This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with resident doctor Nguyen Quynh Giang - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.The prostate gland is a large gland in the body, where many diseases often arise in men when they enter middle age. Therefore, the role of prostate ultrasound is very effective so that doctors can diagnose and treat prostate diseases promptly.
1. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of prostate diseases
Ultrasound is a widely used imaging method to evaluate prostate volume with the advantages of non-traumatic, fast, accurate and effective performance. The purpose of ultrasonography is to help evaluate:Prostate volume to help guide treatment on this basis Parenchymal condition for differential diagnosis from abscess or prostate cancer · Complications due to prostate cancer Benign prostatic hyperplasia such as calculi, pyelonephritis Residual urine output to assess the stage and surgical outcome.
2. Transrectal ultrasound to evaluate the prostate

In general, the acoustic structure of the prostate is relatively uniform except that in thin men it is sometimes possible to distinguish the peripheral and central prostate. On slightly lower cross-sections the fibromuscular and periurethral glands sometimes correspond to the anterior hypoechoic region, and the prostate surrounding and posterior to this region is usually more hyperechoic, even, smooth, and balanced. to both sides. In young people, the transition zone is usually not seen.
3. Some common diseases of the prostate gland detected on ultrasound
As mentioned, ultrasound plays a very important role in the detection or evaluation of common prostate diseases. Some common diseases that can be detected on ultrasound include:2.1. Prostate cysts
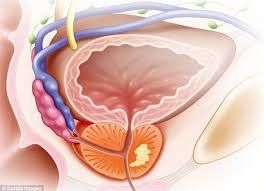
2.2. Prostate cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor-like condition that is common in men over 40 years of age due to hyperplasia of glandular tissue in the transitional, periurethral region. Ultrasound imaging revealed the presence of small-sized hypoechoic structures localized in the transition region. The more they grow, the more the nodules increase in size and number, especially in the anterior to posterior direction, pressing into the bladder lumen, causing the entire prostate gland to enlarge, causing the prostate's cross-section to have a round shape and large size, compressing the prostate glands. outside line. In prostatic hypertrophy, the hyperplastic nuclei also become echogenic structurally heterogeneous.
2.3. Prostatitis
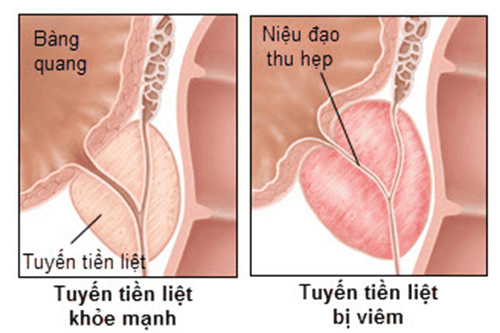
2.4. Prostate cancer Prostate cancer transrectal ultrasound can provide accurate information about the localization of lesions that are suspected by manual rectal prostatectomy and PSA quantification. The image in ultrasound diagnosis of prostate cancer is a hypoechoic lesion of unknown size, 80% of prostate cancers are located in the outer gland and the subcapsular lesion is not more than 3mm, the gland structure will be changed. change completely if the lesion size is larger. The spread of the tumor produces an obliteration of the hyperechoic fatty-fatty tissue surrounding the capsule.
Ultrasound is an imaging method that can identify many prostate diseases. Accordingly, the early detection and diagnosis and treatment of prostate diseases contribute to improving the quality of life of patients. Ultrasound diagnosis of prostate disease is a first-line method, simple and easy to perform in all medical facilities. However, for accurate results, patients should choose reputable medical facilities to perform.
Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern ultrasound machines to perform medical examination and treatment. The entire examination and ultrasound procedure is performed by highly qualified and well-trained doctors both at home and abroad. Especially to improve service quality, now Vinmec also deploys prostate cancer screening and screening packages. This is a common disease in men and has a high risk of death if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
If you have a need for medical examination and treatment at Vinmec, you can register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.