This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Le Thai Bao - Intensive Care Unit - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
1. Definition
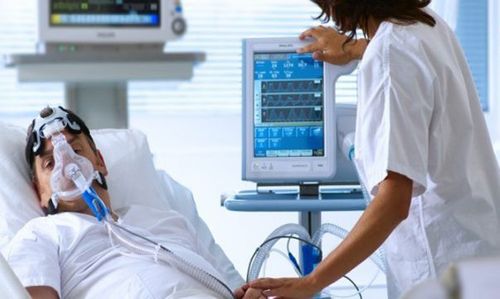
After the patient is removed from the ventilator but the endotracheal tube cannot be extubated, the operator will let the patient breathe in a T-tube. The T-tube can breathe through a tracheostomy tube or through an endotracheal tube.
2. Indication of self-breathing technique with T tube
The patient is able to remove the ventilator, but the endotracheal tube cannot be extubated
3. Contraindications

Patient stops breathing, stops heart Patient is unable to breathe on their own (eg, severe neuromuscular disease...)
4. Technical process of self-breathing with T tube
4.1 Preparation Performer: 01 doctor and 01 nurse specializing in emergency resuscitation or trained in mechanical ventilation.
Consumables:
Oxygen Surgical cap: 03 pcs Surgical mask: 03 pcs Savondoux hand soap Serum line: 01 pcs Sterile gloves: 03 pairs Clean gloves: 05 pairs N2 minor surgical gauze : 05 bags First aid kit:
Ventilator Intubation set or tracheostomy changer Other expenses:
Consumption of electricity, water Fees for steaming, washing tools Treatment of medical waste and biological waste Active Patient:
Explain to Patient (if patient is conscious) and Patient's family/legal representative of the need and risks of mechanical ventilation. Patient/Patient's representative signs a commitment to perform the technique. Patient position: The patient lies with the head elevated 30 degrees (if there is no drop in blood pressure), the head is flat if the blood pressure is low Ventilation at the hospital bed Medical record:
Explain the technique to the patient and family the patient and sign the agreement to agree to the technique, the record of the procedure monitoring.
4.2 Procedure Steps Checking the record: Re-checking indications, contraindications and consent to participate in the technique Re-checking the patient: Vital functions, see if the procedure can be carried out . Perform the technique:
Fully record the parameters of the ventilator mode being performed before switching to T-tube ventilation.
Conduct T-tube ventilation:
T-tube (T tube) Prepare the tube T-shaped, oxygen cord, oxygen humidifier Connecting for patients to breathe T-tube, oxygen 3-4 liters/min T-tube care:
Change the tracheostomy, endotracheal tube, and sputum daily 3. every hour, more times depending on the patient's condition If the patient breathes through a T-tube through a tracheostomy: Replace the tracheostomy tube every 2 weeks or when there is obstruction. Patients with long-term T-tube breathing through an endotracheal tube should consider tracheostomy
5. Technical follow-up
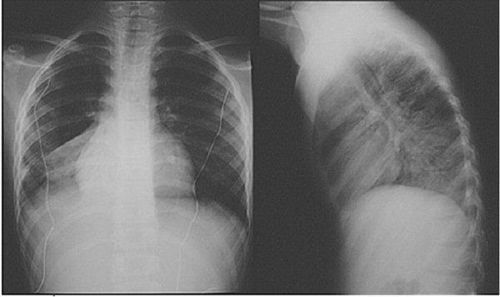
Pulse, blood pressure, electrocardiogram (on monitor), SpO2: Regularly Patient's consciousness compared to before T-tube breathing Blood gas test: Do it after 1 hour, give emergency care when there is any abnormality Usually Measure NIF, Vt daily Chest X-ray: Take emergency scan when there is abnormal development.
6. Complications and treatment
Consciousness: It is necessary to monitor consciousness to see if the patient is awake (coma: Causes of respiratory acidosis, worsening respiratory failure...), if the patient is comatose, check the blood gas again for acid resuscitated and resuscitated the ventilator. Monitor sputum: If the patient has sputum, aspirate the sputum. Obstruction of tracheostomy or endotracheal tube instead of cannula or endotracheal tube. Breathing rate: If the breathing rate is > 30 times/minute, (with the exception of causes such as sputum obstruction, bronchospasm ...) re-breathe the mode of breathing before weaning from mechanical ventilation. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
Artificial ventilation (ventilator): What you need to know 2 commonly used methods of artificial ventilation Complications and care for ventilator patients