This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Cong Trinh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.Currently, computed tomography is widely used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. So what is the operating principle of a computer tomography machine, and how many types of tomography machines are classified?
1. What is a computed tomography scanner?
A computer tomography machine (referred to as a tomography machine, also known as a CT scan machine) is a modern diagnostic imaging device that uses X-rays to penetrate soft tissues inside the body to target. The aim is to reproduce the images from the resulting projection.With the help of computer algorithms, the tomography machine will create each layer of images clearly, detailed and sharp thanks to the extremely high contrast.
Also uses X-rays like an X-ray machine, but is called a computed tomography machine because the detector system to emit X-rays is increased in number of sequences in order to obtain more tomographic images and have a thinner, combined with computer rendering software to create multiple slices of clear images. Currently, tomography machines have the number of slices from 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 to 128, 256 and 512.
Depending on the production unit, the tomography machine of each company will have a speed Different scanning speed and slice thickness, together with rendering software will produce different image quality, specifically:
Scan speed: The higher the scan speed, the faster the capture time, the patient No need to hold your breath for long or many times when taking pictures. Slice thickness: The thinner the slices, the closer they are to each other, will get more images, clearer, better screening because it helps limit the missed lesions.
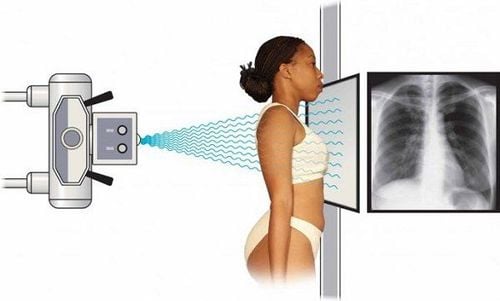
Hình ảnh tia X tác động lên con người khi chụp X-Quang
2. Structure of tomography machine
A tomography machine is composed of the following parts:X-ray generator: The X-ray emitting part has the main structure of an X-ray ball (T - Tube) to emit a thin X-ray beam of standard intensity up to body parts and organs that need to be examined. Processing part: The main structure of the processing unit is X-ray sensitive sensors (D - Detectors) that absorb the X-ray beam emitted from the X-ray ball through the body to receive and process images. images on the computer system. Depending on the tomography machine, the quality and number of different sensors will give different images. In order for the X-ray ball and detectors to rotate, the machine also has a frame, rail and motor system, ... Table system: The table system includes a patient bed, control circuit, and stepper motor. The desk system has the effect of moving back and forth, raising and lowering the control commands of the system and the processing center. Image display and control system: This system of the tomography machine looks like a computer, but has the effect of controlling the camera and managing and displaying the acquired and processed images, as well as information. patient information so that doctors can base on the results to make a diagnosis. Film printer: Like other conventional digital film washing machines, the captured images will be printed by the film printer, making the results for doctors to rely on for diagnosis.
Máy chụp cắt lớp hoạt động
3. Working principle of computer tomography machine
The operating principle of the computed tomography machine is similar to that of an X-ray machine, but it is improved and understood as follows:The patient lies on the slide and is inserted into the scanner. The machine emits an X-ray beam to scan the body and reach the organ or part that needs to be examined. The unit that receives and processes signals converts, reproduces images and displays them on a computer screen specialized in tomography.
4. Classification of tomography machine
Currently, tomography machines have been greatly improved to shorten the time taken to capture, and at the same time obtain clearer and more detailed images, helping to better diagnose and screen. Classification of tomography machines across generations based on the scanning system, number and location of sensors.4.1. 1st generation tomography machine 1st generation tomography machine has the following characteristics:
Structure: The receiver consists of 1 probe, the emitting narrow and parallel x-ray beam is pencil-shaped. Scanning mode: When X-ray is emitted, the X-ray ball of the machine and the transducer move in a direction parallel and perpendicular to the beam, covering the entire plane of the cut. The entire scanning system rotates at an angle, then continues to shift in parallel, sending and receiving X-rays at regular intervals over a distance, repeating the process until a sufficient number of signals are received to reconstruct the image. Currently, the 1st generation tomography machine is no longer used due to the long shooting time, the limited capacity of the X-ray tube, and the low speed of movement.
Máy chụp PET/CT 128 dãy hiện đại hàng đầu thế giới chẩn đoán, điều trị hiệu quả ung thư sớm tại Vinmec
Structure: The machine's probe beam has an amount of about 20 - 30 pieces, arranged adjacent to each other, emitting a scanning beam. fan shaped. Scanning mode: When X-ray is emitted, the system moves in both translational and parallel directions for more efficient use of X-rays, more projections, increased number of rotations and intervals between projections, total system rotation and plane sweep are reduced. The time taken to capture and reconstruct the image of each cut layer takes from 10 - 60 seconds. 4.3. 3rd generation tomography machine 3rd generation tomography machine has the following characteristics:
Structure: The number of probes of the machine increases to several hundred and is fixed with the X-ray tube, located on the ring opposite arc, emitting a fan-shaped X-ray beam at an angle of 30 - 60 degrees. Scanning mode: When X-rays are emitted, the measuring system performs a unique rotational motion, which is to rotate around the subject 360 degrees continuously to capture each slice. As a result, the scan time is short and the X-ray is used efficiently. 4.4. 4th generation tomography machine 4th generation tomography machine has the following characteristics:
Structure: The transducer system gathers many probes and is arranged on the same circle around the patient compartment, separate completely with radiographs. When X-ray is emitted, the X-ray tube and the transducer move and rotate together. Scanning method: When X-ray is emitted, the X-ray ball rotates around the patient and emits a fan-shaped beam, covering the entire area to be imaged. The 4th generation tomography machine has a fast shooting time, takes only a few seconds, and the image noise is low. A tomography machine is a modern imaging diagnostic device that allows to clearly observe and screen the layer-by-layer structure of the internal organs, thereby helping to detect lesions and pathologies.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has put all kinds of modern standard machinery systems in service of image diagnosis, early detection and treatment of diseases, bringing optimal treatment results, Minimizing complications for users, including modern and high-tech CT scanners such as 128-segment CT scan, 256-segment tomography,... In particular, the CT scan process at Vinmec is performed at Vinmec. by a team of experienced and qualified medical doctors, capable of performing diagnostic imaging techniques, will create a feeling of peace of mind, safety and bring accurate results to patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.