This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Resident Doctor, Master Dang Thi Ngoan - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalPremature birth is one of the pregnancy complications that greatly affects newborns, especially those born extremely prematurely. The development of extremely preterm infants at 26 weeks gestation is quite conservative, depending on the health care capacity of each country and many other factors.
However, there are still many positive advances in the treatment and care of infants born 26 weeks premature to improve the quality of life for children later in life.
1. What is extreme preterm birth?
A normal pregnancy lasts about 40 to 42 weeks. Pregnancy for any reason that ends and gives birth to a baby before 28 weeks of gestation are called extremely preterm. The prognosis for survival decreases with the smaller the gestational age.
Babies born before 28 weeks are called extremely preterm Babies born between 28 and 32 weeks are called very preterm Babies born between 32 and 33 weeks and 6 days are called preterm moderate And babies born between 34 weeks and 36 weeks and 6 days are called late preterm The prognosis for very preterm babies is very conservative. Timing of the premature birth is an important factor in treatment and intervention. The more premature a baby is born, the more likely it is to have severe and serious complications. Each extended week of pregnancy makes a very significant difference in survival rates.
Doctors do not always know the cause of extremely preterm birth and prevent complications of preterm birth. Furthermore, studies on the survival rate of premature infants are still limited.
The results of studies vary widely depending on the country, factors related to the child's race, birth weight. However, survival rates for extremely preterm infants and preterm infants with neurodevelopmental complications have improved significantly since 2000.
Tiên lượng cho những trẻ sinh cực non là rất dè dặt
2. Development of 26 weeks premature baby
2.1. Chances of Survival of a 26 Week Premature Baby
A baby born between 20 and 26 weeks is considered viable, or is born during the window period where the fetus begins to have a chance of survival outside ectopic. However, the chance of survival is not much, experts at the University of Utah Health say, a baby born before 24 weeks has less than 50% chance of survival.
However, according to this 2016 analysis of more than 8,300 births in the United States, babies born at 24 weeks have a 68% chance of survival. A 2016 cohort study of more than 6,000 births found a survival rate of 60%. (Utah Health records a 60 to 70 percent survival rate for this gestational age.)
Extremely premature babies can face a number of timelines and sometimes families have to make tough choices. . Fortunately, advances in medicine mean that even the smallest babies can get bigger and stronger in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
The Irish Neonatal Health Alliance says about 40% of babies born at 26 weeks will have health problems. Some of these complications may be immediate, or others may appear later in life.
If babies are born at 26 weeks, they are still considered “extremely preterm”. But a lot can be improved for a developing fetus within just a few weeks of gestation, increasing the chances of survival.
Babies born at 26 weeks were found to have a survival rate of 89% in the 2016 analysis and 86% in the 2016 cohort.
A large difference contributes to the increased survival at 26 weeks versus 24 weeks is the baby's lung development. At around 26 weeks of gestation, the lower part of your baby's lungs have grown and developed tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Your baby is still too premature to breathe on his own, but his lungs will develop and get stronger. Babies will still have to stay in an incubator to warm up with a breathing tube to help them increase the amount of oxygen that provides life.
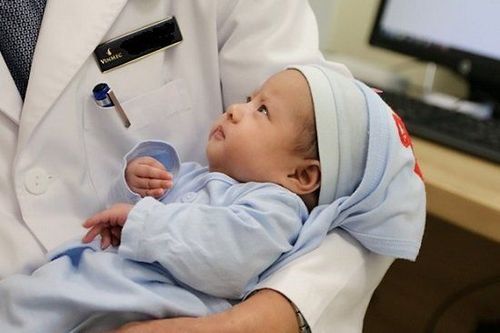
Trẻ sinh ra ở tuần 26 được phát hiện có tỷ lệ sống sót là 89% trong phân tích năm 2016
2.2. Characteristics of premature babies born at 26 weeks
At 26 weeks of pregnancy, the baby is about 35cm long and weighs about 760 grams. But premature babies are often small for their age. A baby born at 26 weeks can fit in the palm of a father's hand. At this age, a premature baby's main job is to develop physically, sleep, and become medically stable to the environment outside the uterus.
Sometimes babies can open their eyes but can't focus. Light or other visual stimuli can put stress on a child's body systems. Doctors will usually cover a baby's incubator, and some neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) dim the lights at night.
Baby's movements are usually jerky, convulsive or startling. Children's bodies do not have many toned muscles and cannot curl. The health care workers will place the baby in a curled position, support the baby's body with pillows and keep the baby warm. This helps children retain their energy.
Premature babies often have breathing problems because their respiratory organs are not fully mature at this time, so babies can also stop breathing. This often happens to premature babies. Breathing is controlled by a part of the brain that is not fully developed, so pauses between breaths are common.
Your baby's auditory and ear structures are fully formed, but he may be very sensitive to outside sounds. Your baby may notice your voice, but he still can't respond to you. Babies cannot breastfeed.
Baby's skin is delicate and sensitive. The nurses will probably encourage you to 'hold' the baby to increase comfort, but not to stroke the baby.
3. What complications can a 26-week-old premature baby get?
About 20% of babies born at 26 weeks may still have some health problems as they grow up. These can include problems with vision, hearing, learning, cognition, behavior, or social skills. Babies born at 26 weeks can also develop heart problems.
3.1. Skin and body heat retention
Premature babies will need to enter an incubator (like a mobile uterus) immediately to keep them warm. These extremely premature babies haven't had a chance to develop brown fat - the fat located just below the skin that helps increase the baby's ability to retain heat. The baby's skin at this time will also be extremely thin and vulnerable.
3.2. Breathing problems
Your baby's lower lungs and airways are only beginning to develop around 24 weeks. For a 26-week-old baby, the lower lung has developed more but is still not completely complete. So this increases the chances of survival for babies born at 26 weeks compared with babies born prematurely at 24 weeks. However, babies born at this time will need help breathing.
3.3. Vision problems
Around the 26th week in the womb, the baby's eyes are still closed. Their eyelids and eyes haven't developed enough to open them yet. Your baby will need to have cotton or soft gauze placed over their eyes to protect them from light and help their vision continue to develop.
In some cases, a child's eyes may not develop as they should, which can lead to vision problems or even blindness later in life.
Besides, in some cases, children need high-dose oxygen intervention and may cause eye complications later on.
3.4. Hearing problems
A premature baby has fully formed ears. Your baby can start hearing outside sounds around 18 weeks. However, your baby's eardrums are still very fragile and sensitive at 26 weeks. Some babies born prematurely may have hearing problems or be deaf.
3.5. Other problems
Some babies born extremely prematurely may have problems affecting the brain and nervous system. Some of these are serious. Complications include cerebral palsy, learning problems, and behavioral problems.
Newborns, especially premature babies, are generally susceptible to respiratory diseases, respiratory infections and gastrointestinal infections if they start eating solids early or storing and preparing milk is not guaranteed. . To protect children's health, parents should do well to exclusively breastfeed their babies for the first 6 months (if possible) and vaccinate on schedule. As soon as a child shows symptoms such as anorexia, fatigue, and crying, the child needs to go to the hospital to be consulted by a specialist for monitoring and treatment.
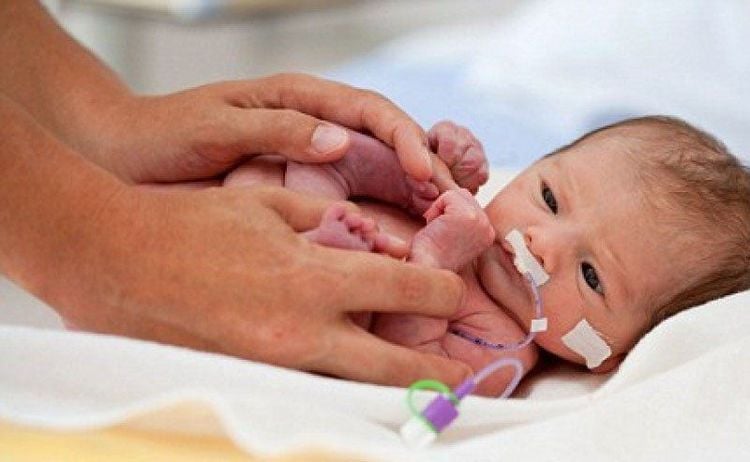
Đối với trẻ sinh non 26 tuần, phần phổi dưới đã có sự phát triển hơn nhưng vẫn chưa thật sự hoàn chỉnh
Newborns, especially premature babies, are generally susceptible to respiratory diseases, respiratory infections and gastrointestinal infections if they start eating solids early or storing and preparing milk is not guaranteed. . To protect children's health, parents should do well to exclusively breastfeed their babies for the first 6 months (if possible) and vaccinate on schedule. As soon as a child shows symptoms such as anorexia, fatigue, and crying, the child needs to go to the hospital to be consulted by a specialist for monitoring and treatment.
To prevent diseases that babies often get, parents should pay attention to nutrition to improve children's resistance. At the same time, add supporting foods containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins,... snacks and less digestive problems.
Parents can learn more:
Why do you need to supplement Lysine for your baby?
The role of zinc - Guidelines for reasonable zinc supplementation
Please visit the website Vinmec.com regularly and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.
References: raisingchildren.net.au, verywellfamily.com