and lethargy. When the blood alcohol concentration is too high, the patient will have alcohol poisoning.
2. Diagnosis of Ethanol alcohol poisoning

Ngộ độc rượu Ethanol cấp gây ra nhiều rối loạn tâm thần và thực thể
Acute ethanol poisoning causes a variety of mental and physical disturbances. To make a diagnosis, clinical symptoms and supportive laboratory tests should be included:
2.1 Signs and symptoms:
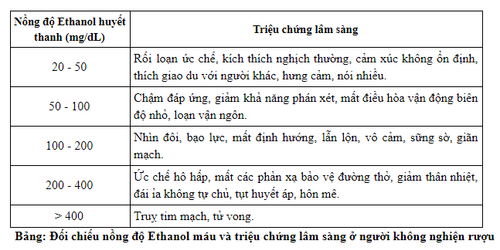
Clinically, symptoms are common across stages and lesions in many different organs: + Arousal phase: euphoria, nervous excitement (happy, talkative), reduced self-control (ataxia, arousal, aggression). Co-ordinated movement disorder: staggered walking.
+ Inhibitory phase: Consciousness gradually decreases, concentration decreases, confusion. Tendon reflexes decrease, muscle tone decreases. Peripheral vasodilation.
+ Coma phase: Coma, weak breathing or stop breathing leading to respiratory failure, aspiration pneumonia. Vasodilation, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmia, pulse collapse. Hypothermia. Hypoglycemia. Convulsions, rhabdomyolysis, electrolyte disturbances, metabolic acidosis.
Sometimes clinical symptoms are secondary to alcohol poisoning such as accidental trauma...
Tests to be performed to diagnose and monitor acute ethanol poisoning are: Quantification of Ethanol concentration (recommended to do more Methanol in the blood, because there is often mixed poisoning) Bilan basic tests: blood gas, blood count, urea, glucose, creatinine, electrolytes, AST, ALT, CPK, electrocardiogram, total urinalysis to help assess the state of organs and prognosis of poisoning poison. Measure blood osmolality (ALTT) by machine. ALTT Gap = Measured ALTT - Estimated ALTT [Estimated Blood ALTT = Na x 2 + Urea (mmol/L) + Glucose (mmol/L)]
The ALTT Gap increases if >10 mOsm/kg, here it is caused by alcohol, but not specifically because of Methanol, Ethanol or Glycol; Estimating alcohol concentration through the ALTT gap [Estimated alcohol concentration = 4.6 x ALTT gap(mg/dL)] , is only applicable when pure Ethanol is present in the blood. Other tests to look for other organ damage or complications in: chest x-ray, CT-scanner of the brain, abdominal ultrasound, gastrointestinal endoscopy... 2.3 Diagnosis
Determine: Based on History alcohol consumption, clinical manifestations and laboratory tests Differentiation: Methanol poisoning Diabetic coma: History, coma due to elevated ALTT, hypoglycemic coma or acidosis. Coma due to drug poisoning: sedation, sedation, opiates: history of drug use, quiet deep coma, tests found toxic substances in gastric juice, urine. Consciousness disorder due to other causes: encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, cerebral stroke...
3. Treatment of acute ethanol poisoning
Nếu bệnh nhân ngộ độc ở mức nhẹ cần cho bệnh nhân nghỉ ngơi và truyền dịch
3.1 Treat mild poisoning
Give the patient a quiet rest. Infusion, Glucose and Vitamin B1. 3.2 Treatment of severe poisoning
Patient is admitted to the hospital in a state of: deep coma, convulsion, sputum stagnation, tongue drop, respiratory failure, weak breathing, apnea... Place patient in a lying position Safe position, open airway, support breathing, improve airway depending on the clinical situation. Hypertonic glucose infusion for the treatment and prevention of hypoglycemia Symptomatic support drugs such as antiemetics when the patient is vomiting a lot, protect the stomach, Vitamin B1 Hypothermia: keep warm. Treatment of combined injuries if there is increased toxicity: + Insertion of gastric tube and suction of fluid
+ Artificial kidney may be considered in the following cases: renal failure, rhabdomyolysis, metabolic acidosis, severe electrolyte disturbances.
Recommended video:
Doctor Trinh Ngoc Duy gives first aid instructions for alcohol poisoning.
Customers who need medical examination and treatment at Vinmec Health System can directly visit the system's facilities nationwide or contact the information HERE.
MORE:
Why can methanol alcohol cause poisoning? Warning symptoms of alcohol poisoning How is alcohol poisoning treated?