This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a Doctor of General Surgery & Anesthesia - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The spine serves as the backbone of the body. But when the vertebrae are pushed forward or backward, it will cause low back pain and difficulty in movement. Therefore, surgery to fix the spine will help release nerve compression and stabilize the spine.
1. When is spine fixation surgery needed?
Patients with spondylolisthesis need surgery to fix the spine. The spine plays an important role in the human body. But when the vertebrae slip forward or backward, it makes it difficult for the patient to walk.1.1. Causes of Spondylolisthesis Spondylolisthesis can occur for many reasons:
Congenital spondylolisthesis usually appears from childhood, potentially progressive. The cause of this condition is due to a developmental disorder Spondylolisthesis due to waist defect due to: Waist defect due to fatigue fracture; Excessively long waist causes fracture and bone healing in the waist region to occur continuously; Traumatic waist fracture causing spondylolisthesis Spondylolisthesis due to degeneration Pathological spondylolisthesis: The cause of this condition is usually infection or cancer that destroys the structure of the spine Spondylolisthesis due to trauma Spondylolisthesis survival after surgery.
1.2 Symptoms of spondylolisthesis

Đau cột sống là triệu chứng của trượt cột sống
Surgery to fix the spine is indicated for patients with unstable cervical spine. The spine is deformed, the physiological curve is lost, and the ligaments are damaged by the attached soft tissue.
For cases where the spine is stable and there is no nerve compression or the patient has respiratory failure, spinal shock is not recommended to have surgery to fix the spine.
Before surgery, the patient was explained carefully the preoperative prognosis, completed the bilan, preoperative tests and clean colon enema before surgery. The patient will be given a temporary external neck brace or continuous traction depending on the damage to the cervical spine.
2. Carrying out surgery to fix the spine
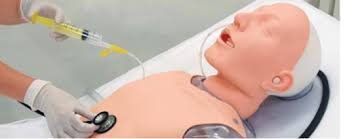
Đặt ống thông dạ dày tránh trào ngược trong quá trình phẫu thuật cố định cột sống
Surgery requiring a neurosurgeon or orthopedic surgeon. Instruments are fully prepared including: Spine surgery tool set; C- arm (brightening curtain); Operating table with head support frame (for patients with cervical spine injury) and screw braces of different sizes
Step 2: Carry out surgery
Patient is placed in a position suitable for surgery art. If the injury is in the neck area, the patient can lie on his or her back (if the neck is anterolateral) or prone (if the cervical spine is fixed in the posterior way). Ideally, the patient's head should be fixed to the head frame. If the chest area is injured, the patient can lie on the stomach. The patient can be placed in a supine position if there is a back or lumbar injury. The patient is under general anesthesia with a ventilator with monitoring of blood pressure, electrocardiogram and venous pressure. At the same time, insert a nasogastric tube to avoid reflux. This helps the surgeon to avoid injury to the esophagus during surgery. Depending on the situation, the surgeon can inject into the surgical area a mixture of Adrenaline + Lidocaine at a rate of 1/10,000 to reduce bleeding. With cervical spine injury, the incision is made along the inner border of the sternoclavicular muscle. cymbal. Use your finger to identify the carotid artery and then use a soft instrument to open and separate the tissue inside the artery all the way to the spine. The next step is to use an instrument to push the mid-neck axial components (trachea, esophagus, thyroid gland) inward, and if necessary, remove the carotid bundle but avoid pressing on the carotid artery. Expose the anterior longitudinal muscle of the spine and fascia. Make an incision along the midline of the spine where the disc and vertebra are damaged and the 2 adjacent vertebrae. Split the muscle as wide to the sides as possible. To expose the 2nd and 3rd cervical vertebrae, it is necessary to extend the incision to the angle of the jaw, then the superior thyroid artery must be ligated and the superior vocal cords may be cut, the cause of the temporary voice disturbance after surgery. For injuries to the thoracic spine, the back incision will be performed as the posterior incision. The procedure is to make an incision in the skin corresponding to the injured vertebra. Then make incision on both sides of the posterior spine, separate the paravertebral muscle to the sides and reveal the anatomical structures. Step 3: Based on the patient's injury to choose a method of fixing the spine. Common methods:
Combined disc removal with screw splints is applied mainly for ligament injuries or simple bone injuries that destabilize the spine. The incision is made along the medial border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, exposing the anterior aspect of the vertebral body. Completely remove the disc body up to the posterior longitudinal ligament. Using the automatic ball (Ecarteur de Cloward) to expose the disc space well and remove the disc to the sides facilitate easy bone grafting. Take a graft from the iliac crest that is about the size of the disc slit that has been widened, and has all three sides of the beak. Then close the graft into the intervertebral disc slot. Removal of the vertebral body combined with a screw brace, placing a titanium cage: Remove the discs above and below the injured vertebrae. The injured vertebral body is removed by tunneling along the midline axis of the vertebral body to the posterior longitudinal ligament, leaving the lateral walls of the vertebral body. Attach the pelvis to the removed bone and screw the splint into the adjacent upper and lower vertebral bodies. At present, it is possible to apply titanium cage replacement for the pelvis in the position of the removed vertebral body. The size of the titanium cage depends on the height of the vertebral body that was removed.
3. Post-surgery
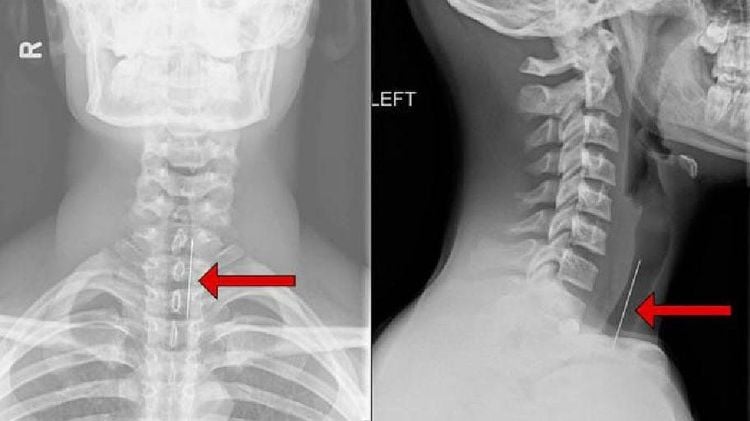
Sau phẫu thuật bệnh nhân cần chụp X-Quang để kiểm tra tình trạng bệnh
After 1 month after surgery, the patient needs X-ray to re-evaluate the condition as well as the results,
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensure professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology, but also outstanding with comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.