This is an automatically translated article.
Many studies have shown that without preventive measures, the rate of HIV transmission from mother to child during breastfeeding can account for up to 30%. If there are not enough conditions to feed the baby with alternative formula, it is imperative to exclusively breastfeed the child, but absolutely not give the child both breast milk and formula, because this has many potential risks. risk of HIV infection in children.1. Learn about HIV/AIDS
HIV medically is a virus capable of causing human immunodeficiency syndrome, it can cause severe damage to the body's immune system and lose its ability to fight back. dangerous diseases that cause death.
People with end-stage HIV infection, also known as AIDS, are very susceptible to opportunistic infections, cancers or diseases related to the immune system. It usually takes about 5 years to go from HIV to AIDS.
Until now, HIV is considered a disease of the century with no cure. Therefore, to prevent HIV infection, it is necessary to have knowledge and understanding about this disease.
2. Can HIV-infected mothers breastfeed their babies?
Breastfeeding by HIV-infected mothers is one of the modes of transmission of pathogens from mother to child. Scientific research has shown that, if a mother infected with HIV does not receive preventive treatment, she will be able to transmit the disease to her baby in stages such as: transmission from the time in the fetus (accounting for about 5- 5 years). 10%), during labor (about 10-15%) and during lactation (about 30%). In particular, if an HIV-infected mother exclusively breastfeeds her child, the rate of HIV infection in 6 months is 20-35%, in 24 months is about 45%.
Mẹ nhiễm HIV cho con bú có bị lây truyền không?
The cause of mother-to-child transmission of HIV during lactation has been determined that HIV-infected breast milk also contains HIV virus. Therefore, the longer a baby is breastfed, the higher the risk of infection. Not to mention, during breastfeeding, if the baby has an infection in the oral cavity or the mother's nipple is cracked or bleeding, the possibility of HIV transmission from mother to child will be very high.
3. Why should HIV-infected mothers not feed their babies breast milk and formula milk?
Although breast milk is always recommended as the best food source for the health and development of infants, helping children to have resistance to many diseases, but for babies born with From an HIV-infected mother, to be safe, health organizations still recommend that infants should be exclusively breastfed.
The reason why babies born to HIV-infected mothers should not be fed breast milk or formula milk at the same time because they do so because the infant's immature digestive and immune systems will be more susceptible to disorders. and increase the rate of HIV transmission from mother to child. Compared with such mixed feeding, exclusive breastfeeding during the first months of life is associated with an even lower risk of HIV transmission.
Therefore, if the family situation is not too difficult, to ensure the safest, mothers should choose to breastfeed exclusively with formula. Currently, along with the development of science, there are many types of infant formula that are considered to be close to breast milk (both in taste and quality) so it will help provide nutrients. complete for children.
4. How to prevent HIV infection while breastfeeding?
If for some reason an HIV-infected mother is forced to breastfeed, the following conditions must be ensured:
The nipples must be cleaned thoroughly before giving breast milk to the baby; Breastfeeding must be done properly to avoid cracking and inflammation of the mother's nipples; In case the child has an infection of the oral cavity or the mother has a skin infection, it is best to treat it completely and then breastfeed the baby directly;
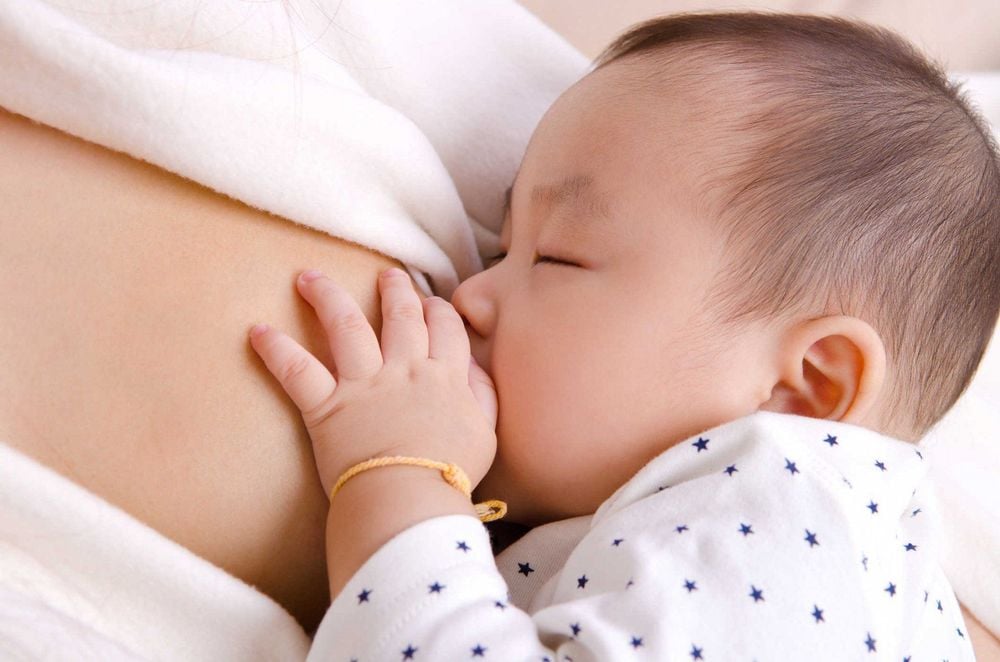

Phải cho trẻ bú đúng cách để tránh làm nứt, viêm đầu vú của mẹ
Milk preparation equipment needs to be sterilized thoroughly, keeping absolute hygiene; Breastfeeding should be stopped as soon as possible, at the latest when the baby has entered the weaning stage; When the child stops breastfeeding, the child must use alternative foods such as powdered milk, powder, porridge, etc. to ensure nutrition. On the other hand, children born to HIV-infected mothers should be monitored and tested periodically to identify HIV status early and provide preventive treatment for opportunistic infections. If the child's test result is HIV-positive, an immediate treatment regimen is required. In case the test result is negative, the baby still needs to be tested after the end of breastfeeding to check for HIV transmission from the mother to the baby during breastfeeding. or not.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.