This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Doan Du Dat - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
FeNO measurement is a simple, fast, non-invasive and highly reliable test. FeNO reflects certain inflammatory mechanisms (among many) of asthma that respiratory function cannot.
1.The role of FeNO . measurement
Nitric oxide (NO) is a biogas produced from the respiratory tract and has a physiological role in the respiratory system. In 1991, Gustafsson et al. found that NO was elevated in patients with respiratory infections including asthma. Since then, many studies evaluating the role of NO in asthma management have been conducted and there is a lot of positive evidence.
Measurement of exhaled NO (Fractional exhaled NO (FeNO) concentration) has become a non-invasive method of quantifying respiratory inflammation being widely used in many countries. is produced from the reaction of converting L-arginine to L-citrulline with the catalysis of the enzyme NOS (nitric oxide synthase).
There are 3 types of NOS yeast: eNOS (endothelial NOS), iNOS (inducible NOS) and nNOS (neuronal NOS). In patients with atopic asthma, interleukine-4 and interleukine-13 induced by the inflammatory response type TH2 (type 2 T-helper lymphocytes) increase iNOS synthesis in bronchial epithelial cells, from which increases the concentration of NO in the bronchial wall. NO from the bronchial wall diffuses into the bronchial lumen due to the concentration difference. Therefore, exhaled NO in FeNO is considered as a direct biomarker for the TH2 type inflammatory response (or eosinophilic inflammation) in asthmatic patients.
Đo FeNO đã trở thành một phương pháp định lượng tình trạng viêm đường hô hấp không xâm lấn
FeNO measurement is a simple, fast, non-invasive and highly reliable test. FeNO is expressed in units of ppb (parts per billion), which is equivalent to one billionth of a liter of NO per liter of exhaled air. FeNO reflects certain inflammatory mechanisms (among many) of asthma that respiratory function cannot. Therefore, FeNO serves the needs of individualizing asthma treatment: detecting groups of patients with inflammatory mechanisms capable of responding to inhaled corticosteroids (ICS: inhaled corticosteroids) or other specific anti-inflammatory drugs; Avoid ICS in patients who are unlikely to respond.
FeNO measurement is the measurement of NO concentration from the lower respiratory tract. The nasal region has a relatively higher concentration of NO than the lower respiratory tract. Therefore, techniques for measuring NO in the lower airways should avoid sampling NO-containing gases from the nasal region. Normally, FeNO fluctuates widely among people but is stable for each person.
2. Factors affecting FeNO . measurement
The following factors can affect FeNO: age (in children: FeNO increases with increasing age); gender (male is taller than female); height (increasing as height increases); smoking status (reduced by smoking); medications you are taking (especially ICS, montelukast, L-arginin); and expiratory flow (decreases as flow increases).
FeNO is elevated in asthmatic patients compared with normal people. Repeated measurement of FeNO during the steady-state phase in asthmatics can determine the normal FeNO value of each patient. FeNO is also elevated in people with atopy, whether asthma or not. In patients with COPD, FeNO decreased during the steady-state period when treated with ICS and increased during exacerbations. FeNO may be elevated in the following conditions: bronchiectasis, viral respiratory infections, systemic lupus erythematosus, cirrhosis, organ rejection disease. FeNO is decreased in the following diseases: HIV infection, pulmonary hypertension, cystic fibrosis.
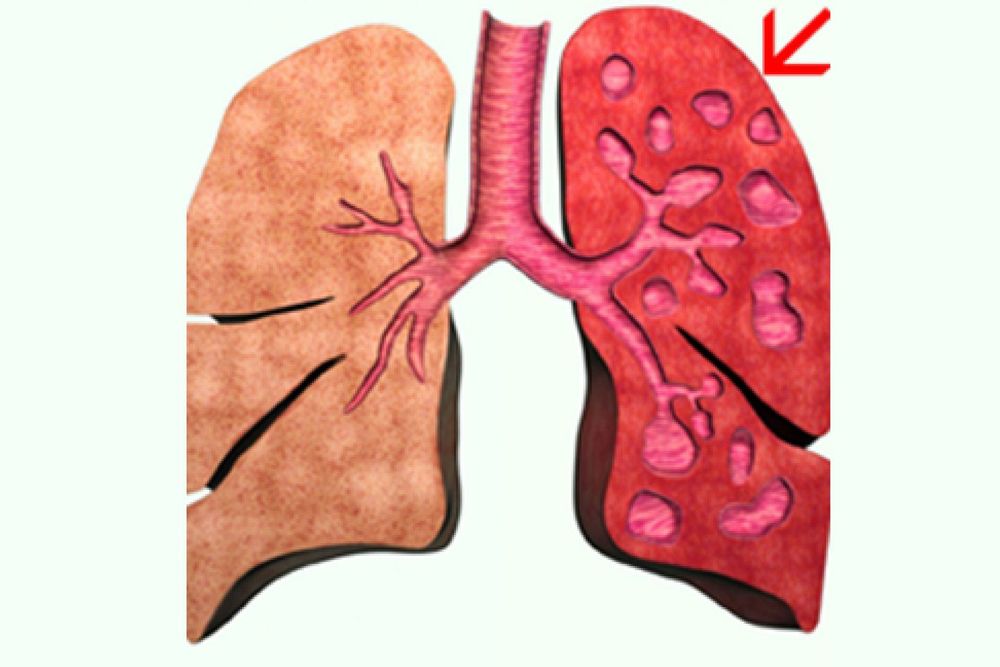
FeNO có thể tăng trong bệnh giãn phế quản
3. FeNO assesses response to corticosteroids
Corticosteroids have a very important role in the treatment of asthma, but in fact we meet many cases of patients with a certain diagnosis of asthma but not responding to corticosteroids.
Studies have also demonstrated that the inflammatory response in the airways can be controlled with corticosteroids if it occurs in the direction of increased eosinophils (eosinophilia) and not in the direction of increased neutrophils (neutrophils). . Therefore, in clinical practice, doctors want to know if their patients are able to respond to corticosteroids before giving them treatment.
In asthma, elevated FeNO indicates eosinophilic inflammation and signals a possible response to corticosteroids. Therefore, many studies have shown that based on this indicator, the status of response to ICS will be better predicted based on spirometry, bronchodilator testing, and peak flow. The American Thoracic Society recommends that FeNO below 25 ppb in adults (and less than 20 ppb in children) is an indicator of failure to respond to inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) therapy, as opposed to FeNO above 50 ppb in Adults (and above 35 ppb in children) are markers of patient response to ICS treatment.

Corticoid
4. FeNO assesses the status of treatment adherence
When a patient has been diagnosed with asthma but the treatment is not effective, then in addition to the reason that the patient has asthma that does not respond to corticosteroids or the treatment regimen is not correct, there is another reason that the patient does not adhere to treatment. . Therefore, a high or stable FeNO increase is an indicator for physicians to review the patient's adherence before deciding to change their treatment. Because FeNO levels are often closely related to patient adherence.
5. FeNO Asthma Treatment Guidelines
Because FeNO is a marker of airway inflammation in the direction of eosinophils and can predict the patient's response to ICS, doctors have proposed a treatment method that takes FeNO to adjust the drug dose for this patient. patient. In this intervention, the patient's dose was increased as FeNO increased and dose decreased as FeNO decreased.
Đo FeNO có khả năng nhận dạng và theo dõi diễn tiến viêm tăng bạch cầu ái toan ở bệnh nhân hen
The goal of this intervention is to well control the inflammatory background of asthma with the most appropriate amount of ICS medication in order to avoid overuse (when inflammation is stable) or under (when inflammatory background is still high). In patients with uncontrolled asthma and low FeNO, clinicians should focus on finding other causes (eg, obesity, GERD, or anxiety disorders) rather than increasing the dose of ICS unnecessarily.
FeNO measurement is a standardized, simple, fast, non-invasive and highly reliable test; has the ability to identify and monitor eosinophilic inflammation in asthmatic patients. FeNO supports respiratory function in asthma diagnosis, predicts ICS response, guides ICS dose adjustment, and assesses adherence. In the treatment of bronchial asthma, doctors should rely on FeNO to rationally treat patients.
FeNO measurement test is one of the contents included in the Asthma Examination and Monitoring Package at Vinmec International General Hospital, in addition to other modern assessment and monitoring tests such as Allergy Specialist Examination, Respiratory function measurement and respiratory function test...
The examination and treatment at Vinmec is performed by a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Having sufficient professional means to diagnose the disease and classify the pre-treatment stage; Quick examination time, thorough consultation, easy compliance with treatment management.
SEE ALSO:
Why measure NO concentration in breathing air when diagnosing asthma? The role of FeNO measurement in the diagnosis and treatment of asthma Asthma examination and monitoring package