This is an automatically translated article.
Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine is an infection of the lumbar spine caused by tuberculosis bacteria. Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine causes destruction of vertebrae and discs, deforming the lumbar spine, abscesses and spinal cord compression. Tuberculosis complications of the lumbar spine can lead to abscesses or paralysis of the lower extremities, sometimes requiring surgery to decompress the spinal cord.
1. What is spinal tuberculosis?
In extrapulmonary tuberculosis diseases such as meningitis, peritoneal tuberculosis, and renal tuberculosis, tuberculosis of the musculoskeletal system accounts for about 20% of cases. Tuberculosis of the spine, also known as tuberculous spondylolisthesis, is an extrapulmonary tuberculosis disease, the most common in the musculoskeletal group. In Vietnam, tuberculosis of the spine accounts for about 65% of cases of tuberculosis of the musculoskeletal system.
Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine is an inflammation of the vertebrae and discs in the lumbar region caused by tuberculosis bacteria. Most tuberculosis of the spine is a secondary lesion, most often after pulmonary tuberculosis. TB bacteria, after passing through the lungs or gastrointestinal system, will follow the blood or lymphatic route to stay in a part of the musculoskeletal system. Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine is caused by localized TB bacteria causing bone destruction in the lumbar spine from L1 to L5, which may be alone or in association with TB of the thoracic spine. The disease can occur at any age, but occurs most often between the ages of 21 and 30 and 41 to 50 years old.
2. Symptoms of tuberculosis of the spine
Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine is a chronic disease, symptoms appear very late and the destruction of the lumbar vertebral body occurs silently. Specifically:
Tuberculosis of the spine also has symptoms of TB infection similar to pulmonary tuberculosis such as mild fever in the afternoon, loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss,... The main functional symptom of lumbar spine TB is pain. . At first, the pain was dull in the lower back, increasing in the evening and when moving, such as standing or walking. Tuberculosis pain in the lumbar spine is increasing in intensity and can be more intense than sciatica if the lumbar spine is severely damaged. Pseudo-sciatica is a symptom of lumbar spinal tuberculosis compressing nerve roots, causing muscle twitching in one or both legs and pain spreading according to the nerve distribution. The lumbar spine is stiff and does not stretch when bending down, as well as limiting the flexion, extension and rotation movements due to the muscles on both sides of the back spine being stiff. If tapping on the posterior spine of the dorsal tuberculous lesion, the patient may experience sharp pain.

Lao cột sống lưng có triệu chứng nhiễm lao như sốt nhẹ về chiều
3. Complications of tuberculosis of the spine
Many complications of spinal tuberculosis can occur as a result of destructive damage to the vertebral body, discs and nerve compression.
Leg atrophy is a common complication in tuberculosis of the lumbar spine. Shrinkage of one or both legs, especially the calves or anterior lateral legs, due to nerve root compression. Symptoms of atrophy and paralysis of both legs. Dystrophy of skin, hair, and nails in the legs when there is nerve root compression. The cauda equina syndrome is caused by damage to the lower lumbar segment. The severity of symptoms varies from sensory disturbances and decreased muscle strength to severe sphincter disturbances and spastic paralysis. A lumbar spine abscess is a bulge on the right or left side of the lower abdomen. If the abscess is large, it will pass through the inguinal ligament down the thigh, sometimes down to the hamstring. Tuberculous abscess can be large and spread to the outside of the thigh or to the back of the buttocks, the triangle area above the posterior iliac crest, down to the sitting area, ... The subcutaneous abscess is too large and can burst, drain pus or create a very pus leak. hard to heal. Motor paralysis of the lower extremities due to spinal cord compression usually appears more slowly, this is the most severe complication of spinal tuberculosis that can lead to death.
4. Imaging diagnosis of tuberculosis of the spine
Indications for X-ray of the lumbar spine to detect tuberculosis of the spine when the disease has progressed for a long time for several months, the damage is too severe. Signs include:
Having a narrow disc compared with other segments. The body of the lumbar vertebrae is irregular, blurred on the upper and anterior part, creating a wedge-shaped lesion. Soft tissue around the lumbar vertebrae is darker, heterogeneous, with calcifications, which is the image of an abscess. Computed tomography (CT) helps to better visualize the destruction of the vertebral body and to plan the fusion surgery.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine helps to diagnose tuberculosis of the spine at the earliest within the first month after the onset of the disease.
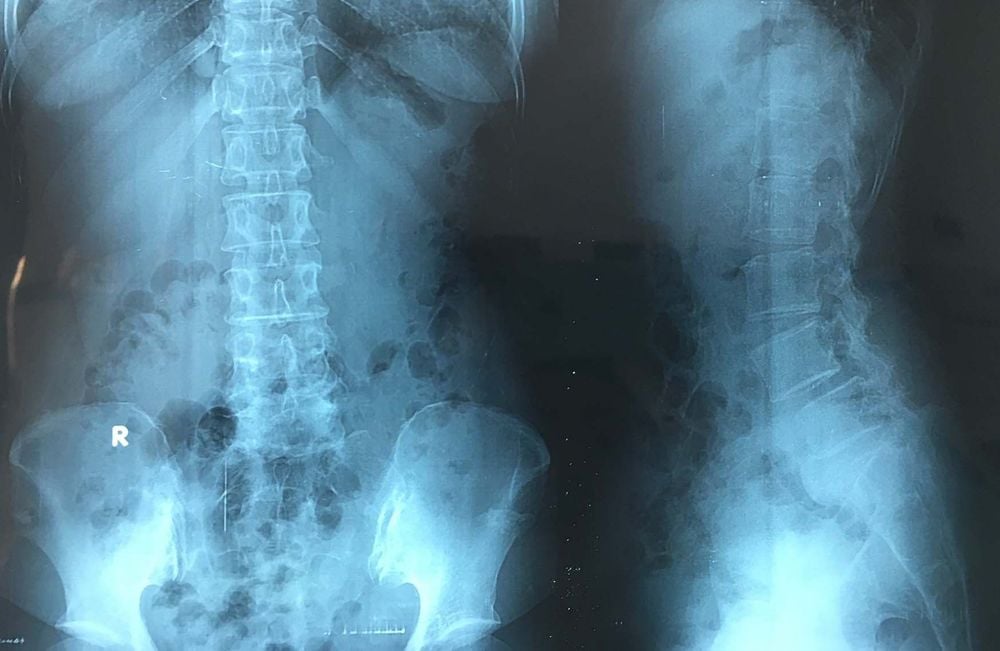
Chỉ định chụp X – quang cột sống thắt lưng phát hiện lao cột sống lưng
5. Treatment of tuberculosis of the spine
Previously, in Vietnam tuberculosis of the spine was a treatment challenge. Currently, with the development of medicine, we have found a cure for spinal tuberculosis in most cases if it is detected early when there are no serious complications. The treatment methods are as follows:
5.1. Internally medical treatment
Use anti-tuberculosis drugs according to the correct regimen (oral or injection). Patients need to drink continuously for a period of time, not arbitrarily stop taking the drug. A combination of pain relievers can be used to control pain. Rehabilitation: rest in hard bed for about 4 to 5 weeks, avoid lifting heavy objects, avoid rapid and sudden changes in position.
5.2. Surgical treatment
Surgery to decompress spinal cord in tuberculosis of the spine needs to be performed promptly. Indications of surgery are tuberculosis lesions of the lumbar spine with spinal cord compression (by large abscesses, dead bones, ...) causing complete or incomplete paralysis of the lower extremities.
Decompression surgery in tuberculosis of the lumbar spine is applied to patients with no severe bone destruction, no kyphosis and no spinal instability.
Surgery to decompress the spinal cord in tuberculosis of the lumbar spine needs to be combined with medical treatment measures, especially taking full anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine is an infection of the lumbar spine caused by tuberculosis bacteria. Tuberculosis of the lumbar spine causes destruction of vertebrae and discs, deforming the lumbar spine, abscesses and spinal cord compression. Therefore, the disease needs to be detected, examined and treated promptly to avoid dangerous complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used modern facilities and equipment along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of experts. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.