This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.The knee joint is an important dynamic joint of the body, bearing the entire force of the entire body. Therefore, there are many diseases that can affect the knee joint. Knee ultrasound is an important imaging method that is simple, easy to use, non-invasive, and low cost to help assess the status of a number of diseases of the knee joint.
1. What is knee ultrasound?
Joint ultrasound is a method of using high-frequency ultrasound waves to examine joints and the soft tissue around the joints, when the ultrasound waves pass through, they will capture images corresponding to the tissues on the machine, thereby helping doctors diagnose. normal or pathological condition.Ultrasound of the knee joint is widely indicated to examine in cases such as joint effusion, arthritis, trauma...
1.1 Advantages of the knee ultrasound method The advantage of this method is that it is easy to perform. present, non-invasive, does not affect the body, has no contraindications, low cost and can be repeated many times to evaluate treatment results.
1.2 Disadvantages of knee ultrasound method Knee ultrasound does not evaluate the components deep inside the joint such as the cruciate ligament, meniscus, articular cartilage... So when a disease of the organs is suspected This should be combined with x-ray and MRI to evaluate the lesion.
Ultrasound of the knee joint is the earliest approach when the patient has abnormal signs in the knee joint, not only helps to diagnose the disease, but also in some suspected cases, the doctor will appoint more necessary tests. necessary for the correct diagnosis of the disease. In addition, ultrasound is used to support the treatment of knee effusion, when aspirating fluid under the guidance of ultrasound to avoid complications.
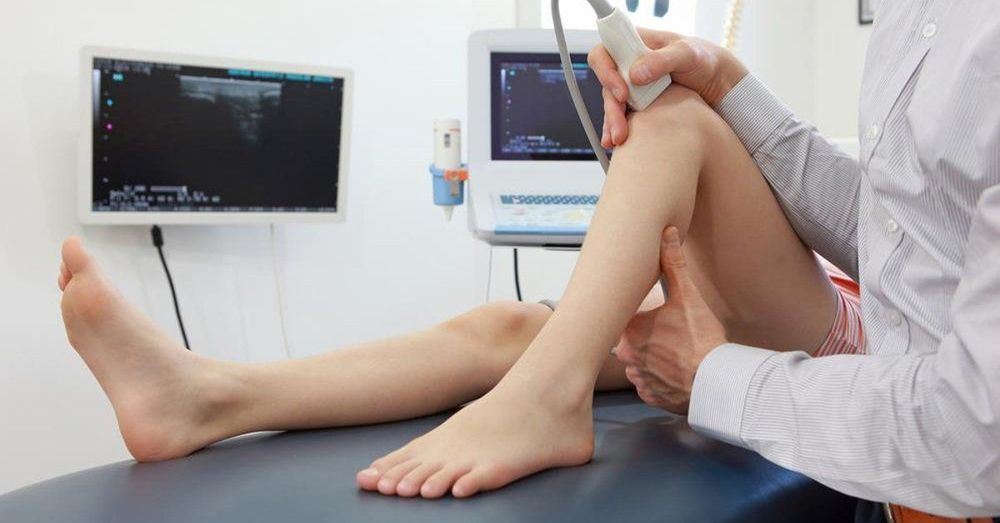
2. The role of knee ultrasound in diagnosing knee disease
When performing an ultrasound of the knee joint, the sonographer will divide the area to be examined into 4 areas including: Anterior compartment (based on the kneecap, this compartment is divided into the upper and lower patella), posterior, internal and outer compartment.When dividing such regions, the anatomical characteristics of each area are different, helping to evaluate the specific pathology of each area around the knee joint.
2.1 Upper patellar compartment Anatomy:
This area just above the patella includes the quadriceps tendon, the suprapatellar bursa between the quadriceps tendon and the femur, followed by and posterior fat organization synovial bag.
Pathology:
During ultrasound, the transducer should be placed in a cross-section along the femur above the kneecap. When ultrasonography of this area can show quadriceps tendonitis (on ultrasound, quadriceps tendon is not uniform, doppler can see increased vascularity); Trauma to the quadriceps muscle can occur after trauma (see image of quadriceps tendon discontinuous, may appear fluid around the quadriceps tendon). In addition, knee effusion can also be seen by measuring the synovial sac on the kneecap. Normally, this synovial pocket is <3mm, when it increases, it is necessary to investigate more areas to evaluate the status of knee effusion. 2.2 Subpatellar compartment This region, when ultrasound from the inferior border of the patella to the tuberous convexity of the tibia, shows the patellar ligament. The main investigation is the pathology of the patellar ligament. The pathology of patellar tendonitis shows an increased blood vessel proliferation on ultrasound, investigating the effects of knee motion on the patellar ligament.
The meniscus structure is visible but difficult to assess, the medial ligament connects from the superior process of the medial condyle of the femoral bone through the meniscus and attaches to the medial surface of the superior tip of the tibia; the gooseberry tendon includes the tendons of the 3 tendons combined; synovial bursa between the gooseberry tendon and the tibia.
Pathology:
Injuries to ligaments and tendons are common in people who regularly play sports. Bursitis between the tendon of the goose and tibia: Ultrasound shows that the fluid at this site is elastic and may change morphology. Paramenioid cyst: On ultrasound, there is a solid fluid mass, when pressed, there is no change in morphology. Degenerative meniscus : Seeing the image of bone spurs folding at an angle and protruding, the meniscus is pushed out of the joint due to the narrowing of the joint space. Medial meniscal tear: The image of the para meniscus cysts located on the inner back of the joint, when flexing the knee will cause more pain for the patient because the fluid in the joint passes through the tear of the meniscus to the outside. 2.4 Outer Compartment Anatomy: In this area, the external ligament is seen starting from the superior process of the lateral condyle and descending to join the distal end of the biceps muscle and attach to the tip of the fibula; iliac band.
Pathology:
The iliotibial band syndrome is common in runners, cyclists or mountain climbers: On ultrasound, inflammation of the synovial sac is seen between the iliotibial band and the lateral epicondyle of the femur. External ligament stretch: Ultrasound showed increased diameter, heterogeneous negative feedback, loss of fibrous structure of the ligament. External meniscal tear: The tibial fibrillation cyst is seen on posterior examination. 2.5 Posterior compartment Anatomy: In longitudinal and transverse views of the popliteal, vascular structures including popliteal artery and vein, calf muscle head, and tibial nerve are seen.
Pathology:
Baker's cyst: Very common in the knee caused by osteoarthritis of the knee. On ultrasound, it is seen as a simple cyst with clear fluid or pieces of tissue inside this fluid cocoon, fluid from the joint enters the fluid cyst in one direction, causing the cyst to gradually enlarge, compressing the structures. around. Causes pain and difficulty in flexing the knee joint. Extra-articular cyst: Fluid cyst can be seen on ultrasound but not a baker's cyst. Popliteal aneurysm: On ultrasound, popliteal blood vessels are abnormal, abnormal in size. Knee ultrasound can detect soft tissue disease around the joint and knee osteoarthritis through the acquired images. However, to have the most accurate ultrasound results, it is necessary to have an experienced sonographer and standard equipment. Therefore, it is advisable to choose an appropriate examination facility to be able to accurately diagnose the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.