This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Senior Doctor, Dr. Vu Van Tam - Infectious Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalStrongyloides are the most dangerous of all gastrointestinal parasites. They can persist for a long time in the body and can cause many dangerous, even life-threatening complications. Understanding the disease is the best way for us to effectively identify and prevent strongyloidiasis.
1. What is strongyloidiasis?
Strongyloidiasis is caused by strongyloidiasis larvae entering the body by entering the body through the skin, following the venous route running up the heart, through the lungs, to the trachea, pharynx, then down the esophagus and intestines to grow into adult worms.
Strongyloidiasis is classified as the most dangerous parasite among gastrointestinal parasites because it can survive for a long time in the human body and cause many dangerous complications, even death. The number of people infected with strongyloidiasis in Vietnam is quite high, accounting for 1-2% of the total population, the disease also has a higher rate of re-infection than other diseases.
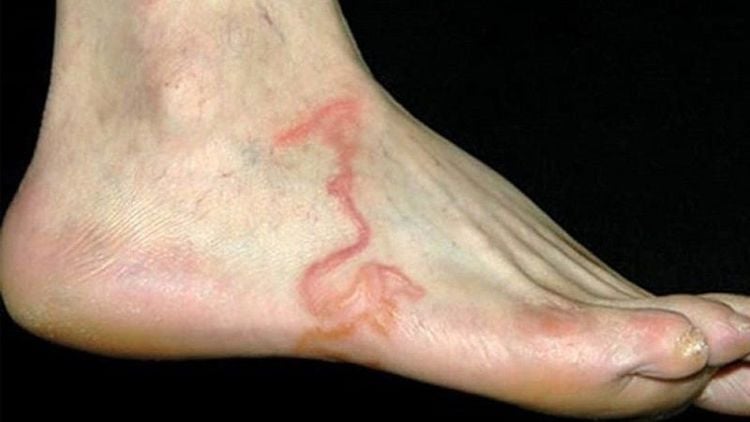
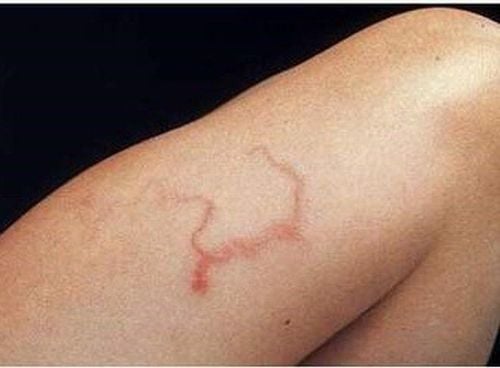
Giun lươn xuất hiện dưới da
2. Causes of strongyloidiasis
Adult strongyloides usually live in the lining of the small intestine and lay eggs here, they can live in the external environment. Strongyloides eggs develop into free-form worms and they are excreted in the feces. When strongyloidiasis eggs are released into the environment, some larvae continue to develop into adult worms and lay eggs in the soil. These larvae can continue to invade the body and parasitize the patient's body.
Strongyloides have horizontal, shallow shells, and two lips in their mouths. Adult female strongyloides have an elongated head and a pointed tail, gium size is about 2mm x 34mm. Male strongyloides are about 0.7 mm x 36 mm, with a hook-shaped tail and two genital spines.
Strongyloides eggs have an oval shape, the size ranges from 50 - 58 μm x 30 -34 μm.
Strongyloidiasis larvae develop very quickly to become larvae with a cylindrical esophagus in the eggs, and they self-extrude right in the small intestine, going out in the feces, so when doing stool testing, it is very rare to see worm eggs. eel in feces. Except, in case the patient has a lot of diarrhea, the eggs of strongyloidiasis can be seen.
When the larvae escape into the environment, they continue to develop into larvae with a cylindrical esophagus, capable of entering the human body through the skin or they live freely outside of the environment. In particular, the hot and humid external environment is suitable for strongyloidiasis larvae to develop, but they can also develop in temperate or cold climates.
3. Symptoms of strongyloidiasis
People with strongyloidiasis do not have typical clinical symptoms, however, some of the following symptoms may be signs of strongyloidiasis.
Epigastric abdominal pain Diarrhea Local skin inflammation when larvae enter the body Blood tests show mild anemia An asthma attack in a person with atopic allergies Ectopic strongyloides can be parasitic in the esophagus, In addition to the above signs, when testing stool by Kato or Kato-Katz technique, results in stools with strongyloidiasis larvae will be available immediately after taking stool for testing.

Người mắc bệnh giun lươn không có những triệu chứng lâm sàng điển hình
4. Incubation period
Reservoir: The human body is the main reservoir for strongyloides stercoralis. Strongyloides can also live in a number of other animals such as dogs, monkeys, apes. Incubation period: Within 2-4 weeks is the time from when larvae penetrate through the skin to develop into adult strongyloides and lay eggs. The eggs then develop into larvae and live outside of the environment. Transmission period: It is the life time of adult female worms from the time they are fertilized and laid eggs. The transmission period of strongyloidiasis can be up to 35 years in the case of self-infection.
5. How to prevent strongyloidiasis
Treatment of strongyloides will take a lot of time and money, so prevention is better than cure. Each person should pay attention to the following issues to limit infection, re-infection and disease transmission in the community:
Hygiene and prevention: good management of feces, water and garbage in the living environment. Sanitize the environment near the house, in the house and the children's play areas. Personal hygiene: Build a civilized lifestyle, always wash your hands before eating, when preparing food, after going to the toilet, do not eat raw vegetables that have not been washed. Periodically 2 times / year need to be dewormed, each time 4-6 months apart. Make sure to always use labor protection while working in contact with soil, especially in areas contaminated with human feces. Strengthen the body's resistance by adding fresh, clean vegetables, exercising daily, and helping to avoid immunodeficiency, avoiding outbreaks. Raise people's awareness in cleaning the community, building sewer systems and treating wastewater up to standards.

Luôn rửa tay trước khi ăn, khi chuẩn bị thức ăn, sau khi đi vệ sinh
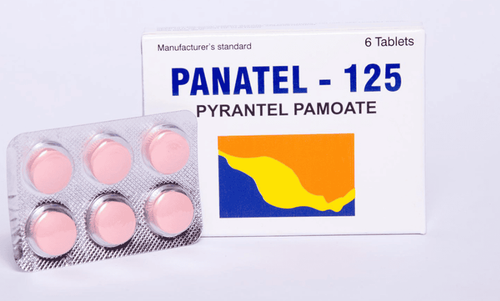
6. Treatment of strongyloidiasis
Drugs to treat strongyloidiasis are often preferred to choose the type that works with many types of worms, is less toxic and uses a high effective dose. In which, the drugs are mainly used such as Ivermectin, Albendazole. However, these drugs need to be carefully controlled by a doctor, treating each patient differently. For people with liver failure, kidney failure, care should be taken when treating strongyloidiasis.
Above is the knowledge about the causes, symptoms and prevention of strongyloidiasis. In case of suspected signs of strongyloidiasis, it is necessary to quickly go to medical facilities so that tests can be performed to determine the disease, prompt treatment and prevent serious complications from occurring.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Department of Preventive Medicine (Ministry of Health)