Cysteine is a semi-essential amino acid synthesized from methionine and serine. It is found in most protein-rich foods, such as chicken, yogurt, cheese, eggs, sunflower seeds, and legumes.
1. N-Acetyl Cysteine and its benefits.
NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine), also known as Acetylcysteine, is a supplemental form of cysteine. Adequate intake of cysteine and NAC is vital for health as they help replenish glutathione, the most potent antioxidant in the body. These amino acids also aid in the treatment of chronic respiratory conditions, support fertility (in cases of oxidative stress-related infertility), and promote brain health. Below are the top 9 health benefits of NAC.
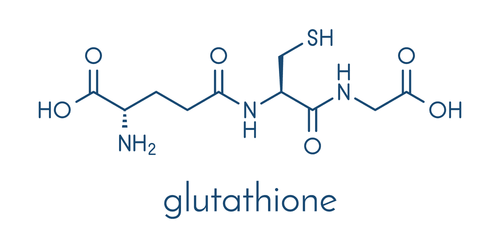
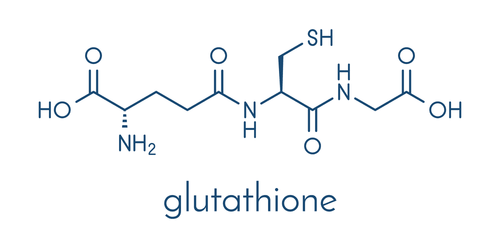
1.1. Produces Glutathione, a powerful antioxidant
NAC is highly regarded for its primary role in antioxidant production. Along with two other amino acids—glutamine and glycine—NAC replenishes glutathione, a key antioxidant.
Glutathione is one of the most critical antioxidants in the body, helping to neutralize free radicals that can damage cells and tissues. It is also essential for enhancing immune system health and combating cellular damage. Some researchers believe it may even contribute to extending lifespan.
Its antioxidant properties are crucial in combating various diseases caused by oxidative stress, including heart disease, infertility, and certain mental health disorders.
1.2. Supports detoxification to prevent or reduce kidney and liver damage
N-Acetyl Cysteine plays a crucial role in the body's detoxification processes. It can help prevent adverse effects from drugs and environmental toxins. In medical settings, NAC is often administered intravenously (IV) to individuals who have overdosed on acetaminophen to protect against or mitigate kidney and liver damage.
Additionally, NAC is utilized in other liver-related conditions due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.

1.3. May improve mental health disorders and addiction behaviors
NAC helps regulate glutamate levels, which is the most important neurotransmitter in the brain. While glutamate is essential for normal brain function, an excess of it combined with reduced glutathione levels can cause brain damage. This imbalance may impact mental health conditions such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and addictive behaviors.
For individuals with bipolar disorder and depression, N-Acetyl Cysteine may help alleviate symptoms and improve overall functioning. Furthermore, research indicates it may play a role in treating moderate to severe OCD. Similarly, an animal study suggests that NAC could mitigate negative effects of schizophrenia, such as withdrawal symptoms, apathy, and lack of focus.
NAC supplements may also aid in reducing withdrawal symptoms and preventing relapse in individuals addicted to cocaine. Additionally, preliminary studies show that NAC might decrease the usage and cravings for cannabis and nicotine.
1.4. Helps reduce symptoms of respiratory-related conditions
NAC can reduce symptoms of respiratory-related conditions by acting as an antioxidant and mucolytic, helping to loosen mucus in the airways. As an antioxidant, NAC helps replenish glutathione levels in the lungs and reduce inflammation in the bronchial tubes and lung tissue.
Individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experience long-term oxidative damage and lung tissue inflammation, leading to blocked airways, shortness of breath, and coughing. NAC supplements have also been used to improve COPD symptoms and lung function. A year-long study showed that taking 600 mg of NAC twice a day significantly improved lung function and symptoms in people with COPD.
People with chronic bronchitis can also benefit from NAC. Chronic bronchitis occurs when the mucous membranes in the lungs, the bronchial passages, become inflamed, swollen, and obstruct the airways. By thinning mucus in the bronchial tubes and increasing glutathione levels, NAC can help reduce the severity and frequency of wheezing and coughing.
In addition to reducing COPD and chronic bronchitis, NAC may improve other lung and respiratory conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, as well as nasal and sinus congestion caused by allergies or infections.
1.5. Helps enhance brain health by regulating glutamate and boosting glutathione
The ability of NAC to replenish glutathione and regulate glutamate levels can enhance brain health. Glutamate, the brain's primary neurotransmitter, is involved in a range of learning, behavior, and memory functions. While glutathione, an antioxidant, helps reduce oxidative damage to brain cells associated with aging, NAC can help regulate glutamate levels and replenish glutathione. As a result, it may provide benefits for individuals with brain disorders and memory loss.
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, can slow down learning processes and memory abilities. Animal studies suggest that NAC may help slow the progression of cognitive decline in individuals with Alzheimer's disease.
Another brain condition is Parkinson's disease, characterized by the degeneration of cells that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine. Both oxidative damage to cells and reduced antioxidant capacity contribute to this disease. NAC supplements appear to improve dopamine function as well as alleviate symptoms such as tremors.
1.6. Improving fertility in both men and women
Around 15% of all couples experience infertility, with male infertility being the primary contributing factor in nearly half of these cases. Male infertility is often linked to insufficient antioxidant levels, which fail to combat the formation of free radicals in the reproductive system. Oxidative stress can lead to cell death and reduced fertility. In some cases, NAC has been shown to improve male fertility.
A condition contributing to male infertility is varicocele, which involves the enlargement of veins inside the scrotum due to free radical damage and often requires surgery. In a study of 35 men with varicocele, 600 mg of NAC was administered daily for three months following surgery. The combination of surgery and NAC supplementation improved semen integrity and the pregnancy rate of their partners by 22% compared to the control group. Another study involving 468 men with infertility found that supplementation with 600 mg of NAC and 200 mcg of selenium for 26 weeks improved semen quality.
Researchers suggest that NAC supplementation should be considered a treatment option for male infertility. Additionally, NAC may enhance fertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) by promoting or increasing ovulation cycles.
1.7. Stabilizing blood sugar levels by reducing inflammation in fat cells
High blood sugar levels combined with obesity contribute to inflammation in fat tissues, which can damage or destroy insulin receptors. This increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Animal studies suggest that NAC may help stabilize blood sugar levels by reducing inflammation in fat cells and improving insulin resistance.
When insulin receptors remain intact and healthy, they effectively remove sugar from the bloodstream, keeping levels within a normal range. However, further research is needed to confirm the effects of NAC on blood sugar regulation in humans.
1.8. Reducing heart disease risk by preventing oxidative damage
Oxidative damage to heart tissues is a common precursor to heart disease, potentially leading to stroke, heart attack, and other severe conditions. NAC may reduce the risk of heart disease by minimizing oxidative damage to cardiac tissues.
Additionally, NAC has been shown to boost nitric oxide production, which aids in the dilation of blood vessels and improves blood flow. This process accelerates blood circulation back to the heart, potentially reducing the risk of heart attacks.
In a test-tube study, NAC combined with green tea appeared to mitigate the damage caused by oxidized LDL cholesterol, another significant contributor to heart disease.

1.9. Enhancing glutathione levels to improve immune function
N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) and glutathione play crucial roles in boosting immune health. Research on conditions associated with NAC and glutathione deficiencies suggests that immune function can be improved and potentially restored through NAC supplementation. This effect has been most extensively studied in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In two studies, NAC supplementation significantly enhanced immune function and nearly fully restored natural killer (NK) cell activity. Elevated levels of NAC in the body may also inhibit the replication of HIV-1.
An in vitro study demonstrated that in cases of immune damage, such as influenza, NAC could disrupt viral replication. This may reduce the severity of symptoms and shorten the disease duration. Similarly, other in vitro studies have linked NAC to the suppression and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation.
2. Dosage
There is no specific recommended intake for cysteine, as the body can produce small amounts. To synthesize the amino acid cysteine, the body requires adequate levels of folate, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12. These nutrients are found in foods such as beans, lentils, spinach, bananas, salmon, and tuna. While most protein-rich foods, including chicken, yogurt, cheese, eggs, sunflower seeds, and legumes, contain cysteine, some individuals choose to supplement with NAC to boost their cysteine levels.
NAC has low bioavailability, meaning it is not well absorbed by the body. The generally accepted daily supplementation dose ranges from 600 to 1,800 mg of NAC. NAC can be administered via intravenous (IV) injection, aerosol spray, or taken orally in liquid or powder form.
3. Side effects
NAC is considered safe for adults when prescribed as a medication. However, high doses may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. When inhaled, it may lead to swelling of the mouth, runny nose, drowsiness, or chest tightness.
Individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications should avoid using NAC, as it may slow blood clotting. NAC has an unpleasant odor, which can make it difficult to consume. If you choose to take NAC, consult your doctor beforehand.
N-Acetyl Cysteine plays several crucial roles in human health, particularly in boosting antioxidant glutathione levels, regulating the important brain neurotransmitter (glutamate), and supporting the body’s detoxification systems. These functions make NAC supplementation a viable therapeutic option for various health issues. However, it is essential to seek medical advice before using NAC for health enhancement.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com