This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Atopic dermatitis is a common skin disease, not life-threatening, severe cases of infection lead to skin infections, leaving scars that cause cosmetic loss. Therefore, early recognition of the symptoms of atopic dermatitis will help improve the effectiveness of treatment and prevention of the disease.
1. What is atopic dermatitis?
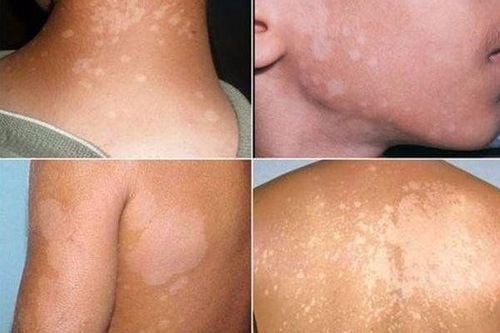
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease that causes dry skin, intense itching, and a red rash. In more severe cases, in addition to the red macules on the skin, there may be blisters, oozing fluid.Atopic dermatitis lasts long (chronic) and tends to flare up in waves when there are favorable conditions such as dry climate, patients often have to be exposed to chemicals, soaps... The disease may be accompanied by asthma or urticaria or allergic rhinitis. Atopic dermatitis is common in infants and young children, although adults can also develop atopic dermatitis.
2. Causes of atopic dermatitis
The cause of atopic dermatitis is not clearly defined, but atopic dermatitis may be the result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors. If one of the family members, such as a parent or sibling, has atopic dermatitis, it is more likely that other family members may also have it.Many factors can trigger or aggravate atopic dermatitis, including low humidity, seasonal allergies, exposure to soaps and detergents, and cold weather onset. In fact, environmental factors can trigger atopic dermatitis symptoms at any time, living in a cold or polluted place can also increase the risk of atopic dermatitis. response. In addition, people living in urban areas and climates with low humidity are also at risk of atopic dermatitis.
One point to emphasize is that food does not cause atopic dermatitis. However, people with atopic dermatitis may be at risk for food allergies. In addition, atopic dermatitis is not contagious, so it is not transmitted between people who have contact with each other.
Emotional factors and stress can sometimes aggravate the condition, but are not the main cause associated with atopic dermatitis.

3. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary widely from person to person, with the most common being dry, itchy, and red skin. Specifically:Dry skin Itching is a hallmark sign of the disease, which can be severe, especially at night. Extreme itching in the skin causes the person to scratch, which in turn makes the itching worse. Red to gray-brown patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, elbows and knees, face, and scalp in infants. Blisters can leak yellow fluid when scratched Thick, cracked, scaly skin. Sensitive skin, may swell.
4. Stages of atopic dermatitis
4.1. In infants Atopic dermatitis in infants usually begins around 6 to 12 weeks of age. It may first appear around the cheeks and chin as a patchy facial rash that can progress to red, scaly, watery skin. Your baby's skin can become infected. As infants become more flexible and begin to crawl, exposed areas such as knees and elbows may also be affected. An infant with atopic dermatitis may be restless and irritable because of the itching. This condition improves by the time the child is 18 months old, although the disease can still recur but is usually milder.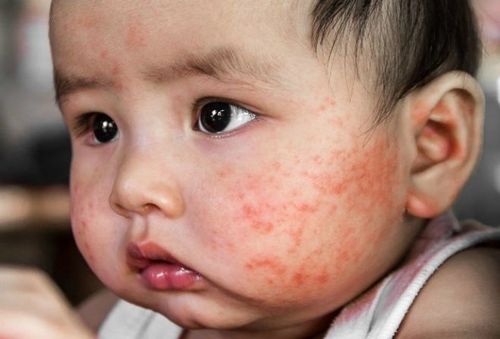
5. Prevention of atopic dermatitis
Patients with atopic dermatitis should limit exposure to environmental factors and chemicals that directly harm the skin.Irritants such as: Soaps, detergents, chemicals... can cause inflammation. Some perfumes and cosmetics can irritate the skin. Chlorine and alcohol solvents, dust mites or sand can also aggravate the condition. Tobacco smoke, animal dander or flower dander and pollen.

6. When to see a doctor?
When you have the following signs of atopic dermatitis, you should see a doctor:Symptoms of atopic dermatitis cause discomfort, affecting sleep and daily activities. Skin infections – red streaks, pus, and yellow flakes Continue to experience symptoms despite trying some home remedies. Rash, infection and fever.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com; medicinenet.com; dermnetnz.org