This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Bang Phong - Internal Medicine - Cardiovascular Intervention cum Head of Heart Failure Clinic, Vinmec Times City International HospitalEchocardiography is a technique that uses high-frequency ultrasound waves to obtain images of the heart and its related structures. From these images, doctors can measure the size and function of the heart's chambers, study the movement of the heart's valves, and evaluate blood through the valves and within the heart chambers.
1. Echocardiography procedure
Cardiovascular ultrasound takes up to 45 minutes. The patient will lie on his side and follow the doctor's orders. The doctor applies gel to the chest and conducts signal detection through the ultrasound transducer. The transducer is connected to the ultrasound machine and monitor by a cable. The ultrasound waves are directed towards the heart, and are reflected and transmitted back to the ultrasound results. Image results will be updated continuously.
Echocardiography is not dangerous to the patient and is a painless technique with a quick implementation time. The patient does not need any special preparation before the ultrasound. Before and after the ultrasound, you can still eat and drink normally and continue to take the medications that the patient is currently taking.
1.1 Observation The images should be described in sufficient detail to allow other echocardiographers to visualize.
All parts of the heart and great vessels should be described. If it is not visible on the image, this needs to be stated. This gives the reader confidence that a systematic study has been done rather than one that focuses on a limited area.
The sequence should be reasonable, but will vary among ultrasound technicians and by type of study. The most important features can be described first, or each anatomical area can be discussed in turn.
Preliminary explanations may include aids to understand (rheumatic mitral valve disease). The degrees of stenosis or regurgitation of descriptive observations are used for documentation.
There is no consensus on the reporting of minor abnormalities (mild calcification of the mitral ring), normal variants (eg, Chiari net), or normal findings (eg, mild mitral regurgitation). . Suggest descriptions in the text, but omit them when concluding.
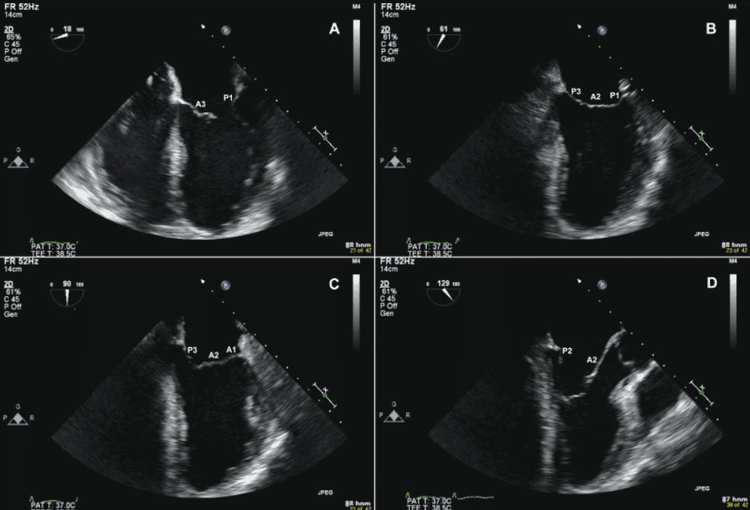
The conclusion will integrate and summarize the measurements and describe the observations to answer the question posed by the requester. It will identify any abnormality (eg, mitral regurgitation), its cause (mitral valve prolapse) and any secondary effects (LV dilation and overactivity).
Conclusions must be understandable to a non-echocardiographer and may need to be modified to match the knowledge and expectations of the requester despite the majority of echocardiographic results. most accurately interpreted by a cardiologist.
Counseling should not be given routinely, but be sure to refer the non-cardiologist to the importance of the results, and the importance of the clinical findings to inform the physician. treating doctor.
Much of the clinical advice required from echocardiographic findings that need to be integrated with broader clinical judgment is not readily available to the direct sonographer. However, it is possible to provide reasonable management advice implicit in the report, depending on the question asked and the sonographer's qualifications.
2. What to do when the echocardiogram results are abnormal
Echocardiographic results are summarized briefly and easily understood by a non-cardiologist and consistent with the knowledge and expectations of the requester. However, for accurate interpretation of echocardiographic results, minimal knowledge of cardiology and general medicine is required. Therefore, to ensure accuracy in diagnosis, it is necessary and important that echocardiographic results are read and interpreted by a cardiologist.
When receiving abnormal echocardiography results, it is important to inform the treating doctor for the most appropriate next course of action.
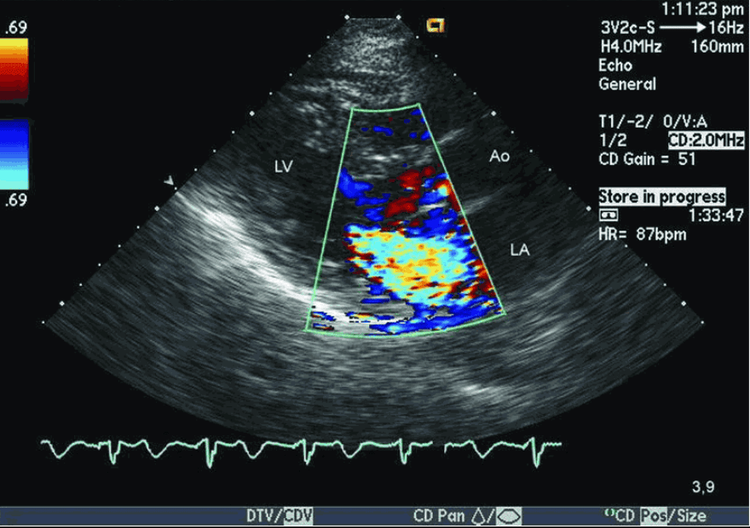
3. The role of echocardiography in the assessment of heart failure
Echocardiography is a very useful test in the diagnosis of heart failure. Echocardiography helps to evaluate both morphology and function of the heart such as: heart size; left ventricular systolic and diastolic function; regional movement disorders; heart valve diseases; pericardium ; congenital heart disease . An important indicator now often also determined through echocardiography is the ejection fraction. Normally, the ejection fraction for a healthy heart is between 55% and 70%, when an ejection fraction below 55% is a warning sign of heart failure.
Through echocardiography, doctors can collect a lot of useful information that is important in determining the cause and extent of heart failure as well as choosing an appropriate treatment.
In addition to the evaluation of ejection fraction, echocardiography is also used to evaluate diastolic heart failure including: determination of left ventricular relaxation and assessment of left ventricular filling pressure. Left ventricular relaxation is described as the time it takes for the left ventricle to relax during diastole to receive blood from the left atrium through the mitral valve. The normal heart is very elastic and ready to receive blood during the left ventricular filling phase. When relaxation is compromised, the left ventricle cannot expand easily, which increases left ventricular preload, causing an increase in left atrial pressure, leading to acute pulmonary edema.

Left ventricular relaxation is best evaluated by tissue Doppler imaging, the left ventricular end-diastolic filling velocity is determined to be Ea. Normally Ea is greater than or equal to 10 cm/s. Relaxation disorder when Ea is less than 10 cm/s.
An indication of left ventricular preload is the mitral (E) transverse maximal initial diastolic filling velocity, which is determined by the velocity of blood flow through the mitral valve. Left ventricular filling pressure can be assessed by the ratio of mitral valve (E) blood flow velocity and myocardial tissue velocity during early diastole. A high ratio (eg, E/Ea ≥ 15) indicates increased left ventricular filling pressure (left atrial pressure ≥ 15 mm Hg), a low ratio (eg, E/Ea ≤ 10) when filling pressure normal left ventricular filling (left atrial pressure < 15 mm Hg).
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.