This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Tran Hong Nhat - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Coarctation of the aorta is a birth defect that, if left untreated, can lead to many life-threatening complications.
1. Overview of coarctation of the aorta
Coarctation of the aorta is a fairly common congenital heart disease, with an incidence of about 8% and is often associated with other complex congenital heart diseases, especially common in Turner syndrome and Noonan syndrome.Signs of coarctation of the aorta:
Very high blood pressure accompanied by an abnormal difference in blood pressure between the upper and lower extremities. The inguinal pulse is weak and may not be detected in severe cases. On auscultation, a systolic murmur was heard in the left subclavian region. Coarctation of the aorta should be detected and treated early because it can lead to life-threatening complications, such as:
Thoracic aortic dissection Hypertension Hypertension
Chest X-ray: With specific images of 3-arc signs in the aorta. However, it is also normal to not see any symptoms. Electrocardiogram: The electrocardiogram showed signs of increased left ventricular load. Doppler echocardiography: helps diagnose coarctation of the aorta with increased blood flow through the stenosis, but is often useful in young children, and is more difficult to assess in adults. CT scan of the aorta: As a diagnostic tool. On radiographs, the location, stenosis morphology, collateral circulation and other associated lesions were identified.
2. Surgical method for coarctation of the aorta
2.1. Surgery is indicated when: The patient has been diagnosed with coarctation of the aorta with a pressure gradient of 20-30 mmHg or more. Accompanied by one or more symptoms: Upper extremity hypertension difficult to control with medical treatment, congestive heart failure, left ventricular hypertrophy... 2.2. Contraindications: Surgery has no absolute contraindications, there are some relative contraindications such as:
Fixed pulmonary hypertension Severe heart failure, severe renal and hepatic dysfunction Other complex congenital heart disease Complications Active infection Chest deformity, left pleural thickening due to trauma or disease.
Executor: Team of medical and surgical specialists, anesthesiologists and resuscitators. The patient is fully explained about the surgical method and the risks that may be encountered after surgery. The previous afternoon was washed twice with water mixed with betadine, changed all clean clothes. Brush your breasts with soap containing betadine before applying an antiseptic solution to the surgical area. Performing surgery:
The patient is lying on the 90 degree side Anesthesia endotracheal ventilation 1 lung Using a double-barreled endotracheal tube, collapse the left lung. Technique If necessary, perform axillary-femoral bridge by artificial pulse. Open left posterior thoracic cavity, in 3rd - 4th intercostal space. Open pleural space exposes the entire area of coarctal stenosis up to the origin of the aspiration. subclavian pulse. Clamp the aorta above and below the isthmus. Surgical treatment of coarctation of the aorta using one of the following techniques: End-to-end anastomosis, patching, widening the aorta, replacing the aortic segment with an artificial vessel, using an inferior artery flap left blow to remove the lesion of isthmus, restore aortic circulation. Then stop the bleeding, close the pleura, install the pleural drainage system. Close the chest according to anatomy.
3.Monitor and handle complications after surgery
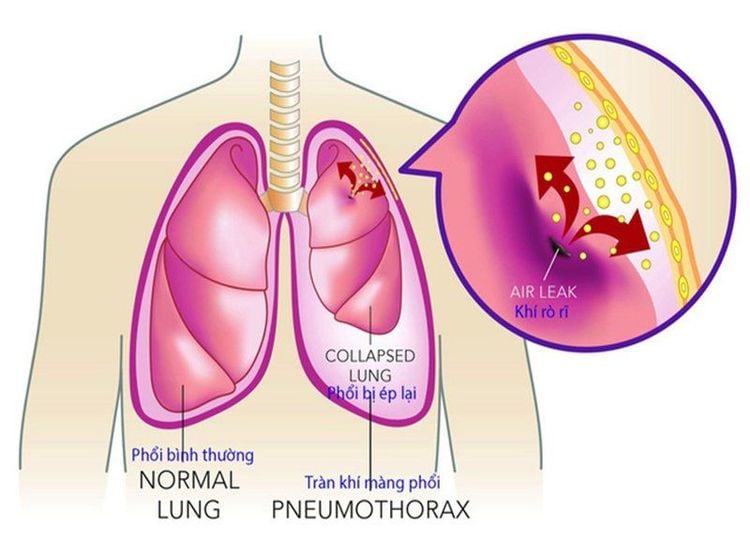
Complications and treatment of complications after surgery:
Hemorrhage, pneumothorax: Depending on the severity, the choice of medical treatment, pleural drainage or severe need to re-operate. Atelectasis: Use physical therapy, bronchoscopy to aspirate sputum, if not, re-operate. Heart failure: Treat with heart medications. Post-operative infection: Find the bacterial cause of the infection, treat with antibiotics according to the results of the antibiogram. Residual stenosis: Medical treatment and monitoring, dilation, or reoperation if superficial is not effective. Nerve damage: Medical treatment and monitoring of injuries Post-operative monitoring
Monitor vital signs Take chest x-ray immediately after the patient returns to the recovery room. Monitoring complications of hemothorax, pneumothorax, incision monitoring, drainage Echocardiography re-evaluate before discharge and routine monitoring To protect cardiovascular health in general and detect early signs of heart attack and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital. The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.