This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
The etiology and pathogenesis of idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerosis are still unclear, available studies suggest that long-term intake of herbal medicines or medicinal tinctures containing the bactericidal geniposide is recognized as one of the main causes of spontaneous mesenteric atherosclerosis.
1. Research on the effect of geniposide on the colon
In an Asian study, the authors described 8 patients with mesenteric atherosclerosis who were chronically exposed to Chinese herbal medicines or medicinal tinctures. The mean age of the 8 participating patients was 75.7 years old and the male predominance (all 8 patients were male). The patients had a 5-40 year history of ingestion of Chinese herbal liquids containing geniposide and exhibited typical imaging features (eg, fibrous calcifications along the colonic and mesenteric vessels or interstitial junctions). associated with thickened colonic wall on CT images). The calcification was limited to the right mesenteric vein in 6 of 8 patients (75%) and involved the left mesenteric vein in 2 cases (25%) and the calcification extended to the mesentery. mesentery in 1 of them. Thickening of the colonic wall mainly occurs in the right and transverse colon. The mean patient CT score was 4.88 (n=7) and the mean alcohol consumption index was 5680 (n=7). After Spearman's correlation analysis, the mean CT score of the disease showed a significant positive correlation with the mean alcohol consumption index (r = 0.842, P < 0.05). The detailed formulation of all patients' herbal water prescriptions was studied, and the herbal ingredients were compared to identify toxic agents as a probable causative factor. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) imaging and colonoscopy were reviewed to determine the extent and severity of mesenteric atherosclerotic disease and the presence of inflammatory-associated findings. colon. The CT score of the disease is determined by the distribution of mesenteric vein calcification and colonic wall thickening on CT images. The drinking index of medicinal alcohol is calculated from the daily quantity and number of years of drinking of Chinese medicinal alcohol. Then, Spearman's correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the correlation between the alcohol intake index and the CT disease score. The authors concluded: Long-term intake of Chinese herbal liquid containing bactericidal agents may play a role in the pathogenesis of idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerosis.2. Assess the extent of the disease through the CT Scan scale
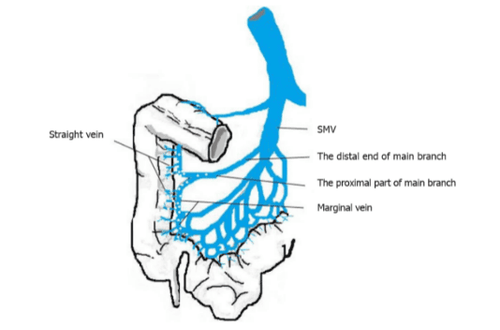
All patients have punctate or linear calcifications on CT images. The mesenteric vein calcification involved the ascending colon of all patients and extended to the transverse colon in 4 (Figures 1 and 2). In 2 of 8 patients, lesions extending to the colon gradually decreased. In 1 patient, the entire colon was involved (Figure 3). Calcification was limited to the right mesenteric vein in 6 out of 8 cases (75%). In 2 cases (25%), the left mesenteric vein was involved. Diffuse septal thickening in the affected area was observed in 7 patients. One patient presented with calcifications without obvious colonic wall thickening. Wall thickening is commonly seen in the right and transverse colon.
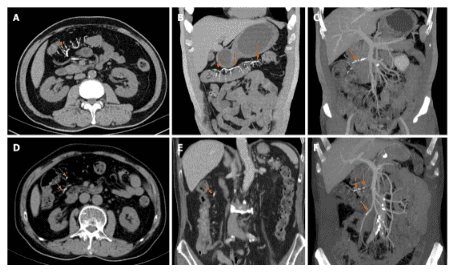
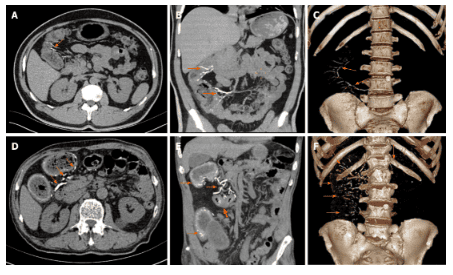
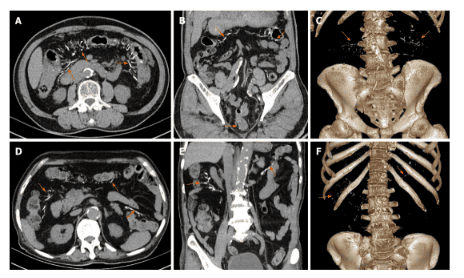
Poor renal function and long-term treatment of malignancies prolonging genipin clearance exacerbated the severity of mesenteric venous sclerosis and decreased colonic absorptive capacity
In the above study , 2 patients had atherosclerosis extending to the left colonic vein branch, 1 had chronic nephritis and 1 had been treated 5 years earlier with endocrine and radiotherapy for prostate cancer, which is rare in Spontaneous mesenteric atherosclerosis. The researchers speculate that poor kidney function and long-term treatment of melanoma prolong the clearance of genipin, an active metabolite of geniposide, allowing genipin to accumulate in the posterior venous branches. upon absorption, thereby exacerbating the severity of mesenteric venous sclerosis and reducing the absorptive capacity of the colon. Genipin, which is not completely absorbed by the ascending and transverse colon, is absorbed from the left colon, leading to sclerosis and calcification of the left colic vein. In addition, systemic microvascular disease that complicates diabetes and leads to chronic hypoxia can increase the vulnerability of the colon wall and colonic veins. Therefore, chronic nephritis, malignancies, and diabetes may increase the risk of progression of idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerosis. Severity of idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerosis is related to oral index , which reflects daily oral liquid drug intake and duration of exposure
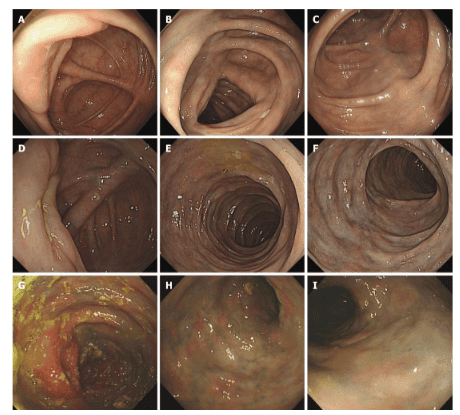
Effects on vessel walls are time and dose dependent, and that may be related to colon flora and colonic absorptive capacity colon. Spontaneous mesenteric atherosclerosis has characteristic features on both CT and endoscopic examination, so the diagnosis is relatively easy. Histopathology normally shows fibrosis and calcification of the venous wall and collagen deposition around the vessel wall. Due to the superficial location of the lesion, the pathological value of specimens obtained during colonoscopy for the diagnosis of idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerotic disease is limited and resected specimens may be required. deep observation. Treatment strategies for idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerosis can be determined on an individual basis. Patients with mild symptoms or no symptoms can be treated conservatively, eg discontinuing the use of Chinese herbal medicine. Surgical treatment is necessary if serious complications such as colonic obstruction, necrosis, intestinal perforation or massive bleeding occur. However, the presence of poor circulation may mean that colectomy is not an appropriate treatment and it must be chosen carefully.
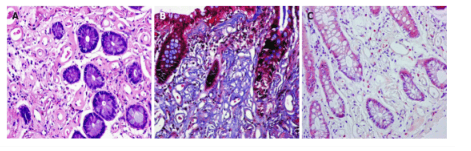
Conclusion
This research evidence supports that genocide is more likely to be associated with idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerotic disease. Clinical conditions, including chronic nephritis, malignancies, and diabetes mellitus, may be risk factors for idiopathic mesenteric atherosclerosis. It is recommended that long-term use of Chinese herbs and medicinal alcohols should be avoided, especially prescriptions or formulations containing gardenia. Both endoscopic examination and radiographs can lead to an accurate diagnosis even if biopsy results are inadequate or inconclusive.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References Wen Y, Chen YW, Meng AH, Zhao M, Fang SH, Ma YQ. Spontaneous mesenteric atherosclerosis associated with long-term oral administration of geniposide. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27 (22): 3097-3108 [DOI: 10.3748 / wjg.v27.i22.3097 ]