This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
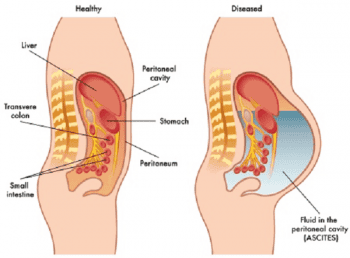
Normally, there is no water in the abdominal cavity between the parietal and visceral leaves of the peritoneum. For some reason, there is water in the abdomen, causing ascites. Through examination, doctors can diagnose diseases related to ascites.
1. Clinical examination of ascites syndrome
Clinically, when examining ascites to make a conclusion, it should be based on the following symptoms:
1.1 Look
Skin look:
Abdominal skin is glossy or slightly swollen, navel is convex. Depending on the type of cause, there may be collateral circulation: The veins under the skin of the abdomen are enlarged, tight, and tortuous. The abdomen stretches out to the sides when lying down. The abdomen sags forward and down when standing or sitting. Abdominal morphology: If the water is too tight, it can bulge through weak abdominal muscles, forming pockets of water just below the skin (stomach).
1.2 Touch
Touching with two hands will see the abdomen stretch if the amount of water is large. Look for waves crashing to determine the amount of water in the abdomen.
A hand is placed in the center of the abdomen (hands of the assistant or the patient's hand). A doctor's hand is placed on a patient's flank disease. The other side of the doctor patted the other side of the patient's ribs. If there is water in the abdomen, the hand placed will feel like waves bouncing back after each stroke of the other hand. Waves are present only when the amount of water in the abdomen is high or moderate, and is free.
When there is water in the abdomen, but a solid organ in the abdomen enlarges (spleen), if we lightly press on that organ, it will sink deep and then slowly rise to touch the hand, feeling like a stone floating in the air. a cup of water.
MORE: Diet for people with cirrhosis and ascites
1.3 Typing
Typing is the surest method of identifying ascites. The patient lies on his back, the doctor knocks from the navel area around in the shape of a spoke, if there is ascites, we can see it in the upper part and opaque on the sides in the lower area. The limit of the opaque area is a curved, concave face facing upwards. Depending on the amount of water more or less, the limit of the turbidity area is wide or narrow.
2. Types of Ascites
2.1 Global ascites with little water
Diagnosis is more difficult than multi-water type. Through looking or touching to find signs of breaking waves, it is difficult to detect. The definitive diagnosis here is mainly by percussion combined with vaginal and rectal examination and especially ascites with water aspirated. In difficult-to-identify cases, aspiration laparotomy can be used to make the diagnosis.
2.2 Localized ascites
Due to the peritoneal adhesions in many places, the water is localized in one area but does not spread to the whole abdomen. Percussion, the abdominal cavity is opaque, the inner places are alternating. There are places where there is tension like water, hard places are slightly painful because of the adhesion of the peritoneum. Gently poking the suspected water areas may draw out the water.
3. Ascites Tests
After aspiration, we need to identify ascites, there will be the following types:
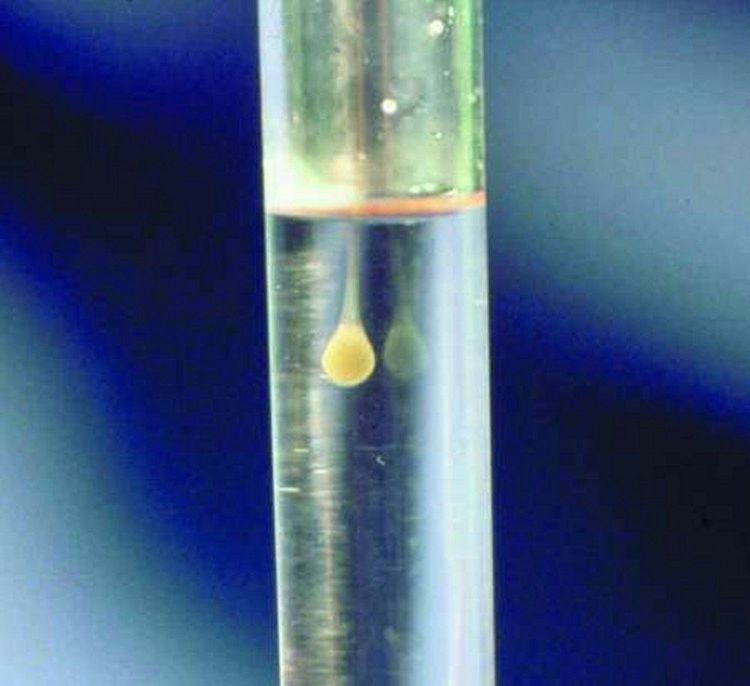
Clear, white or slightly yellow water: Usually low protein water, seen in kidney inflammation, heart failure causing so ascites. Lemon juice: Usually due to high protein content found in inflammatory or tumours. Bloody water: Blood here does not clot, often due to tumor or inflammatory causes Cloudy water like pus: Due to purulent inflammation in the abdomen, rare. Turbid water like rice water (cultivation): Very rare. Do the Rivalta test:
The purpose of this test is to assess the amount of protein in the ascites, thus determining the cause. Procedure: Use a beaker to add 100ml of distilled water, add 4 drops of acetic acid, and then gradually add ascites drop by drop. Positive reaction: The small amount of ascites will gradually become cloudy white suspended in the glass of water like cigarette smoke. Thus, the protein in the ascites is high > 30g/liter and the cause of ascites is usually inflammation or tumor. We call it inflammatory ooze. Negative reaction: Clear ascites, no cloudy white phenomenon. The amount of protein here is low < 30g / liter and is caused by water from blood vessels or intercellular spaces seeping into the abdomen. We call it permeation. MORE: Is cirrhosis of the liver ascites contagious?

Other tests:
Protein quantification. Find bacteria (microscopic and culture). Find cells: Red blood cells, white blood cells, cancer cells. Determination and quantification of mortgages. Look for other chemical components like urea. Based on the physical examination and test results will help the doctor accurately diagnose the disease causing ascites. Thereby, there is a timely treatment plan for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.