This is an automatically translated article.
Trachoma is caused by the bacteria Chlamydia Trachomatis. Trachoma, if left untreated, or treated late, can cause damage to the cornea, affecting the function of the eye.
1. What is trachoma?
Trachoma is considered a chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea. The cause of trachoma is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia Trachomatis, which is capable of causing disease in the eyes, genital tract in adults, respiratory tract and lungs in children. In addition, many other micro-organisms can also cause trachoma such as:
Low and crowded living conditions: Low living conditions allow infectious bacteria to live and grow faster or live in poor conditions. Narrow spaces also have a higher risk of infection. Poor hygiene and sanitation: Poor hygiene and lack of hygiene, especially in the eyes, make it more susceptible to disease. Besides, not having a toilet or living in a place with many insects such as flies and mosquitoes makes the disease easier to spread.
Vi khuẩn Chlamydia Trachomatis gây ra bệnh đau mắt hột
When trachoma, common lesions include:
Trachoma: Round in shape, raised on the surface of the conjunctiva or the edge of the cornea, gray-white, surrounded by blood vessels. Gonorrhea: This is a chronic inflammatory reaction caused by lymphocytes, plasmo... causing conjunctival edema, opacity, covering the underlying vascular system. . Papillary: Pink, vascular axis in the middle, radiating surrounding capillaries. This is vasodilation, proliferation of capillaries and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Scar: This is a lesion of trachoma that has progressed for a long time. Usually in the upper eyelid cartilage conjunctiva, white fibrous bands are star-shaped, branched.
2. Trachoma symptoms and stages of development

Đau mắt là một trong các triệu chứng thường gặp của bệnh mắt hột
Symptoms of trachoma include:
Mild itching and irritation of the eyes and eyelids (swelling); The eyes have a lot of discharge, containing mucus or pus. Sensitivity to light and eye pain. Glandular tissue that lubricates the eye, including the tear-producing glands, can be affected, leading to a worsening dry eye condition. Papillary and granular, often appear upper eyelid cartilage conjunctiva, lower eyelid conjunctiva may be, same pattern, irregular size. Some blood membranes appear in the cornea, the blood film is located in the superficial layer and the upper part of the cornea. There are scars and pits on the cornea. The stages of development of trachoma include:
Trachoma follicle: At this stage, there are at least 5 granules on the upper eyelid cartilage conjunctiva, the size of which must be 0.5 mm. above. Trachoma follicle prevalence is indicative of the prevalence of trachoma in the community. Trachomatous inflamation Intense: The upper eyelid cartilage conjunctiva is infiltrated as red or thickened. That gonorrhea obscures 1/2 of the blood vessels on the upper eyelid cartilage conjunctiva. Eyelid Scarring: When infection for a long time leads to scarring of the inner eyelid. The scars have white lines. Trichiasis: Scarring of the eyelids causes the eyelashes to grow inward and rub against the cornea. Corneal opacities: The cornea will be affected by inflammation. Inflammation leads to scratching leading to corneal clouding, secondary infection leading to corneal ulceration and possibly partial or complete blindness.
3. Complications due to trachoma
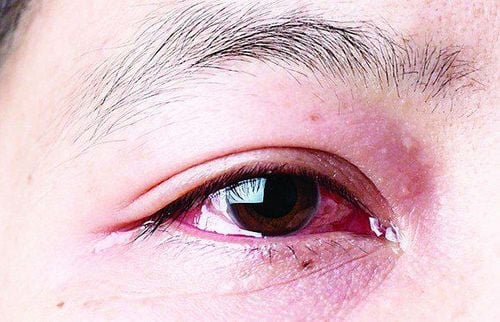
Người bị bệnh mắt hột có thể dẫn tới viêm kết mạc mạn tính
People with trachoma can lead to complications such as:
Chronic conjunctivitis: Caused by red, itchy, lumpy eyes; Ingrown hairs, drooping hairs: Due to damage to the conjunctival margin of the eyelids, the eyelashes are crooked, deformed, constantly rubbing against the cornea, resulting in damage, scratches, corneal ulcers, corneal clouding. . Blindness: The main cause is poor hygiene, leading to bacterial infections that cause pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the eyelid cartilage: Causes thickening of the eyelid margin, fibrosis, and deformation of the eyelid cartilage. Corneal ulcer: Causes eye pain, eye pain, photophobia, resulting in corneal distortion, astigmatism, corneal opacity and blindness. Superinfection: The main cause is trachoma, which makes the cornea damaged and susceptible to bacterial, viral and fungal infections, leading to corneal ulcers. Corneal granuloma: This granuloma can extend into the pupillary area and sometimes the entire cornea. Astigmatism: Caused by calcifications and trachoma scars that rub on the cornea for a long time, causing the cornea to be jagged, misaligning the path of light, causing astigmatism, vision loss; Inflammation of the lacrimal gland, blocked tear duct: This complication can lead to blurred vision, watery eyes. Dry eyes, dry cornea: Due to atrophy of the ducts, decreased secretion, dry white eyes, blurred completely, can lead to corneal ulcers, corneal perforation and blindness.
4. Treatment and prevention of trachoma
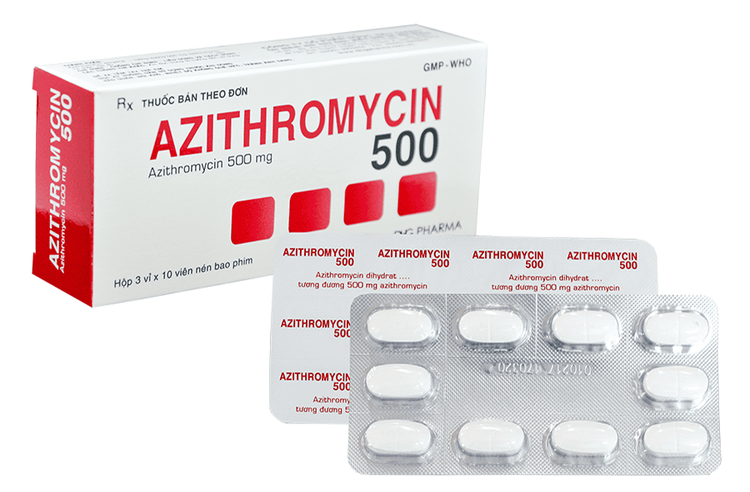
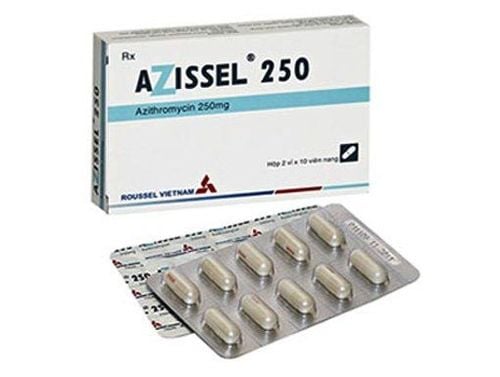
Thuốc kháng sinh azithromycin để điều trị với trường hợp bệnh mắt hột không biến chứng.
Treatment of trachoma should follow the following regimen:
The antibiotic azithromycin (1 dose 1 year) is used in uncomplicated trachoma. This medicine kills the bacteria, then the eye will clear up on its own. When the disease is in the active phase, the patient should apply tetracycline 1% ointment or erythromycin every 8 hours and use it for at least 6 weeks. In addition to applying ointment, the patient needs to wash his face with soap and water. Because the disease can cause very weak or almost no immunity, trachoma can still be re-infected after treatment. Therefore, if the patient has a complication of drooping hair, ingrown hairs, it is necessary to go to a doctor to have the doctor burn or pluck the hairs, surgery to pop the eyelashes out in the case of ingrown hairs.
Prevention of trachoma:
If you live in an area with trachoma epidemics, you need to keep clean, especially the eyes. Limit the sharing of cleaning supplies. Improve living conditions: create clean water, kill flies. Water for personal hygiene must be clean. If you detect red, swollen eyes... you should immediately go to the nearest medical facility. Proper waste management: Dispose of animal and human waste properly. If someone in the family has trachoma, it is necessary for the patient to be treated at a hospital with reputable eye specialists. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Causes of entropion in the eyes How is Blepharitis treated? Keratitis: Causes, symptoms, and ways to prevent it