This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.The FibroScan ultrasound method is an ultrasound method that can assess the stiffness of the liver and the degree of liver fat without causing pain or discomfort to the patient and with high accuracy.
1. FibroScan . method of elastography of liver tissue
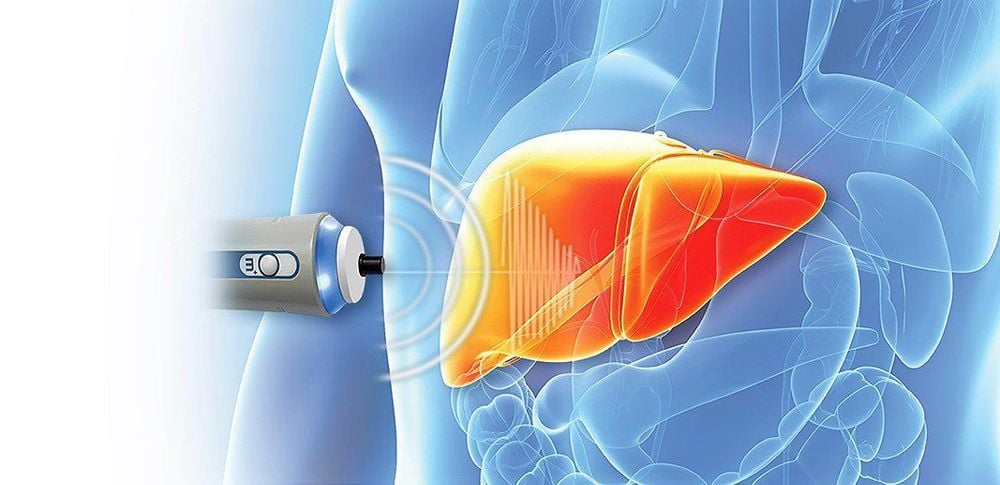
The FibroScan ultrasound method is a revolution in providing elastographic results of liver tissue, to assess the degree of cirrhosis and fatty liver. FibroScan is capable of simultaneously measuring the degree of fibrosis and steatosis of the liver by calculating from the ultrasound signal in a controlled echogenicity based stiffness measurement.FibroScan method has outstanding advantages that can replace liver biopsy in diagnosing the degree and stage of cirrhosis. Non-invasive, no discomfort and pain for the patient, and the accuracy is comparable to a liver biopsy.
FibroScan evaluates liver stiffness by measuring the velocity of elastic shear waves in the liver parenchyma generated by an external mechanical impulse, thanks to a 50 Hz vibrator and variable wave speed form measured by a 3.5 Hz dc ultrasonic transducer. The speed at which the shear wave propagates is directly related to the stiffness of the medium through which it passes. The propagation speed of shear waves is higher in hard tissues than in soft tissues.
The elasticity of the liver is expressed in units of kPa (kilopascals) ranging from 2.5 - 75 kPa and is measured between a depth of 25mm to 65mm with a diameter of 1cm. This means that the liver volume assessed by FibroScan is 100 times larger than the liver volume examined by liver biopsy. The result of liver elastography (E) is the median value of at least 10 valid measurements.
2. Clinical significance of ultrasound elastography of liver tissue using FibroScan . method
2.1 Clinical significance of the results of liver fibrosis Degree of liver fibrosis is measured by FibroScan through liver stiffness. The cut-off value of liver stiffness in chronic liver diseases is expressed in units of kPa corresponding to the degree of liver fibrosis.Liver fibrosis is divided into 5 grades according to the Metavir classification, which are:
F0: no fibrosis F1: mild fibrosis F2: significant fibrosis: fibrosis spreading to the perivascular areas of the liver F3 : severe fibrosis: extensive fibrosis and junction of cirrhotic liver areas F4: cirrhosis or advanced cirrhosis. Liver stiffness measured by FibroScan in degrees of cirrhosis may vary depending on the etiology of the chronic liver disease. Therefore, the best interpretation of results is done in combination with the following parameters:
Biochemistry (AST, ALT, AST/ALT, Albumin, Total Albumin/Protein,...) Hematology (no. platelet count, prothrombin time, INR,...) Other clinical symptoms The results should therefore be read by a physician experienced in chronic liver diseases.
Liver stiffness in kPa, horizontal bars represent the degree of cirrhosis expressed in F, divided into 9 grades, indicated by 9 different colors, depending on the cause of cirrhosis:
Hepatitis B HCV-HIV co-infection Hepatitis C recurrence after liver transplantation Hepatitis C virus Chronic cholestatic diseases Alcoholic cirrhosis Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
The liver fibrosis groups F2, F3 and F4 in patients with biliary obstruction have mean liver stiffness, respectively: F2 = 9.10 ± 3.30 kPa, F3 = 11.02 ± 3.31 kPa and F4 = 22.86 ± 12.43 kPa. Hardness was significantly different between the F2 and F4 groups with P = 0.002, and between the F3 and F4 groups with P = 0.000. However, there was no significant difference between F2 and F3 (P = 0.593). The area under the AUROC curve for the F4 hardnesses is 0.866.
The cutoff value of liver stiffness for cirrhosis grades F4 is 15.15 kPa with sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (+), and negative predictive value (-) respectively. The responses were 0.857, 0.917, 0.750 and 0.957. Using the FibroScan method in evaluating the effectiveness of the treatment of hepatitis B and C, it was found that liver stiffness decreased after antiviral therapy.
Some studies have also shown that the risk of developing HCC increases in tandem with liver stiffness. The higher the risk of developing cancerous epithelium in patients with higher FibroScan values. The value of liver stiffness can be considered as an independent risk factor for the development of HCC
2.2 Clinical significance of the results of the FibroScan measurement of hepatic steatosis FibroScan method Non-invasively can be used to quantitatively assess the degree of hepatic steatosis. The mean (calculated in CAP) or median liver steatosis in NAFLD as measured by FibroScan according to several authors.
Unlike liver stiffness, liver steatosis (CAP) was not affected by the degree of hepatitis (r = -0.025, P > 0.05), cirrhosis (r = 0.068, P > 0.05) or cause of liver disease.
The optimal cut-off values for diagnosing fatty liver at levels S1, S2 and S3 are 219.5, 230.0 and 283.5 dB/m, respectively. The cut-off values of hepatic steatosis (CAP) in patients with fatty liver with levels ≥5%, ≥34% and ≥67% were 253, 285 and 310 dB/m, respectively. The accuracy (area under the curve: AU ROC) of liver steatosis (CAP) in patients with fatty liver with grades ≥5%, ≥34% and ≥67%, respectively, was 0, 92, 0.92 and 0.88.
FibroScan elastography of liver tissue can easily detect patients with cirrhosis and fatty liver. No significant difference was found between the group of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the group with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in each degree of fatty liver
Measurement of liver stiffness after ultrasound elastography of liver tissue by FibroScan method shows the degree and stage of cirrhosis and fatty liver. The FibroScan method provides accurate results equivalent to a liver biopsy, with outstanding advantages such as fast implementation, no pain, no discomfort for patients and low cost.
Specialist I Le Nguyen Hong Tram graduated as a Doctor of General Internal Medicine at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City. Ho Chi Minh, doctor has many years of experience in the examination and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, especially gastrointestinal - hepatobiliary diseases, gastrointestinal endoscopy and general internal diseases. Currently, Dr. Tram is working at the Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
>> See also: Elastography of liver tissue: What you need to know - Master's article, Doctor Lam Thi Kim Chi - Radiologist - Diagnostic Imaging Department - International General Hospital Vinmec Danang.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.