This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thuc Vy - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Nerve fiber bundles make up nerves, which are complex structures inside the brain. Magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fibers is a method to diagnose neurological diseases in which axons are damaged.
1. What is magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fibers?
Magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles, also known as tension diffusion magnetic resonance imaging, is a modern imaging technique, applied to detect and search for axon-related lesions. nerve. Thereby, limiting the damage caused by the intervention and treatment process.
2. Indications/Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles
Magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles is indicated in the following cases:
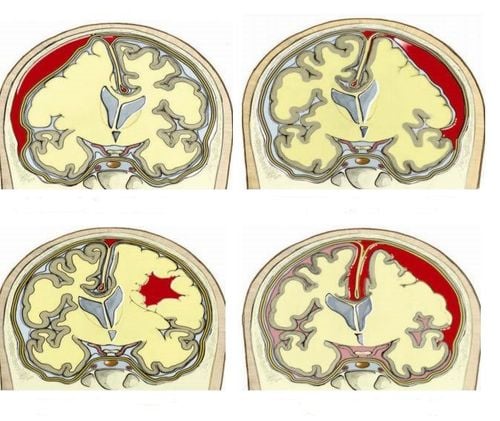
Location of brain tumor adjacent to axonal bundles or tumor growth and invasion of axon bundles. Searching and detecting related lesions between the cerebrovascular malformation area and the axon bundle. Cerebral infarction, bleeding causes damage to white matter, multiple sclerosis, ... Epilepsy, or birth defects of the brain such as split brain, ectopic gray matter.
Chụp cộng hưởng từ bó sợi thần kinh để chẩn đoán các bệnh lý về não
Magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles is contraindicated in the following cases:
Absolutely contraindicated in patients using electronic devices such as pacemakers. Relatively contraindicated in patients with ferromagnetic metals. The patient has photophobia or is unable to be alone. In case the patient is excited, unable to lie still, sedation can be used.
3. Procedure for performing magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles
The procedure for imaging nerve fiber bundles includes the following steps:
Step 1: Place the patient supine on the scanning table, select and locate the signal receiver coil, move the imaging table into the magnetic cavity of the camera, locate the area to be captured. Step 2: Depending on the purpose of the scan, select the appropriate diagnostic pulse sequences. The commonly used pulse sequences are T1, T2, FLAIR, cutting directions include transverse, horizontal and vertical. Step 3: Conduct normal diffusion pulse sequences, then calculate the apparent diffusion coefficient map to assess the lesion. Depending on the detected lesion to perform the necessary pulse sequence. Step 4: Capture nerve fiber bundles with pulse sequence and direction suitable for the purpose to be detected and diagnosed. Step 5: The technician runs each pulse and processes the images, selects the necessary images to print and sends to the doctor. The resulting image must ensure that the axon bundles are clearly displayed, without blur, without drooping, with enough pulse sequences. Based on that, the doctor will analyze and make a diagnosis.
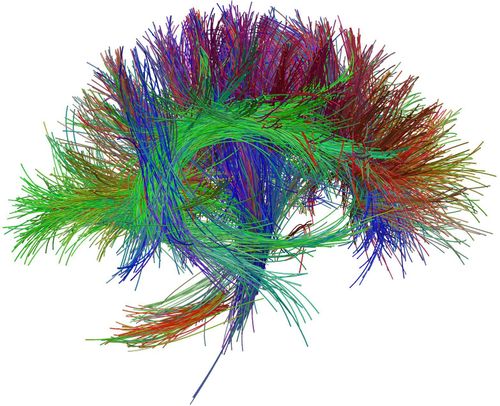
Chụp cộng hưởng từ bó sợi thần kinh (Hình ảnh minh họa)
Note, during magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles, it is necessary to monitor the patient's pulse, blood pressure and consciousness. After the procedure, ask the patient to stay for follow-up.
Thanks to the development of modern medicine, today, lesions and diseases related to nerve fibers and nerves are detected and diagnosed thanks to the technique of magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fiber bundles. However, in order to provide the best image for a suitable treatment regimen, patients should choose addresses with quality modern magnetic resonance imaging machines.
To meet the needs of examination, imaging and treatment of diseases related to the nervous system as well as many other diseases, Vinmec International General Hospital has brought modern equipment such as: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scan, X-ray, .. in medical examination and treatment, diagnostic imaging, including neurological-related diseases. Therefore, the diagnostic imaging results bring true and clear images for effective medical examination and treatment.
For detailed advice on magnetic resonance imaging techniques, please come directly to Vinmec medical system or book online HERE.