This is an automatically translated article.
Although drugs are a common cause of acute immune-mediated thrombocytopenia in humans, drug-induced thrombocytopenia is often unrecognized at baseline. Usually, drug-induced thrombocytopenia occurs 1 to 2 weeks after starting a new medication or is used suddenly after a single dose when a previous medication has not been used continuously. However, severe drug-induced thrombocytopenia can occur soon after taking antiplatelet or antithrombotic drugs.1. What is drug-induced thrombocytopenia?
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia includes thrombocytopenia caused by prescription drugs and also by beverages, foods, and herbs. This is an important clinical problem for hematologists because drug-induced thrombocytopenia is often sudden and severe, and can cause bleeding and death.However, in many patients, the cause is the drug is often not recognized in the first place. In hospitalized patients, new-onset thrombocytopenia can be attributed to complications such as sepsis. Likewise, in previously asymptomatic patients, drug-induced thrombocytopenia is often misdiagnosed as immune thrombocytopenic purpura with inadequate treatment outcomes.
Even when a diagnosis of drug-induced thrombocytopenia has been considered, the cause of the drug may still be unclear as the patient may not think that self-administered medications such as supplements, beverages, etc. , foods or herbs have also been associated with bleeding symptoms on the skin and therefore should not be reported to your doctor.
Although the recovery of drug-induced thrombocytopenia is rapidly initiated within 1 to 2 days of discontinuation of the drug and usually completes within a week, drug-dependent antibodies are acquired through the immune system. causes platelet destruction that can persist for many years afterward. Therefore, it is important that the cause of the drug is identified as soon as possible and that the drug is avoided in the patient's life.

Giảm tiểu cầu gây ra bởi các loại thuốc có chỉ định và cả các loại đồ uống, thực phẩm và thảo dược
2. What is the pathogenic mechanism of drug-induced thrombocytopenia?
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia is a relatively common and sometimes serious clinical disorder characterized by the presence of drug-dependent antibodies that bind to platelets and cause platelet destruction. Antibodies that cause drug-induced thrombocytopenia differ from conventional antibodies in that they are specifically structured to bind to the glycoprotein component of the cell membrane of platelets.In the past twenty years, the pathogenesis of drug-induced thrombocytopenia has been better understood and test kits for the presence of antiplatelet antibodies due to certain drugs have been developed. However, knowledge about the molecular nature of these immune responses is still gaping. Accordingly, the indication for drug use should always be considered, especially in subjects who already have low platelet counts with drug groups that have evidence of causing thrombocytopenia due to drugs as well as drugs in general.
3. When should I suspect drug-induced thrombocytopenia?
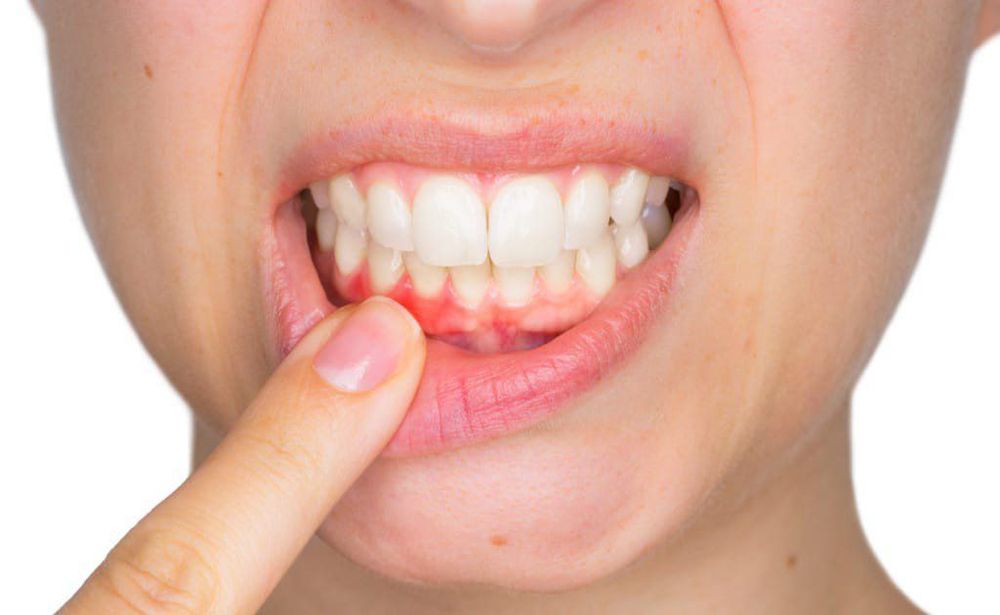
Chảy máu nướu khi đánh răng là một dấu hiệu cần lưu ý
Several drugs have been observed to cause drug-induced thrombocytopenia including:
Furosemide Gold, used to treat arthritis Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Penicillin Quinidine Quinine Ranitidine Sulfonamide Linezolid and other antibiotics Statins When thrombocytopenia, the patient is detected by the symptoms of coagulation dysfunction as can cause:
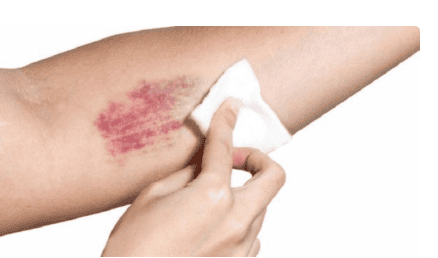
Abnormal bleeding; Bleeding gums when brushing teeth; Easy bruising on the skin; Spontaneous appearance of red spots on the skin. Next, the doctor will need to do more tests to evaluate the number and function of platelets with the number of platelets on the peripheral blood count always being the first criterion. In addition, the demonstration and quantification of drug-dependent antiplatelet antibodies is important to confirm the etiology of drug-induced thrombocytopenia.
However, such tests are not available and take a certain amount of time, it is impossible to wait for test results before deciding whether to discontinue the drug that may cause illness. Furthermore, drug-dependent antibody tests may be negative in patients with drug-induced thrombocytopenia.
The reason is that the test method is not sensitive enough to detect some antibodies, some drugs are insoluble in water and difficult to incorporate into chemicals, and the pathogenesis in the body is sometimes different. certain in vitro test models. Therefore, the diagnosis of drug-induced thrombocytopenia with a suspected drug is a real challenge, and it is necessary to weigh the indications with the benefits and risks associated with each individual case.
4. How to treat drug-induced thrombocytopenia?

Tình trạng giảm tiểu cầu do dùng thuốc có thể phục hồi trong vòng 1 đến 2 ngày sau khi ngừng thuốc
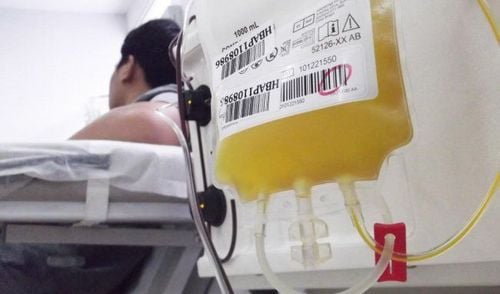
Fortunately, however, drug-induced thrombocytopenia is reversible within 1 to 2 days of discontinuation of the drug, and recovery is usually complete within a week. Even so, platelet transfusions may still be necessary to control if bleeding is excessive.
Concurrently, corticosteroids may also be used if the diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura or immune thrombocytopenia cannot be excluded. However, if the platelet count returns to normal, a higher possibility of drug-induced thrombocytopenia should be suspected and corticosteroid therapy should be discontinued. Conversely, if thrombocytopenia recurs and it is certain that the patient has not taken the suspected drug again, the diagnosis of drug-induced thrombocytopenia should be excluded.
Additionally, in drug-induced thrombocytopenia, drug-dependent antibodies can persist for many years and patients should be advised to avoid medications that cause thrombocytopenia throughout life. At the same time, patients also need to be aware of the use of drugs, do not arbitrarily use specific drugs and foods, including herbs without professional advice.
In summary, drug-induced thrombocytopenia can also be considered a common side effect with the main mechanism due to disorders in the immune system. Although this condition is rapidly reversible upon discontinuation of the drug, it is extremely important to identify the cause and avoid its use, in order to avoid the risk of recurrent drug-induced thrombocytopenia at high levels. more serious.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.