This is an automatically translated article.
Community transmission is when there is no clear source of infection in a new community. It occurs when health officials are no longer able to identify an infected person after coming into contact with someone who has had contact with people from the original infected communities.
For example, community transmission is widespread in the United States, which means that cases occur in people who do not have any contact with others from hot areas of known outbreaks such as Florida, Arizona or even Brazil
1. Massive community transmission means loss of control
Community transmission is infection acquired in the community. Contrast with nosocomial infection (i.e. nosocomial infection). Imported cases are relatively easy to control through early detection, testing, testing and isolation. In contrast, community transmission signals a loss of viral control to varying degrees.
When community transmission occurs, it is necessary to act very quickly to partially slow down the transmission of the virus, combined with other measures such as "tracing", large-scale testing, isolation social,... Measures should be taken quickly and promptly.
In February, the World Health Organization released a document to guide countries on managing and responding to widespread community transmission of coronavirus.
In the document, WHO suggests that once community transmission occurs on a large scale, efforts to detect and track individual cases are no longer prioritized. Instead, resources should focus on tracking the spread and character of the virus, identifying and managing severe cases, preventing transmission of the virus, informing the community, and reducing the impact of the virus. impact on the economy and society in general.
Once community transmission has occurred on a large scale, control will become very difficult, and the economic, health and human impacts can plunge the country into a full-blown crisis .
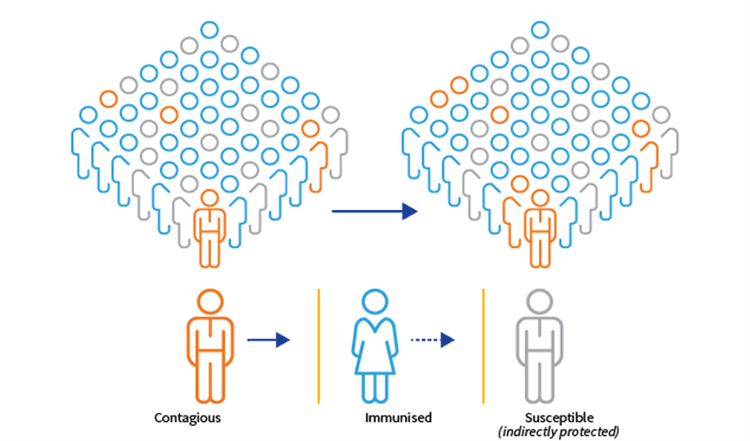
Ciệc lây nhiễm cộng đồng xảy ra ở quy mô lớn, các nỗ lực nhằm phát hiện và theo dõi các trường hợp riêng lẻ không còn được ưu tiên
3. Measures for tracing (tracing)
Traceability is a measure used by health departments to prevent the spread of infectious disease. This is a measure to identify cases of the disease and then trace back those who have been in close contact with them in a certain period of time. From there, the request for mandatory isolation or the request for voluntary isolation at home will be conducted.
This process typically includes:
Interviewing people with COVID-19 to identify all those with whom they have been in close contact during which time they may have spread the virus Inform close contacts of the risk Ask close contacts to get tested Monitor close contacts for signs and symptoms of COVID-19 Provide services that contacts may need while they are self-isolating To prevent the spread of COVID-19, close contacts are asked to stay home and maintain social distancing (at least 2 meters) from others for up to 14 days after their last contact with others. people with COVID-19. These close contacts should self-monitor by checking their temperature twice daily and continuously monitoring for symptoms of COVID-19.

Đeo khẩu trang khi ra ngoài để phòng dịch Covid-19
In the situation that the COVID-19 epidemic in Vietnam has occurred, community transmission has occurred, to prevent the COVID-19 epidemic, the most important thing is to stay at home, limit contact, practice wearing masks, washing hands when going out and Practice social distancing of at least 2 meters for everyone.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: webmd.com, abc.net.au, cdc.gov