This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Imaging plays an important role in the process of diagnosis and treatment of diseases at an early stage so that a treatment regimen can be devised to protect human health. Accordingly, performing liver imaging can detect many diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis.
1. Common liver disease group
1.1 Diffuse liver injury
Fatty liver: Fatty liver is the accumulation of too much fat in the liver, fat makes up at least 5-10% of the weight of the liver. Fatty liver is the result of toxic metabolism, infection or ischemia in the liver. Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a late stage of liver diseases such as hepatitis or chronic alcoholism, the main mechanism is the development of scar tissue causing fibrosis. Intrahepatic cirrhosis (injury to hepatocytes, bile): hepatitis (viral, autoimmune), alcoholism, sclerosing cholangitis, iron infection, copper Posthepatic cirrhosis (Budd-Chiari syndrome): venous obstruction liver (coagulation disorder, metastasis) Pre-hepatic cirrhosis: common due to schistosomal schistosomiasis causing periportal fibrosis, portal hypertension, ... Hepatitis: liver parenchymal injury, causing liver function is impaired. Hepatitis can be caused by viral infection, bacteriophage infection, toxicity, or autoimmune. Lymphoma: Lymphoma, also known as lymphoma is a type of cancer in the lymphatic system, lymphoma can affect many organs in the body, including the liver. Scattered small abscess lesions Liver schistosomiasis Parenchymal calcifications1.2 Liver cystic and cystic lesions
Liver cyst: Liver cyst is a phenomenon that forms an empty space containing fluid in the liver, it is considered a benign tumor, not causing cancer. Caroli: This is an inherited recessive disorder of the biliary tract. Biloma: Biloma is a condition in which bile or blood clots in the liver, usually after liver injury. Liver abscess: is a condition in which the liver is damaged, the liver is infected with bacteria or parasites, then the liver will show swelling of pus and the formation of small holes. Cystic cyst: disease caused by the flat tapeworm Echinococus granulosus, forming cysts in the visceral organs, especially in the liver and lungs. Parenchymal necrosis (after trauma, after treatment: embolization, radiofrequency ablation, ...)
Áp xe gan gây tổn thương gan do nhiễm khuẩn
1.3 Traumatic liver damage
Contusion of liver parenchymal hematoma Injury of blood vessels after trauma1.4 Nodular, solid mass
Hepatocellular carcinoma Liver metastasis Liver hemangioma Liver adenoma Focal nodular dysplasia1.5 Damage to blood vessels in the liver
Portal hypertension: Portal hypertension represents a pathological state consisting of a variety of symptoms and clinical signs of a severe stasis of the portal system: splenomegaly, collateral circulation, hemorrhoids , ascites,... Budd-chiari syndrome: also known as hepatic vein occlusion, occurs when a blood clot blocks the veins of the liver, obstructs the liver's vascular system, and obstructs the flow of blood vessels. blood flow to the heart. Portal venous gas: this is not a specific disease but a possible sign in emergency abdominal pathologies. Vascular damage after trauma2. Imaging techniques are often applied in the diagnosis of liver disease
2.1 X-ray
Conventional X-ray Vascular X-ray2.2 Ultrasound
Black and white ultrasound Doppler ultrasound Elastic ultrasound Dynamic ultrasound with contrast agent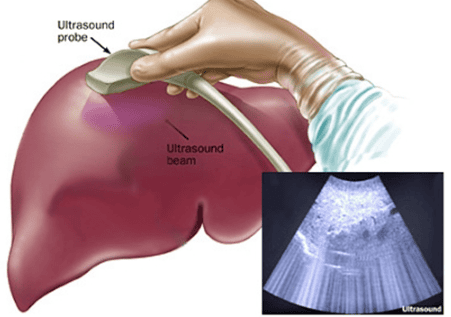
Siêu âm là chẩn đoán hình ảnh thường dùng trong chẩn đoán bệnh lý gan
2.3 Computed tomography (CT) X-ray
Non-contrast CT Multi-contrast contrast-enhanced CT2.4 Magnetic Resonance (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance without Contrast Contrast Magnetic Resonance Magnetic Resonance with Tissue-Specific Contrast (hepatobiliary) Special Magnetic Resonance: elastography, perfusion, spectrum.
Chụp MRI giúp chẩn đoán bệnh lý gan
3. The role of imaging in diagnosing some liver diseases
Fatty liver: Ultrasound image of fatty liver is hyperechoic compared with renal parenchymal, normal liver, portal vein wall creating a characteristic image called “light liver”, smooth liver surface, normal liver. large and light,... Besides, there are some other imaging methods such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Imaging can detect fatty liver, but not fully assess liver function and many other lesions. Cirrhosis: Ultrasound has a role in determining the diagnosis: liver parenchyma, liver margins, helping to orient the cause of cirrhosis, finding consequential lesions (splenomegaly, portal hypertension, intra-abdominal fluid). ,...), and ultrasound helps to differentiate cirrhosis from other liver diseases. Hepatitis: For patients with acute and chronic hepatitis, liver ultrasound can show liver lesions, liver size increases, but the image of liver parenchyma has not seen any significant changes. Hepatic cysts: ultrasound helps confirm the diagnosis (number, nature of cysts), differential diagnosis, find other associated lesions Venous hypertension of: imaging tests used in the diagnosis include: Contrast esophageal x-ray, splenic-portal X-ray (for image and extent of portal vein dilation and poor, fibrous image of portal vein branches that drain into the liver help us assess indirect liver cirrhosis), distal hepatography (evaluating the size and size of the liver) Liver abscess: ultrasound, abdominal CT are important imaging tests to help detect liver abscesses. Lymphoma: Imaging tests such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be used to identify tumors or swollen lymph nodes. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Doppler ultrasound is used to obtain information about blood flow in the arteries and veins and helps provide enough information for a diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome. A CT scan can show enlargement of the liver and changes in liver tissue density due to abnormal blood flow. Liver cancer: commonly used imaging tests in the diagnosis of liver cancer include: selective hepatic angiography, which helps to visualize the enlarged arteries in the liver by the tumor, and specific images of liver cancer. liver cancer, MRI has high diagnostic accuracy, helps to detect invasive venous lesions in the liver, chest X-ray (detects lung metastases), portal vein scan, laparoscopy ,...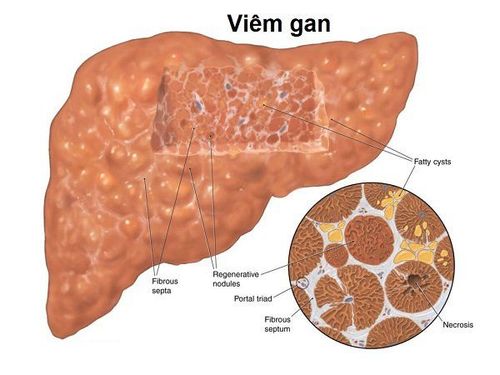
Siêu âm giúp chẩn đoán bệnh gan nhiễm mỡ
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is implementing a hepatobiliary screening package that includes all tests, diagnostic imaging of liver diseases so that patients can soon have an examination and treatment plan. minimize possible dangerous complications.
Especially now in order to improve quality, Vinmec continues to equip a system of modern medical machinery, providing a full range of technical facilities, ultrasound machines, magnetic resonance imaging, x-ray, imaging background digitization,... to give the best diagnostic and test results.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International Hospital from December 2017, Doctor Dang Manh Cuong has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging in Transport Hospitals. Hai Phong, MRI Department of Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital and Diagnostic Imaging Department of Becamex International Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.